MC4 connector overheating – Causes and solutions
MC4 connectors are essential components in PV systems, used to establish secure connections between solar panels and the inverter. However, during operation, they can experience overheating or scorching, which poses safety risks and can lead to unstable system performance.
1. The role of MC4 connectors in photovoltaic systems
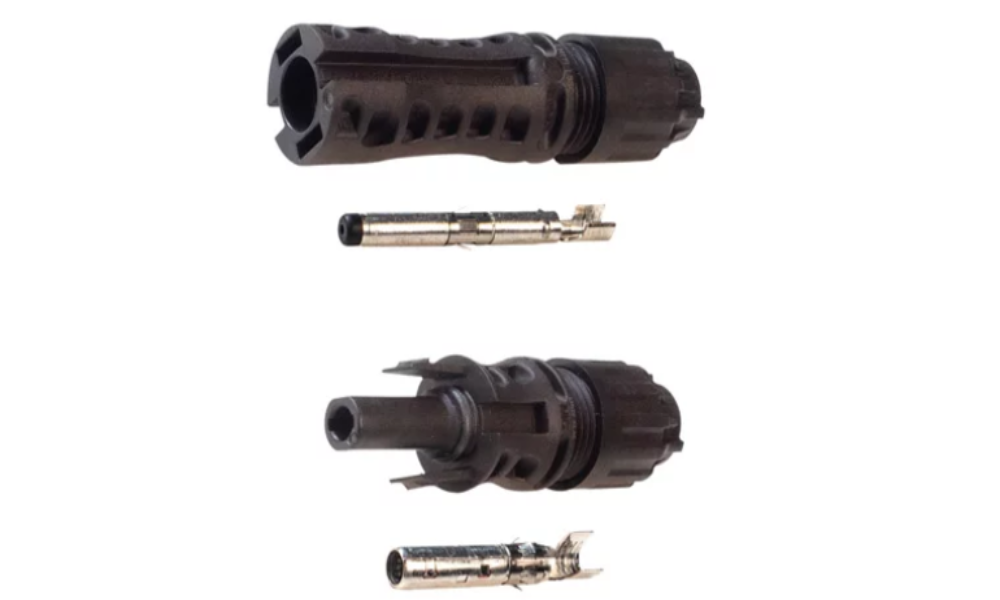

The MC4 connector is an important accessory in solar power systems, used to connect solar panels and inverters.
Because solar power systems are installed outdoors and exposed to harsh environmental conditions such as strong winds, high temperatures, and UV radiation, standard electrical connectors are prone to damage and can significantly reduce the efficiency of energy transfer into the system.
MC4 connectors are designed to ensure a weather-resistant electrical interface that remains stable and reliable for decades. Their snap-fit locking mechanism prevents accidental disconnection during power transmission. This design securely locks the male and female connectors together, even in extreme conditions, and can only be released manually.
MC4 connectors are particularly crucial in both on-grid and off-grid solar systems, where safe and independent operation is essential. To maintain this level of safety, MC4 connectors help prevent DC arcing by blocking moisture intrusion at the contact point and maintaining consistent contact pressure.
From an installation standpoint, the plug-and-play design of MC4 connectors eliminates the need for electrical tape, wire stripping, or crimping tools. This reduces installation time significantly and minimizes wiring errors.

The operating environment of the MC4 jack or the installation technique may lead to overheating.
2. What is MC4 connector overheating?
MC4 connector overheating in a solar PV system occurs when excessive heat builds up at the connection point, often resulting in melted plastic, browning, or even fire. This issue is primarily caused by increased electrical resistance due to factors such as:
- Loose connectors or poor contact
- Improper or low-quality crimping
- Dirt and oxidation reducing conductivity
- Corrosion at the contact interface
- Overcurrent or voltage exceeding the connector’s rated capacity
These problems create serious safety hazards, cause energy losses, and may even damage the entire solar system. Overheating is a critical fault in PV installations, indicating a compromised connection that requires immediate inspection and corrective action to prevent fire or system failure.
