What are twisted pair cables? Comparing UTP and STP cables
UTP and STP twisted pair cables are commonly used for network connections. However, these two types of cables have distinct differences in structure and characteristics. Let’s explore them in detail in the article below!
1. What are twisted pair cables?
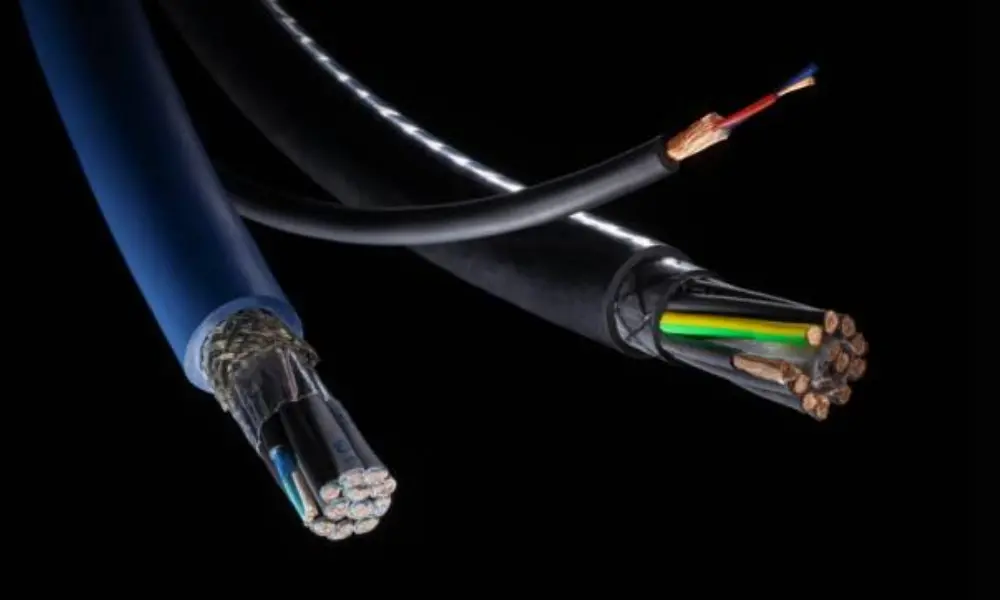

A twisted pair cable is a type of cable commonly used in telephone systems and most modern Ethernet networks. It consists of two insulated copper wires twisted together to form a circuit that transmits signals. The twisting reduces crosstalk - interference caused by adjacent wire pairs.
When current flows through a wire, it creates a small circular magnetic field around it. By placing two wires close together and twisting them, their magnetic fields cancel each other out, minimizing external interference. This design technique enhances the cable’s ability to resist EMI. The result is a “self-shielding” effect, achieved by combining wire twisting and signal cancellation, which protects each pair from noise.
Twisted pair cables are the most cost-effective cabling option used in local area networks (LANs). They are widely employed in data transmission and applications where signal noise immunity is required.
There are two basic types of twisted pair cables:
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
>>See more: Overview of LAN and type of LAN cables
2. Understanding UTP cables
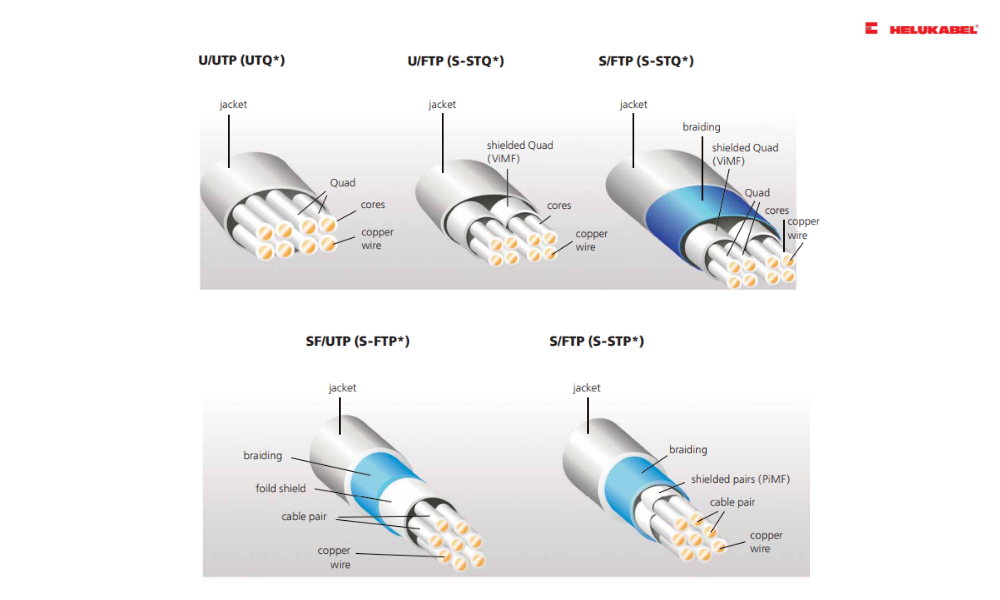
UTP cables (no additional shield) and STP (with additional shield)
2.1 What are UTP cables?
UTP cable is a type of network cable consisting of twisted copper wire pairs enclosed in an outer protective sheath. Its defining feature is the twisting of wire pairs, which helps reduce interference from external sources. Thanks to this design, UTP cables can transmit data reliably and are widely used across various networking applications.
UTP relies solely on the cancellation effect between twisted pairs to minimize signal degradation from EMI and radio frequency interference (RFI). Each twisted pair in a UTP cable typically has a different twist rate to reduce crosstalk.
In network installations, UTP cables are commonly terminated with RJ45 connectors - 8-pin connectors used extensively for Ethernet LAN connections.
Computer network UTP cables typically contain four twisted pairs of copper wires, with conductor sizes of 22 or 24 AWG. These cables have a characteristic impedance of 100 ohms, which distinguishes them from telephone twisted pair cables with about 600 ohms impedance.

