What is RS485? What are the differences between RS485 and RS232?
What is the RS485 port? How does the RS485 standard differ from RS232? Let’s explore its features, operating principles, and HELUKABEL’s compatible cable series in the article below.
1. What is serial communication?

Serial communication is a method of data transmission, also known as "serial interface." It’s similar to USB or Ethernet ports commonly seen in modern computers. In manufacturing facilities, serial communication is used to connect various devices. One of the most widely used standards for serial communication is RS485.
So why don't companies use USB or Ethernet to transmit data between devices? The reason is that compared to serial communication, USB and Ethernet are more complex and expensive. Serial communication is also deterministic - meaning it can avoid data collisions - making it more reliable when multiple devices are connected simultaneously. In other words, serial communication is better suited for this purpose than typical USB or Ethernet.
There are several types of serial communication standards, including RS232, RS422, and RS485. Among them, RS485 is the most used. This standard allows devices not only to connect within a local network but also to share a single communication bus with multiple RS485 devices communicating with one another. This makes it ideal for building synchronized and efficient multi-node systems.
2. Understanding the RS485
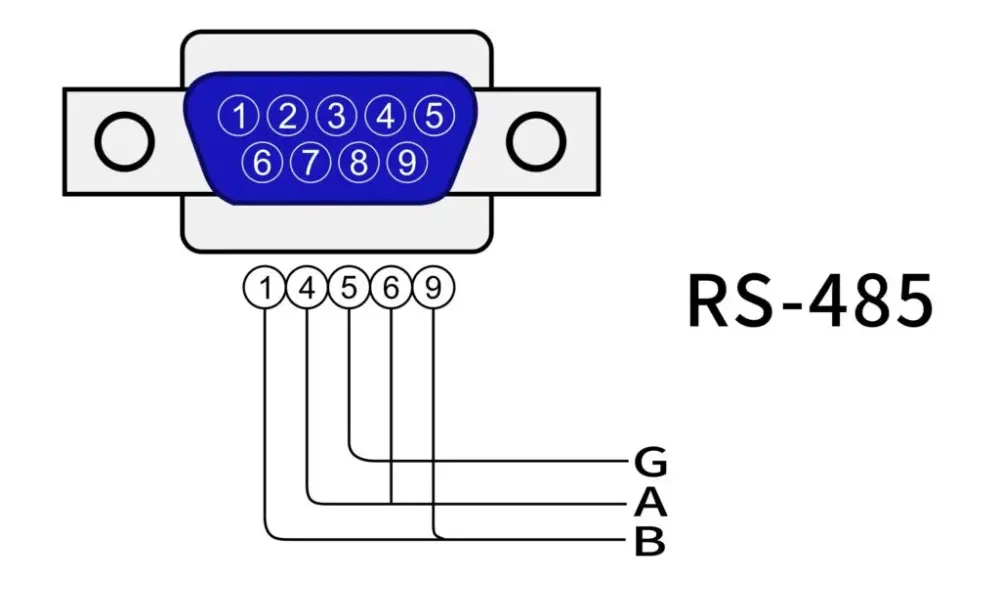
2.1 What is RS485?
In serial communication, there are various standards, and RS485—also known as TIA-485(A) or EIA-485 - is one of them. It was developed by two organizations: the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA).
RS485 is an industrial standard that defines the electrical interface and physical layer for communication between electrical devices, whether in point-to-point or multi-point configurations.
Key capabilities of RS485 include:
- Stable data transmission over long distances (up to several hundred meters)
- Reliable operation in high-electromagnetic interference (EMI) environments such as factories and industrial zones
- Support for connecting multiple devices on a single transmission line (bus)
RS485 is strictly an electrical standard - it specifies voltage levels and signal types, but it does not define how data is encoded, formatted, or the transmission speed. These aspects fall under communication protocols.
To effectively transmit and interpret data via RS485, it is typically paired with protocols such as:
- Modbus
- ASCII
- Profibus
- Or custom protocols tailored to specific systems
2.2 Two common RS485 wiring methods
RS485 transmits data using two twisted wires, known as twisted pair cable. The twisted structure effectively resists electrical interference, making RS485 particularly well-suited for noisy environments like factories, production facilities, and industrial electrical systems.
In RS485-based industrial communication networks, two common wiring methods are used:
| Half-duplex | Full duplex | |
| Wiring type | 2 wires | 4 wires |
| Advantages | Supports multi-device communication; most common setup | Allows simultaneous bidirectional data transmission |
| Disadvantages | Cannot transmit in both directions at once | Does not support multi-point connections |