3. Causes of MC4 connector overheating
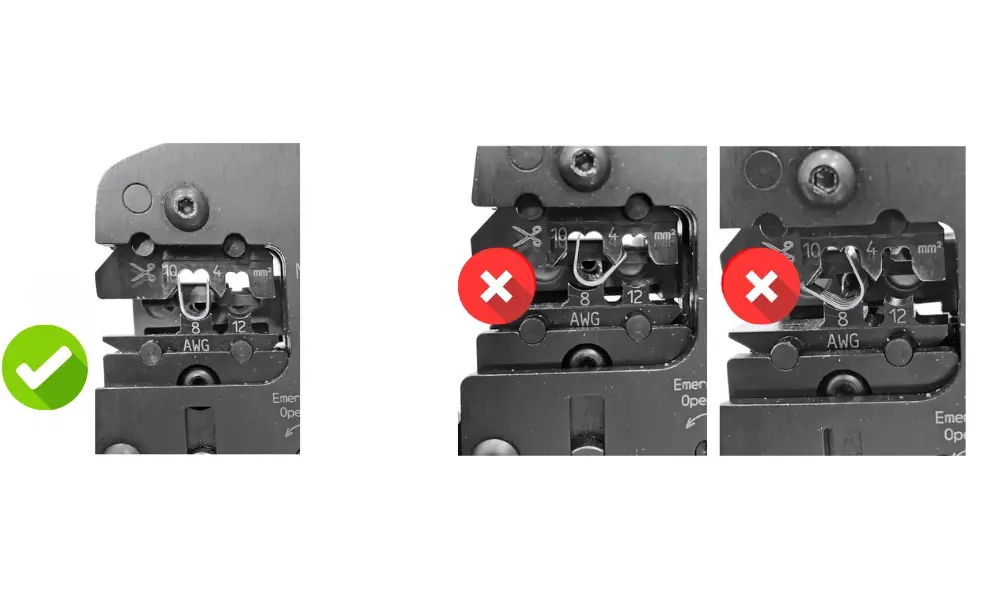
Make sure that the contact is placed in the housing and is held by the clamping bracket
3.1 Improper crimping technique
Incorrect crimping is one of the primary causes of loose or poor contact within MC4 connectors. When the crimped terminal does not achieve sufficient compression force, the contact resistance increases, resulting in excessive heat generation. This heat buildup can melt the plastic housing, cause discoloration, or even lead to arcing.
Common terminal crimping errors:
- Using a non-standard or incompatible crimping tool for MC4 terminals
- Applying insufficient force or crimping off-center
- The crimp barrel not tightly enclosing the conductor strands
- The cable slipping out of the terminal after a period of operation
Solution:
- Use the correct manufacturer-recommended MC4 crimping tool.
- Follow proper crimping procedures to ensure maximum contact surface and compression.
- Perform a continuity or contact-resistance test to verify the crimp quality.
- Replace any terminals that are poorly crimped or deformed during installation
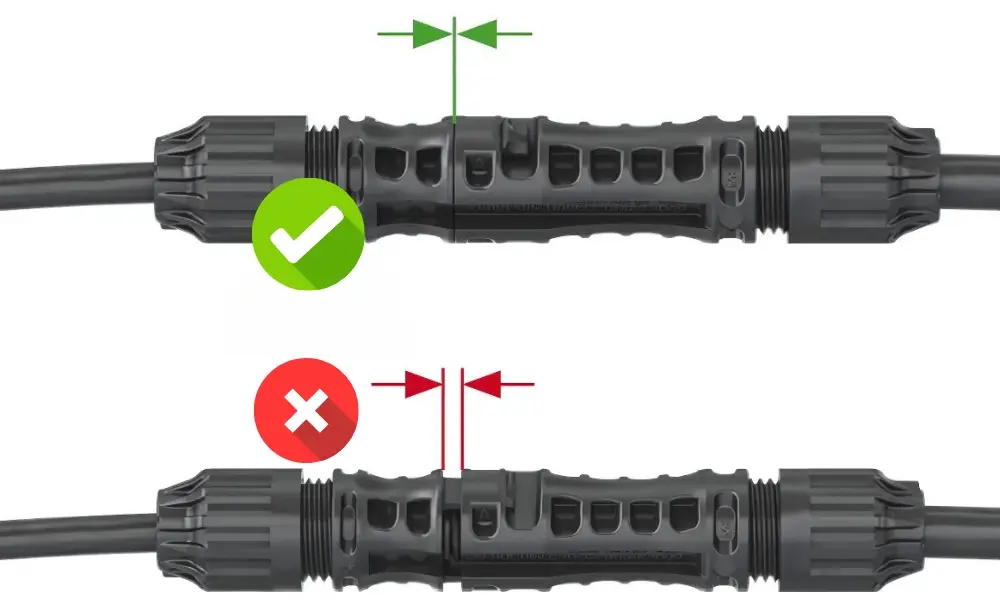

Mate the cable coupler until a "click" can be heard
3.2 Incompatible MC4 connectors leading to poor contact and overheating
Another common cause of MC4 connector overheating is mixing connectors from different manufacturers. Although many products on the market are advertised as “MC4 compatible,” each manufacturer uses different mechanical tolerances and connector designs.
When two MC4 connectors from different brands - or with mismatched standards - are paired together, the following issues can occur:
- Poor mating contact
- Increased contact resistance at the connection point
- Insufficient compression force, resulting in excessive heat generation
- Misaligned or incompatible sealing gaskets (IP65/IP67), making the connection vulnerable to moisture ingress and oxidation
Over time, these problems lead to abnormal heating, melting of plastic housing, voltage drop, and reduced system performance.
To ensure safety and maintain PV system efficiency, the following practices are recommended:
- Use MC4 connectors that are uniform and from the same manufacturer
- If using cross-brand connectors, ensure they have verified compatibility certifications
- Avoid using MC4 connectors that show signs of wear, deformation, or damage

Select a DC cable with a cross-section suitable for the MC4 connector
3.3 Using incompatible DC cables
A common installation error in solar PV systems is using cables with a smaller cross-section than required. When the conductor does not have sufficient current-carrying capacity, its electrical resistance increases, causing excessive heat generation as current flows through it. This issue not only heats the entire cable length but becomes especially dangerous at the MC4 connection point, where resistance tends to concentrate.
PV modules generate continuous DC current. Therefore, if the cable size is undersized or the MC4 connector is not rated for the appropriate current/voltage, the increased resistance will cause both the cable and the connector to heat up rapidly.
To ensure safety, efficiency, and long service life of the PV system, you should always:
- Choose the correct cable cross-section (4 mm², 6 mm²) based on current and cable run length
- Use DC solar cables that comply with industry standards
- Install high-quality MC4 connectors with the correct current and voltage ratings
- Verify compatibility between cables and connectors, and ensure proper installation techniques
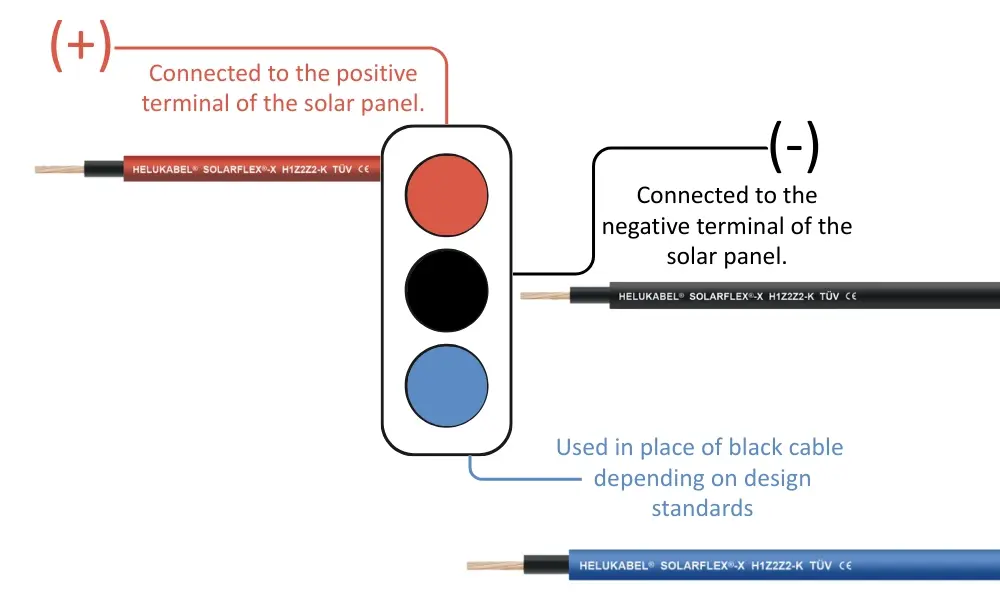
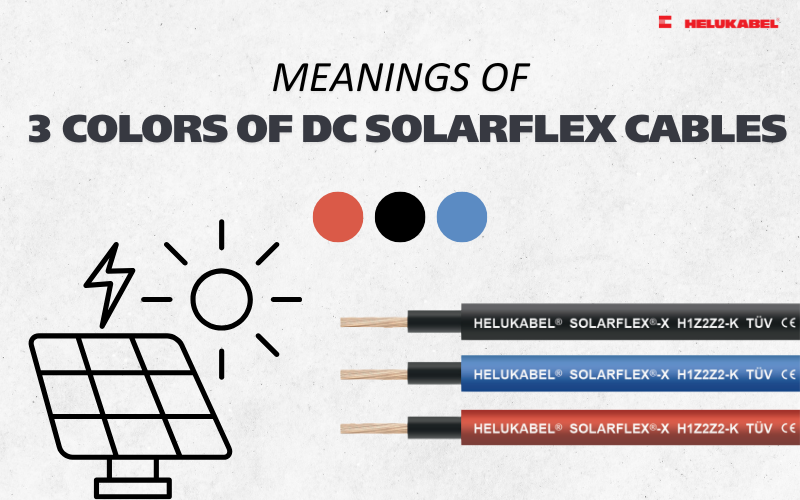
Connecting the correct polarity (+/-) is extremely important to ensure performance and safety.
3.4 Reverse polarity
In a solar PV system, correct polarity (+/–) is critical to ensuring both performance and safety. When polarity is reversed, the electrical current flows in the opposite direction, leading to efficiency losses, abnormal heating at the MC4 connectors, and potential damage to the inverter, charge controller, or even the PV modules.
Incorrect polarity also increases the risk of MC4 connector overheating because abnormal current flow can cause higher contact resistance, generating excessive heat that may melt the housing or trigger electrical fires.
However, MC4 connectors are designed as polarized connectors, meaning they can only be mated in one orientation. This design ensures:
- Prevention of accidental reversal of positive and negative conductors
- Reduction of human error during installation
- Stable, safe, and technically compliant system operation
This polarity-specific structure allows installers to easily ensure that the positive (+) conductor is always connected to the positive terminal, and the negative (–) conductor to the negative terminal, minimizing wiring mistakes.
3.5 Water and dust ingress leading to connector corrosion
In outdoor installations, MC4 connectors are continuously exposed to rain, sunlight, high humidity, and dusty environments. When water or moisture enters the MC4 connector, it can corrode the metal contact surfaces, increase electrical resistance, and cause overheating, short circuits, or even fires. This is one of the most common reasons for reduced power transmission efficiency in solar PV systems.
Over time, MC4 connectors may also experience oxidation, dust accumulation, and natural wear - especially in harsh outdoor conditions. When contact surfaces become oxidized or gradually loosen, the electrical resistance increases, causing the connector to generate excessive heat, melt the plastic housing, burn the terminals, or damage the cables. This not only reduces system performance but also significantly increases electrical safety risks.
Solution:
- Use MC4 connectors with IP67/IP68-rated water and dust protection.
- Ensure correct installation, secure locking, and avoid placing connectors in areas prone to water accumulation.
- Prioritize genuine, brand-consistent MC4 connectors to reduce oxidation and extend system lifespan.