2.2 Advantages and disadvantages of UTP cables
Advantages:
- Compact size, with an outer diameter of around 0.43 cm (0.17 inches), making installation easier - especially in space-constrained environments.
- Easy to install and bend, with lower costs compared to other network cables.
- Widely compatible with common networking standards, making UTP the most prevalent choice.
Disadvantages:
- More susceptible to electromagnetic and radio frequency interference than coaxial or fibre optic cables.
- Shorter signal transmission distances due to higher attenuation compared to coaxial or fibre optic cables.
3. Understanding STP cables

3.1 What are STP cables?
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cable is also a type of twisted pair cable, but with an added shielding layer around each wire pair. This shielding reduces EMI, crosstalk, and signal leakage - making it ideal for protecting networks from external noise.
In Ethernet networks, STP helps mitigate both internal crosstalk and external noise such as EMI and RFI. While STP cables often require specialized connectors, they can sometimes be used with standard RJ45 connectors under certain conditions.
Despite their superior noise protection, STP cables are more expensive and complex to install. The shielding must be grounded properly at both ends; otherwise, it may act like an antenna and attract interference instead. Due to the higher cost and complex grounding requirements, STP is rarely used in typical Ethernet deployments today.
>>See more: What is crosstalk? How to prevent crosstalk?

3.2 Advantages and disadvantages of STP cables
Advantages:
- Superior interference protection: The shielding significantly reduces external EMI and RFI, making STP ideal for industrial environments.
- Signal integrity: Reduced crosstalk and attenuation help maintain high-speed, stable data transmission.
- Longer transmission distances: STP can transmit data over greater distances without signal degradation, suitable for large-scale networks.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost: Due to its more complex structure and shielding, STP is more expensive than UTP.
- Lower flexibility: The metallic shielding reduces flexibility, making STP harder to bend and install in tight spaces.
4. Comparing UTP and STP cables
4.1 Similarities
Both UTP and STP cables share these common traits:
- Twisted pair structure: Designed to reduce interference and crosstalk.
- Used in Ethernet networks: Common in LANs including Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet.
- RJ45 connector compatibility: Both can be terminated with RJ45 connectors.
- Support for multiple standards: Compatible with various networking standards and speeds.
- Distance limitations: UTP typically supports up to 100 meters; STP can reach up to 1000 meters under optimal conditions.
4.2 Key differences
| UTP cables | STP cables | |
| Additional shielding | No | Yes |
| Earthing | Not required | Required |
| Data speed | Lower | Higher |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Speed | 10-1000 Mbps | 10-100Mbps |
| Crosstalk protection | Low | High |
| Attenuation | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower, suitable for general use | Higher, suitable for complex network systems |
| Cable classification | By Category such as Category 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5e, 6, 6A, 7 | By shielding type: Foil, Braided |
5. FAQs when chosing UTP and STP cables
Choosing between UTP and STP depends on your installation environment and technical requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Operating environment: UTP is ideal for low-interference areas like offices and homes. STP is better for industrial environments with high EMI or RFI.
- Budget: UTP is more cost-effective if advanced shielding is not necessary.
- Ease of Installation: UTP is easier and quicker to install. STP requires careful grounding and is less flexible.
- Performance needs: For standard LANs or surveillance systems, UTP offers sufficient performance. For high-speed, long-distance, or industrial networks, STP is the better investment.
When exploring twisted pair cables, you’ll often come across abbreviations like U/UTP, F/UTP, F/FTP, and S/FTP. These markings indicate the type and level of shielding used in the cable:
- U (Unshielded): No shielding
- F (Foil Shielding): Aluminum foil
- S (Braided Shielding): Metallic braid
- TP (Twisted Pairs): Twisted pair structure
When designing a network infrastructure, users not only need to decide between UTP and STP cables, but also often face a key question: Should I choose twisted pair cables or fibre optic cables?
The main differences between twisted pair and fiber optic cables lie in their transmission material, bandwidth, resistance to interference, transmission distance, and cost. Twisted pair cables (like UTP or STP) use copper conductors and are a more economical solution. They are suitable for short to medium distances but are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and have limited bandwidth and transmission range.
Fibre optic cables, on the other hand, transmit data via light through glass or plastic fibers. They offer much higher bandwidth, long-distance transmission capabilities, and are immune to EMI. However, they come with higher installation and equipment costs.
The decision depends on your network performance requirements and budget.
Another type of cable commonly used alongside twisted pair cables - especially for network connections, television signal distribution, and radio transmission - is the coaxial cable.
Coaxial cables offer better shielding against electromagnetic interference and higher bandwidth, making them suitable for long-distance signal transmission and environments with significant electrical noise. However, when it comes to ease of installation, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with modern networking technologies, twisted pair cables (UTP and STP) remain the more popular choice.
6. HELUKABEL’s twisted pair cable solutions for networking
HELUKABEL offers a complete range of cables and accessories for network connectivity, suitable for everything from office environments to industrial facilities and high-speed data systems. Product offerings include:
- UTP and STP twisted pair cables from Cat5 to Cat7A
- Single-mode and Multimode fibre optic cables, along with optical patch cords
- Coaxial RG cables
- RJ45 connectors and a full range of network installation accessories
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |









