HELUKABEL’s flat cables, originating from Germany, feature an extremely small bending radius and flexible design, offering optimal solutions for confined spaces.
1. What are flat cables?
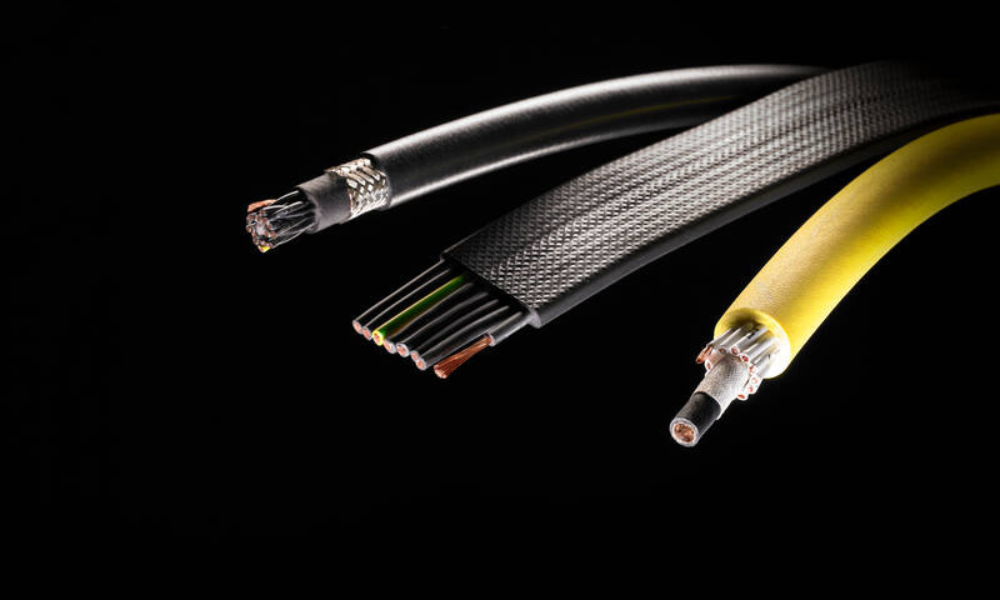

Flat cables, also known as ribbon cables, are flat, rectangular designs composed of multiple conductors placed parallel to each other and fused into a single strip. They are designed for terminating a series of insulation displacement contact (IDC) connectors. The fixed conductor spacing, and consistent shape ensure uniform electrical characteristics, including impedance, capacitance, time delay, crosstalk, and signal loss.
2. Benefits of using flat cables
Flat cables offer the following outstanding advantages:
- High flexibility: Thanks to their compact design, flat cables are highly flexible, particularly in applications with high bending, such as in robotics, festoon systems, automated processing equipment, or confined spaces. This flexibility is achieved because flat cables bend uniformly along the same plane, reducing twisting and stress. With a small bending radius, flat cables are the optimal solution for tight spaces and are designed to endure tens of millions of torsion cycles
- Reliability: The conductors in flat cables are evenly spaced, ensuring consistent travel distances. The parallel conductor arrangement in flat cables helps eliminate many common wiring errors and malfunctions. As a result, flat cables deliver superior electrical performance, including faster signal transmission, reduced signal skew, and higher current-carrying capacity due to the straight, consistent path for current flow.
- Lightweight: Flat cables typically eliminate the need for redundant insulation, fillers, and tapes. Moreover, their construction is mechanically strong, so large conductors are not necessary to increase strength. Consequently, the cross-sectional area of flat cables can be minimized to meet the necessary current-carrying capacity or voltage drop requirements.
- Ease of termination and identification: Flat cables are easier to terminate and identify than round cables due to their parallel conductor arrangement. This design also simplifies repairs and enhances robustness by evenly distributing stress and load throughout the cable.
3. Applications of flat cables
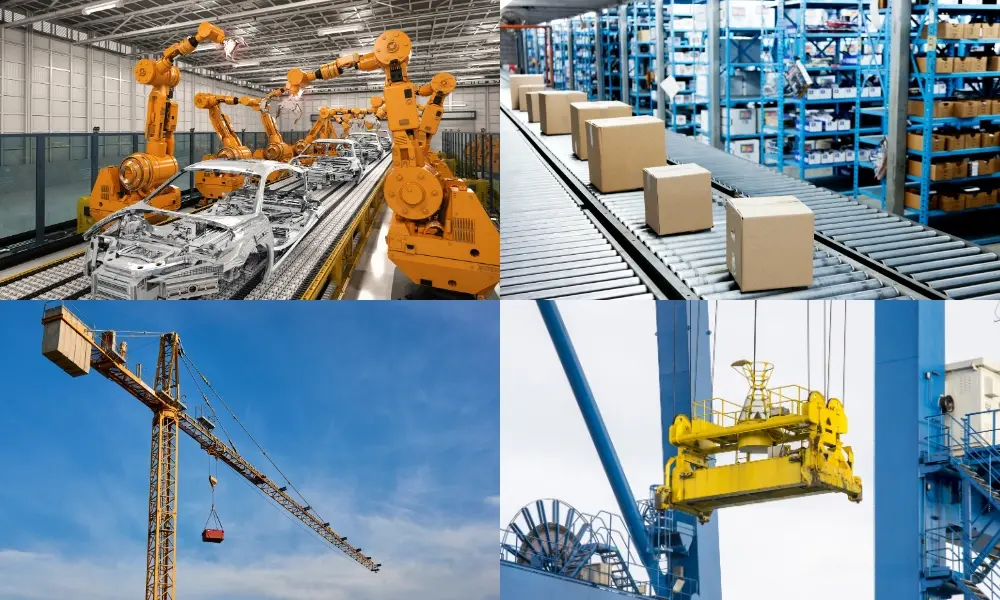

Flat cables are particularly well-suited for applications that demand flexibility or have tight space constraints. Due to their flat and thin design, they are easier to bend and can fit into confined spaces or tight corners without breaking. Common applications include:
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications often involve complex, densely packed arrays of wires. Flat cables are ideal for navigating tight spaces and conserving space.
- Robotics: Robotics applications frequently require highly intricate designs in compact areas. As technology becomes smaller and lighter, using the appropriate cable for limited spaces is crucial.
- Cranes: Some crane manufacturers prefer flat cables over round ones due to space constraints and the need for constant bending. Flat cables provide power and control signals while enduring moderate environmental challenges.
Automation, automotive, construction, and mining industries
4. HELUKABEL’s flat cables
HELUKABEL is a German supplier of flat cables that meet the diverse needs of many industries. With a commitment to quality and durability, our flat cables are designed to withstand harsh working conditions and provide outstanding performance.
4.1 PVC-flat cables
This is a type of flat cables is made from special PVC material, with outstanding oil resistance and anti-interference properties, exhibiting the following characteristics:

- Operating temperature: -5°C to +70°C (flexing), -40°C đến +80°C (fixed installation)
- Nominal voltage:
≤ 1 mm² U0/U 300/500 V
≥ 1,5 mm² U0/U 450/750 V
- Test voltage:
≤ 1 mm² 2000 V
≥ 1,5 mm² 2500 V
- Minimum bening radius: 10 x cable thickness
- Radiance resistance: up to 80x106 cJ/kg (up to 80 Mrad)

4.2 PVC-flach-CY cables
The technical data of this special PVC flat cables can be found as follows:
- Operating temperature: -5°C to +70°C (flexing), -40°C to +80°C (fixed installation)
- Nominal voltage: U0/U 300/500 V
- Test voltage: 3000 V
- Minimum bening radius: 15 x cable thickness
- Radiance resistance: up to 80x106 cJ/kg (up to 80 Mrad)

4.3 NEO-flach cables
Neo-flach flat cables are made of special Neoprene material, mainly used as trailing cable for crane systems, floor conveyor systems and racking control units. Some features of this type of flat cables:
- Operating temperature: -30°C to +80°C (flexing), -40°C to +80°C (fixed installation)
- Nominal voltage: U0/U 300/500 V
- Test voltage: 3000 V
- Minimum bening radius: 10 x cable thickness
- Radiance resistance: up to 50x106 cJ/kg (up to 50 Mrad)

4.4 NEO-flach-C cables
Compared to the NEO-flach cables, the NEO-flach-C flat cables are equipped with an additional anti-interference layer, helping the signal transmission process to be unimpeded. Technical data of this cable line:
- Operating temperature: -30°C to +80°C (flexing), -40°C to +80°C (fixed installation)
- Nominal voltage: U0/U 300/500 V
- Test voltage: 3000 V
- Minimum bening radius: 15 x cable thickness
- Radiance resistance: up to 50x106 cJ/kg (up to 50 Mrad)