2.3 Applications of RS485
RS485 is widely used in computer systems and automation environments. Notable applications include Robotics, telecommunication base stations, motor controllers, video surveillance systems, or even home appliances
In computer systems, RS485 is used to transmit data between controllers and drives. In aviation, commercial aircraft cabins utilize RS485 for low-speed data transmission, thanks to its simple wiring, which helps reduce cable weight and complexity.
RS485 is especially prevalent in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and industrial production line environments with high electromagnetic interference. In such systems, RS485 often serves as the physical layer for many standard and proprietary automation protocols, with Modbus being one of the most common.
3. Understanding RS232

3.1 What is RS232?
RS232 is a type of serial communication—transmitting data one bit at a time over a single transmission line. RS232 supports two data transmission modes:
- Synchronous transmission: Data is sent according to a clock signal
- Asynchronous transmission: More common, especially in communications between computers and peripheral devices
RS-232 originally used 25-pin DB-25 connectors, though the newer DB-9 connectors with 9 pins are now standard. Each pin has a specific function defined by the standard.
3.2 How RS232 transmits data
In RS232, data is transmitted unidirectionally over a single signal wire. For bidirectional communication, at least three wires are required: RX (receive), TX (transmit), and GND (ground), in addition to optional control signals.
RS232 works by sending signals through a wire from one device to another. These signals are represented by different voltage levels that indicate the data being transmitted. The voltages can be either positive or negative, with 0V used as a reference. RS232 also includes a clock signal to synchronize data transmission between devices.
4. Comparison of RS485 vs RS232
RS485 offers many improvements over RS232, including greater transmission distance, multi-point communication, and better noise immunity. However, these two standards are not direct replacements for one another.
RS232 is more suitable for simple, short-distance, point-to-point connections - such as between a computer and a peripheral device. RS485, on the other hand, is better suited for industrial environments or building automation systems that require stable, long-distance communication with multiple connected devices.
| RS232 | RS485 | |
| Connection type | Point-to-point; only two devices at a time | Multi-point; up to 32, 128, or 256 transceivers depending on the chipset |
| Transmission distance | Up to 15 m | Up to 1200 m |
| Noise immunity | Single-ended signal, higher voltage range, weaker EMI resistance | Differential signal, lower voltage range, stronger EMI resistance |
| Transmission speed | Maximum 20KB/s | Up to 10 Mbps at shorter distances |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Design | Simple: easier to implement with fewer components | More complex when multiple devices are connected |
5. HELUKABEL’s RS485 cables
HELUKABEL offers a wide range of RS485-compatible cables for various applications. Some featured products include:
5.1 PAAR-TRONIC-Li-2YCY/PAAR-TRONIC-Li-2YCYv

PE-insulated data cable with twisted pairs, for interference-free transmission of data and signals over longer distances. The twisted-pair lay-up prevents electrical unbalances within the cable and this thus effectively suppresses cross-talking effects. The high transmission
rates are particularly suitable for RS 422 and RS 485 interfaces; suitable for fixed installations in dry, damp and wet rooms, but not outdoors.

5.2 RS485 HELUDATA® 2919 PE/PVC-TP-C 30 GREY / HELUDATA® 2919 PE/PVC-TP 30 GREY
UL-approved data cable for applications in industrial automation and process control; for fixed installation in dry or damp environments.

5.3 PROFIBUS SK cables
Some PROFIBUS SK cables from HELUKABEL include :
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |