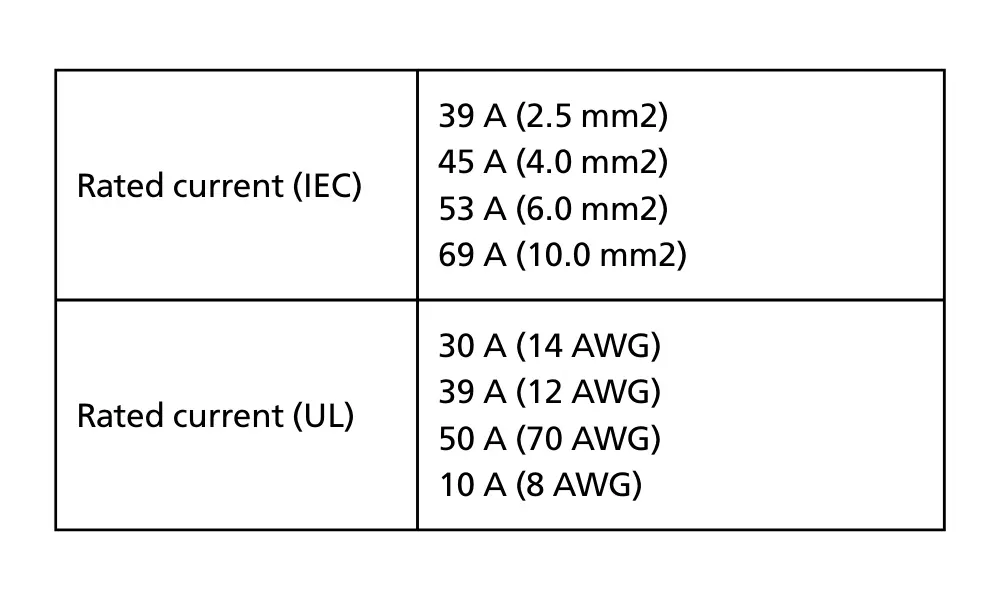
Rated current specifications for the MC4-Evo 2A connector
- system lifespan.
3.6 Voltage and current ratings – Critical factors to prevent MC4 connector overheating
For a solar PV system to operate safely and reliably, MC4 connectors must be selected according to the system’s rated voltage and current. Incorrect ratings significantly increase the risk of overheating, melting, arcing, and potential fire hazards.
- Rated voltage of MC4 Connectors: Each MC4 connector has a maximum DC voltage rating - typically 1000 VDC or 1500 V DC. If the system voltage exceeds this limit, the connector may experience arcing, insulation breakdown, and severe damage.
- Rated current of MC4 connectors: MC4 connectors usually have a rated current between 30 A and 50 A, depending on their design. This rating must be equal to or higher than the maximum operating current of the PV string. When current exceeds the connector’s limit, the electrical resistance at the contact point increases, causing localized heating and melting of the connector housing.
If the MC4 connector does not meet the correct voltage and current requirements of the system:
- The connector may overheat, discolor, or melt.
- Contact surfaces can oxidize and increase resistance, leading to voltage drop and reduced system efficiency.
- The risk of arcing, sparking, and fire ignition increases significantly.
- The entire PV string may shut down, resulting in major system losses.
4. How HELUKABEL’s MC4-Evo 2A connectors prevent overheating
The MC4-Evo 2A connectors supplied by HELUKABEL are engineered to deliver stable power transmission and high electrical safety in solar PV systems. As an upgraded version of the previous MC4-Evo 2, this model is now widely used across the photovoltaic industry.
Several design enhancements allow HELUKABEL’s MC4 connectors to effectively prevent overheating:
- High-quality tin-plated copper contacts ensure low electrical resistance and maintain long-term conductivity, reducing heat generation at the contact point.
- PA insulation performs reliably in extreme temperatures ranging from –40°C to +85°C, UV-resistant, suitable for all climatic conditions
- Precision-designed locking mechanism prevents accidental loosening, ensuring a stable contact force and eliminating micro-arcing - one of the primary causes of localized overheating.
- Certified current and voltage ratings (UL) guarantee that the connector can safely handle high-power operating conditions without overloading.
- IP65/IP68 water-tight sealing protects against moisture ingress, oxidation, and corrosion, all of which increase contact resistance and lead to overheating.
- Optimized compatibility with HELUKABEL DC cables ensures a perfect mechanical and electrical fit, further reducing resistance and thermal buildup.
With these features, HELUKABEL’s MC4-Evo 2A connectors significantly enhance power transmission efficiency, minimize the risk of overheating, extend system lifetime, and reduce maintenance costs for solar PV installations.
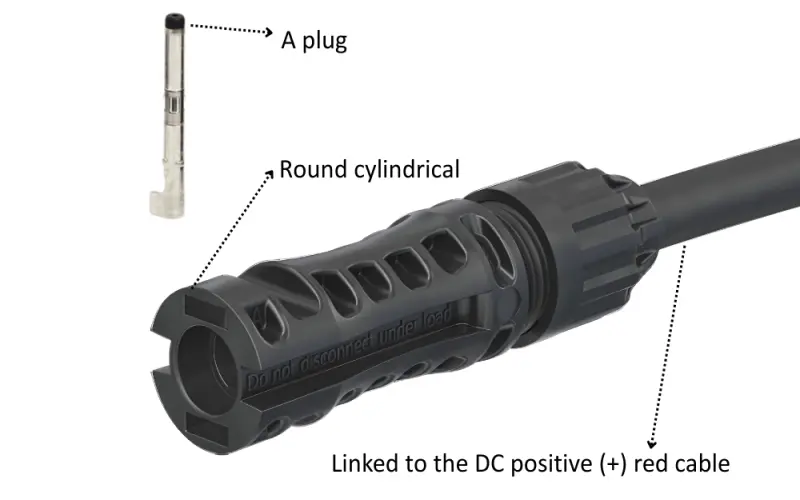

MC4-Evo 2A male connector
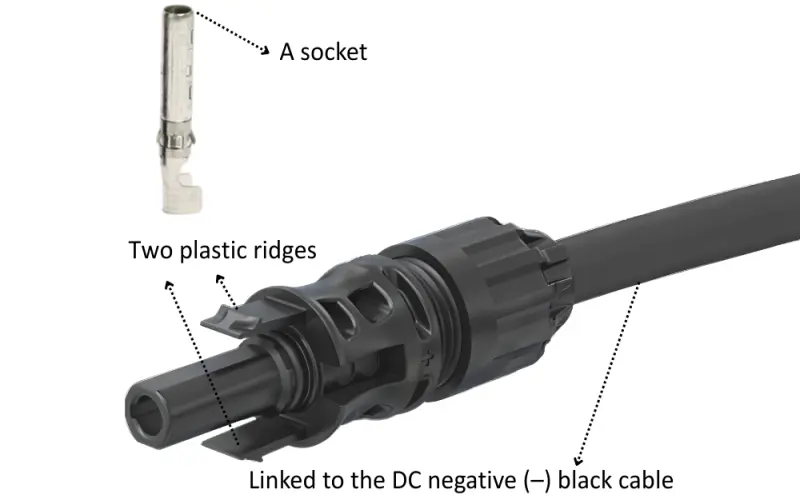

MC4-Evo 2A Female Connector
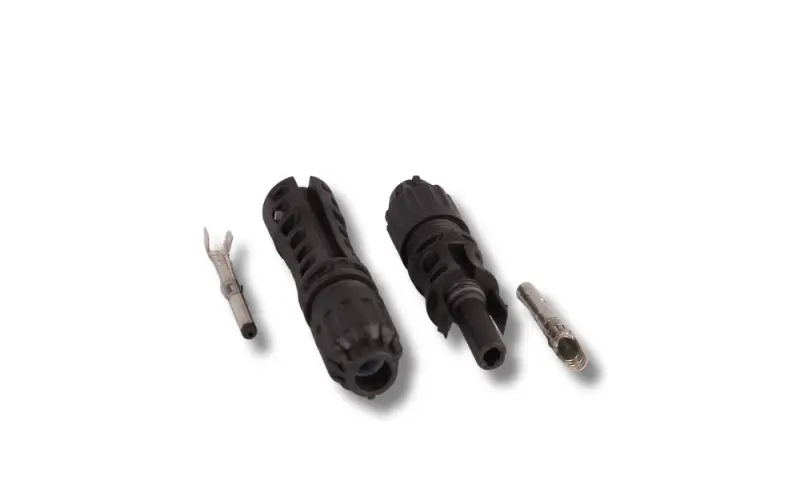

Complete set of MC4-Evo 2A connectors
If you still have questions, don't hesitate to contact the HELUKABEL Vietnam engineering team for detailed answers.
Contact Information HELUKABEL Vietnam
| HELUKABEL Vietnam 905 Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam | Phone:
+84 28 77755578 Email: info@helukabel.com.vn | Connect with us on |
| Order through our online channels Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder | ||