Understanding cable lugs: What are they and how are they classified?
The stability of an electrical system does not rely solely on the cables themselves but also on the smallest connection points. With cable lugs, HELUKABEL provides a seamless, safe, and high-performance connection solution.
In the complex world of electrical systems, where safety and transmission efficiency are always critical, sometimes it is the smallest details that make the biggest difference. One such detail is the cable lug – the “unsung hero” of every electrical connection.
These small metal connectors act as crucial bridges between electrical conductors and devices, ensuring that electricity flows safely, stably, and efficiently. With cable lugs, connections become more secure, reducing the risk of short circuits, overheating, or sparks, thereby protecting equipment and extending the lifespan of the electrical system.
1. Understanding cable lugs
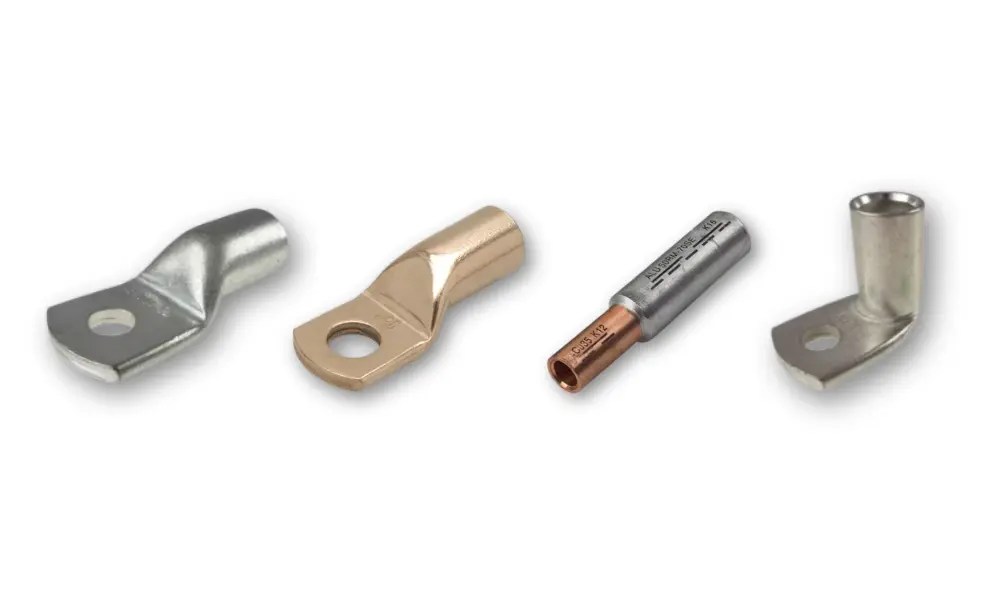

Some cable lugs from HELUKABEL
1.1 What are cable lugs?
A cable lug is a metal accessory designed to connect electrical cables to devices, terminals, or other cables. Cable lugs come in various shapes, sizes, and standards, suitable for different cable diameters and specific application requirements.
They are typically made from highly conductive materials such as copper, aluminum, or brass, ensuring excellent electrical conductivity and superior mechanical strength. Thanks to their conductive metal design, cable lugs create neat and stable connection points, guaranteeing optimal electrical contact while minimizing the risk of loosening, overheating, or damage to the connection during operation.
Because of these advantages, cable lugs are widely used in both residential and industrial electrical systems, particularly at connection points such as:
- Between electrical cables and transformers
- Between cables and switchgear, circuit breakers, or busbars
- Electrical motors, batteries, and inverters
- Charge controllers, distribution units, or other electrical control devices
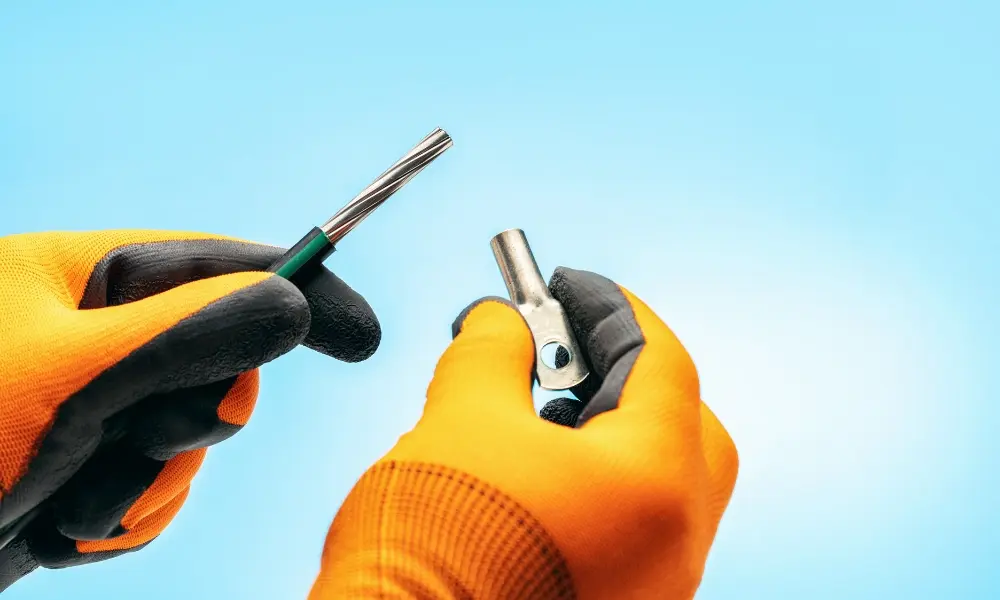

With cable lugs, connections become more secure
1.2 Key benefits of cable lugs in electrical systems
Cable lugs do more than just connect wires - they play a critical role in ensuring the safety, performance, and reliability of the entire electrical system:
- Enhanced safety: Cable lugs securely hold conductors in place, preventing loose connections and reducing the risk of short circuits, overheating, or fire. Some types also feature insulating layers, which prevent electrical leakage and protect users during operation.
- Improved electrical transmission efficiency: Cable lugs are made from high-quality conductive materials, such as copper or tin-plated aluminum, and are designed to create tight connections with low electrical resistance. This ensures stable current flow, minimal energy loss, reduced heat generation, and more efficient system operation, ultimately lowering operating costs.
- High reliability: Cable lugs provide strong mechanical connections, maintaining system stability under vibrations, impacts, or mechanical stress. With tin-plated coatings that resist oxidation and corrosion, lugs maintain consistent electrical performance over time, especially in humid or harsh environments.
- Easy installation and maintenance: Standardized designs allow for quick, precise, and secure crimping, reducing installation time while ensuring high-quality connections. Cable lugs are also easy to remove or replace, making periodic maintenance and inspections convenient.
2. Distinguishing cable lugs from common cable accessories
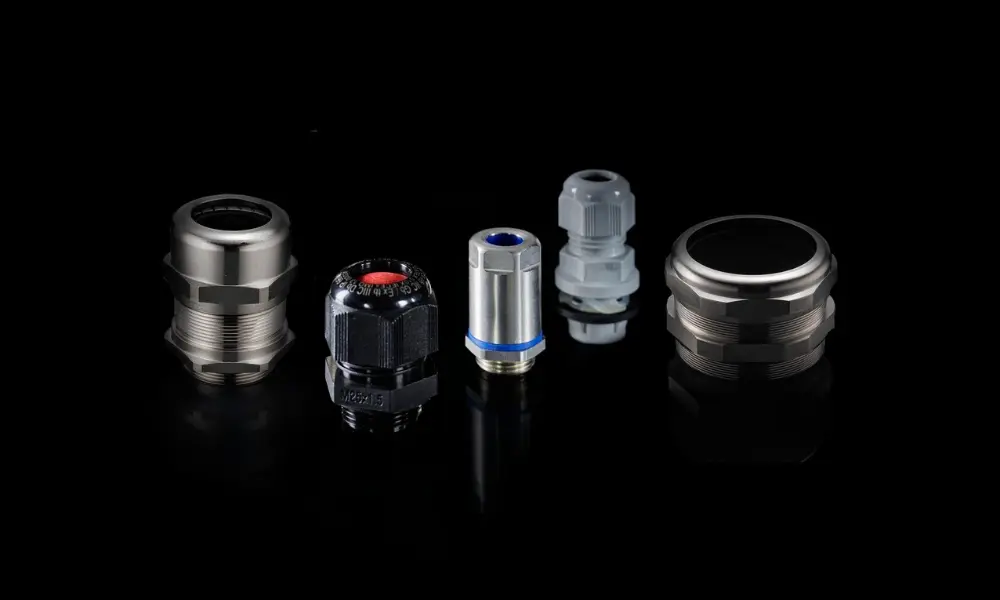

2.1 Cable lugs vs. cable glands
Both cable lugs and cable glands play important roles in securing and protecting electrical cables; however, their functions and designs are entirely different.
- Function: Cable lugs are used to connect conductors to electrical devices such as switches, sockets, or to join sections of cable together, ensuring a secure and safe electrical connection. In contrast, cable glands serve to fix and seal cables where they enter equipment or enclosures, reducing mechanical stress, preventing damage, and protecting against environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and vibration.
- Design: Cable glands typically feature threaded structures that allow the cable to be tightly clamped into the device. Cable lugs, on the other hand, come in various shapes such as ring lugs, flat lugs, or parallel lugs, with each type designed for a specific electrical connection purpose.
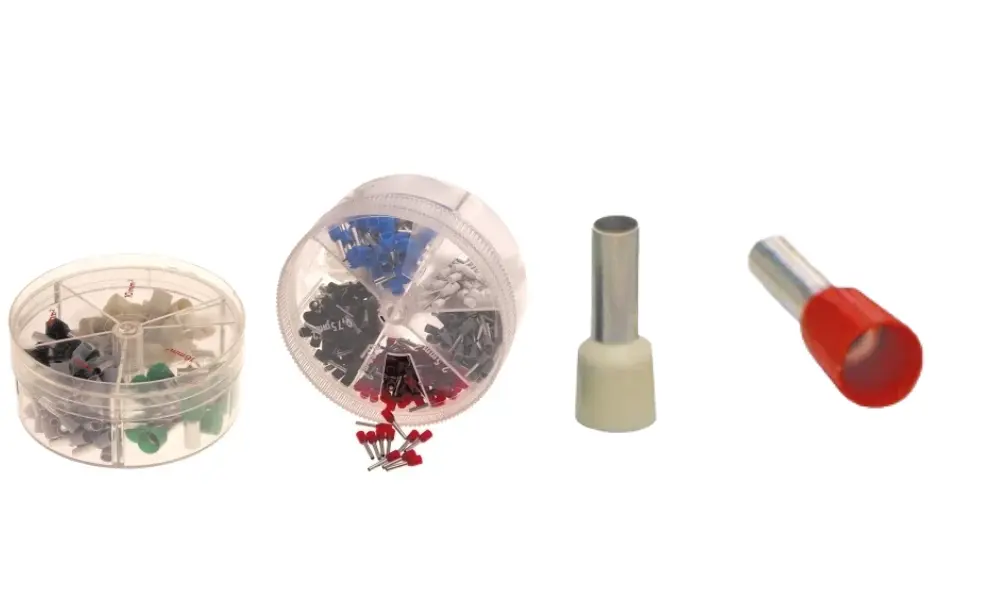

2.2 Cable lugs vs. ferrules
Both ferrules and cable lugs are accessories used to connect electrical conductors, but they differ significantly in purpose and design.
A ferrule is a small metal tube crimped onto the end of a multi-stranded conductor to hold the strands together, prevent fraying, and ensure stable electrical contact when inserted into a terminal block or screw terminal.
A cable lug, on the other hand, is a connector with a bolt hole, used to secure the conductor to devices, busbars, or connection points. It provides both a strong mechanical connection and reliable electrical conductivity, especially for high-power circuits.
In other words, ferrules are used to finish the wire end, while cable lugs are used to connect the wire to equipment or an electrical system.
3. Applications of cable lugs
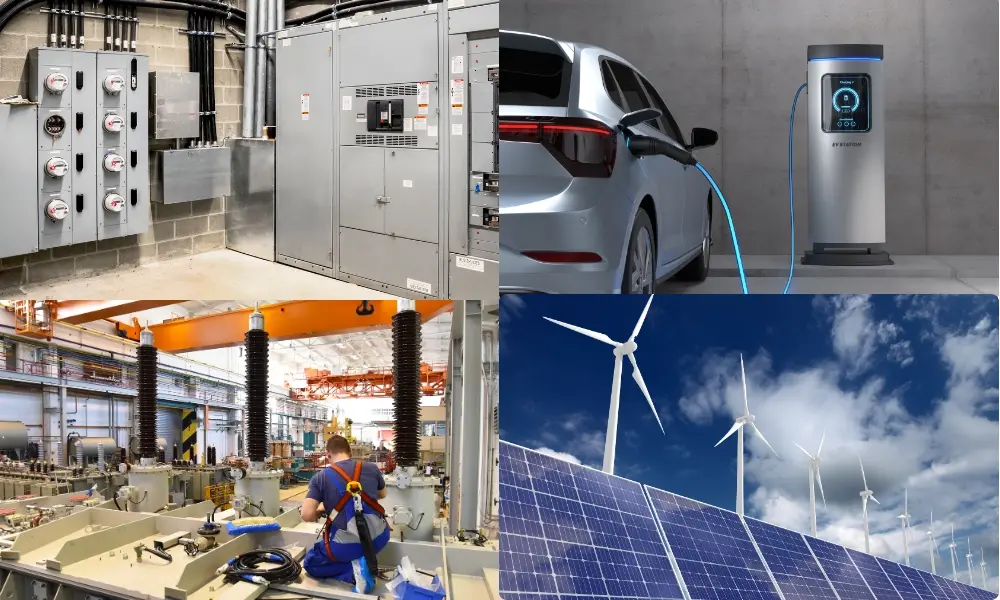

Depending on environmental conditions and technical requirements, cable lugs are widely used across various industries:
- Industrial automation: In factories, control panels, and industrial drive systems, cable lugs are used to connect motors, inverters, and control devices.
- Power distribution systems: In residential and commercial installations, cable lugs connect conductors within electrical panels and distribution boards, ensuring stable and safe current flow.
- Renewable energy: In solar and wind power systems, cable lugs play a crucial role in connecting solar panels, inverters, and battery storage units. Using pressed copper lugs reduces energy loss and maintains long-term reliability.
- EV technology: EV charging stations require high-power, safe electrical connections. Cable lugs are used to link high-capacity conductors to the power source and charging units.
- Telecommunications and data centers: Cable lugs are used in power supply and grounding systems, enhancing safety and stability across the network infrastructure.
- Marine and offshore applications: Cable lugs are applied in electrical systems on ships, offshore platforms, and underwater equipment. Stainless steel or specially tin-plated lugs are often used to increase durability and ensure safety in harsh marine environments.
4. Types of cable lugs
Choosing the correct type of cable lug is a key factor in ensuring a safe, reliable, and long-lasting electrical connection. The variety of cable lugs available today reflects the diverse applications, conductor structures, and environmental conditions encountered in the field of electrical engineering. Cable lugs can be classified based on several key characteristics, including:
- Material: Typically made of copper, aluminum, or tin-plated alloys.
- Termination method: Crimped, soldered, or bolt/screw connections.
- Design/shape: Tube, ring, Y-type, spade, or pin-style lugs, each suited to specific connection points.
- Technical standards: Such as DIN 46235, EN 13600, UL, or IEC.
- Insulation status: Non-insulated (bare) or insulated lugs.
- Barrel type: Standard barrel, flared barrel, or double barrel for flexible cables.
5. Classification of cable lugs by material
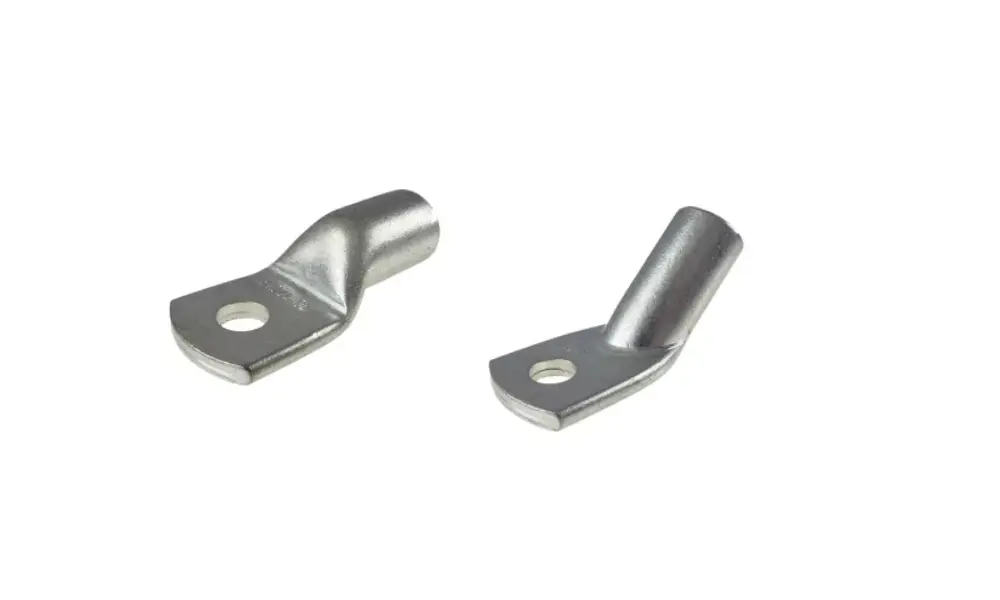

HELU-S-RK-CU and HELU-S-RK-45-CU-UL copper cable lugs
5.1 Copper cable lugs
Copper is still considered the standard material for high-performance electrical connections due to its superior electrical and mechanical properties, which are difficult to match with other materials. Characteristics of copper cable lugs:
- Excellent electrical conductivity.
- High mechanical strength, capable of withstanding vibration and impact in harsh environments.
- Good corrosion resistance, especially when tin-plated, which increases the longevity and stability of the connection.
- Low thermal expansion coefficient, reducing deformation or loosening of connections with temperature changes.
- Drawbacks: Heavier and more expensive than aluminum, but offers superior performance and reliability.
Copper cable lugs are commonly used in high-current applications or grounding systems. Conductors are secured to copper lugs either by crimping or soldering, depending on the specific type of lug.
Datasheet of HELU-S-RK-CU and HELU-S-RK-45-CU-UL copper cable lugs
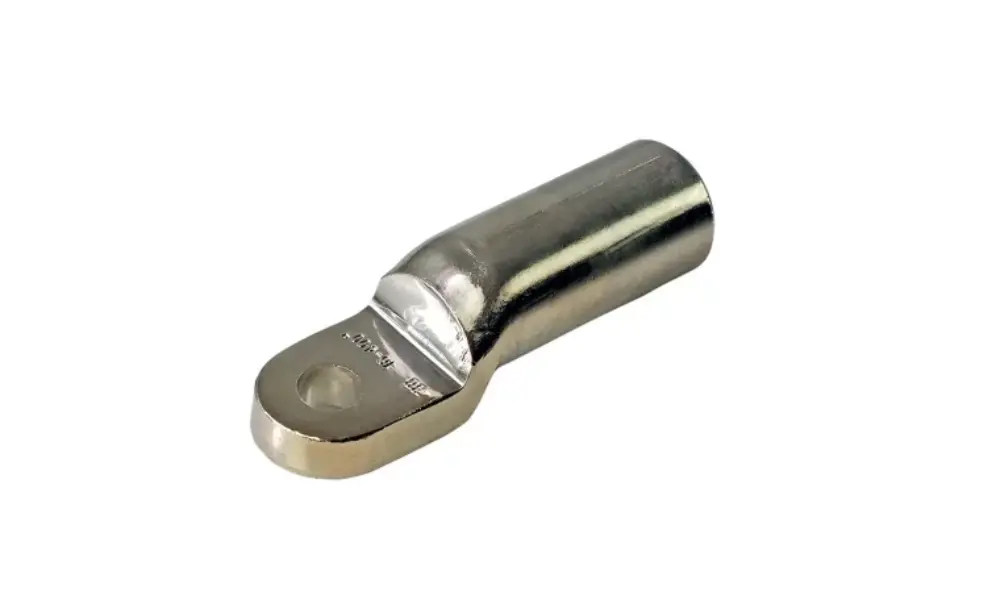

HELU-S-PK-AL-FG-VZN aluminum cable lug
5.2 Aluminum cable lugs
Aluminum cable lugs provide an alternative to copper, especially in applications where cost and weight are important factors. However, when using aluminum lugs, the following considerations should be noted:
- Aluminum lugs have lower electrical conductivity compared to copper.
- They are prone to oxidation when exposed to air, forming a thin, hard oxide layer with high resistance - requiring proper handling during connection.
- Aluminum has a higher thermal expansion coefficient than copper, so attention must be paid to the tightness of the connection to prevent loosening or deformation over time.
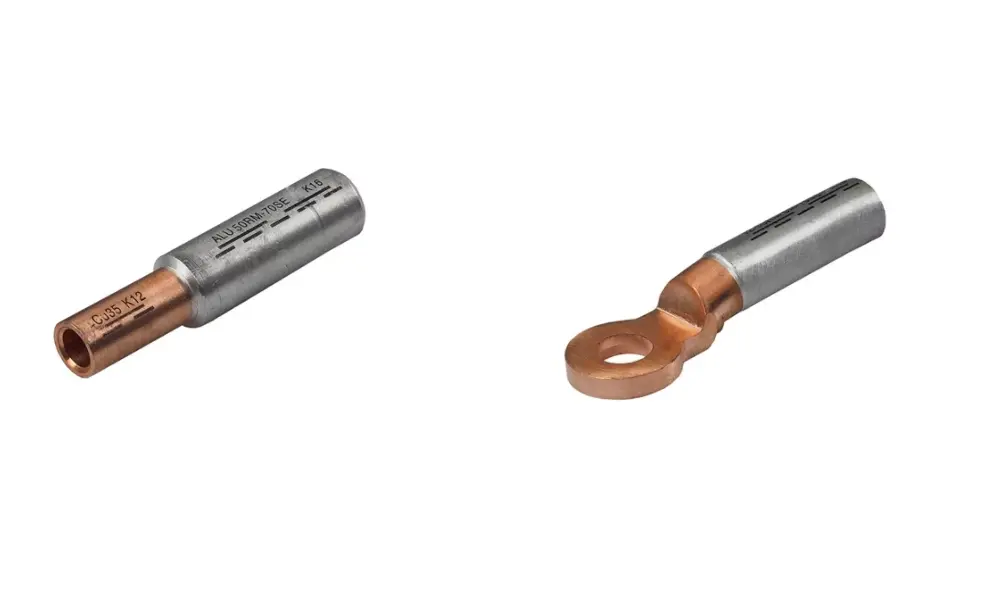
HELU-S-PV-AL CU (left) and HELU-S-PK-AL CU (right) cable lugs
5.3 Bimetallic cable lugs
Bimetallic lugs are primarily used when connecting aluminum conductors to copper busbars or contact points. Using a lug made entirely of copper or entirely of aluminum in such cases can cause galvanic corrosion due to the difference between the two metals, leading to contact corrosion and reduced connection quality over time.
To address this issue, bimetallic lugs are designed with an aluminum barrel and a copper contact. The two parts are friction-welded to create a strong, durable connection that ensures optimal electrical conductivity and low transition resistance between aluminum and copper.
Datasheet of HELU-S-PV-AL CU and HELU-S-PK-AL CU cable lugs
6. Classification of cable lugs by termination method
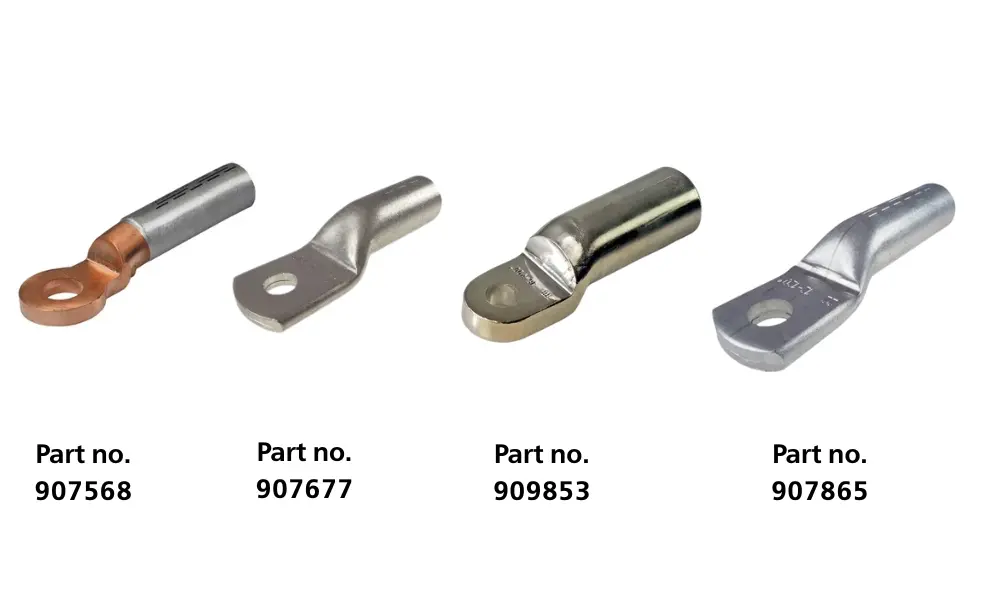

Compression cable lugs of HELUKABEL
6.1 Compression cable lugs
Compression cable lugs are the most commonly used type of cable lug in modern power transmission and distribution applications. This termination method uses a specialized crimping tool - manual, hydraulic, or battery-operated - along with compatible crimping dies to tightly compress the lug barrel around the conductor. The result is a fixed, durable connection with optimal electrical conductivity.
Some representative HELUKABEL cable lug products include: HELU-S-PK-AL/CU (907568), HELU-S-PK-CU-DIN (907677), HELU-S-PK-AL-FG-VZN (909853), HELU-S-PK-AL-DIN (907865), HELU-S-PK-CU (907679).
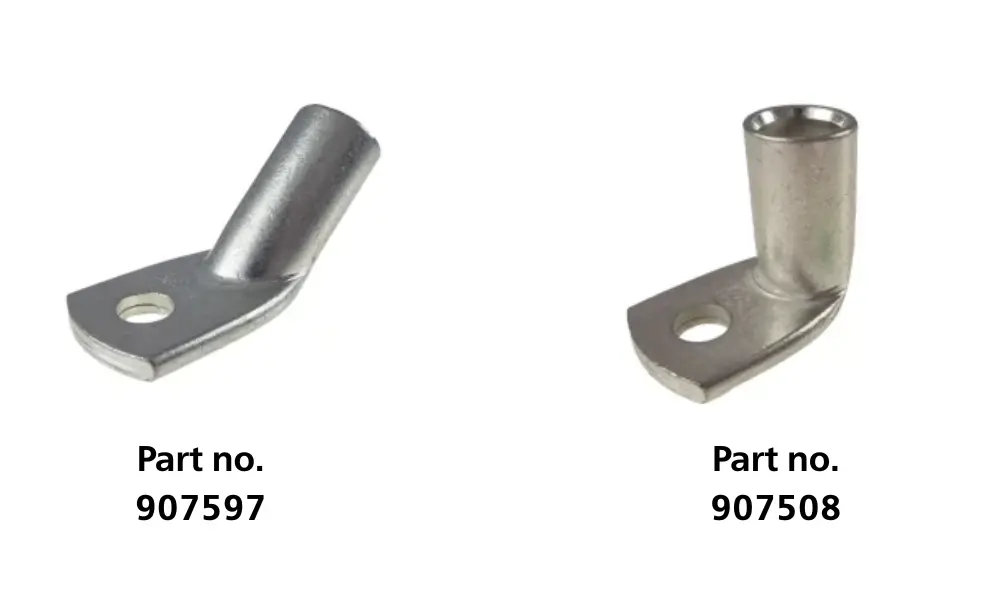

6.2 Tubular cable lugs
Tubular lugs, also known as standard cable lugs, are used more widely than DIN compression cable lugs. In terms of dimensions and length, tubular lugs differ from DIN lugs - they are generally shorter and have different barrel sizes.
In addition to the standard version, tubular lugs are available in 45° and 90° angled variants.
Some HELUKABEL tubular lug products include: HELU-S-RK-CU (907303), HELU-S-RK-F-CU (907409), HELU-S-RK-90-CU-UL (907508), HELU-S-RK-45-CU-UL (907597).
6.3 Mechanical cable lugs
Mechanical cable lugs are designed with a set-screw or shear-bolt mechanism to secure the conductor inside the lug barrel. Unlike compression lugs, they do not require specialized crimping tools for installation.
6.4 Solder cable lugs
Solder cable lugs are connected to the conductor through a soldering process. In this method, both the lug and the conductor are heated, and solder is applied to form a fixed and durable electrical connection.
This method provides excellent electrical conductivity, as the solder layer reduces contact resistance and prevents oxidation at the connection point. However, precise soldering is required - improper technique can damage the conductor or result in a cold solder joint, compromising the quality of electrical transmission.
7. Classification of cable lugs by shape

Ring cable lugs
7.1 Ring cable lugs
Ring lugs are the most commonly used type for electrical cable connections. The lug’s head has a circular (closed-loop) shape, ensuring a secure connection between the conductor and the connection point.
The main advantage of ring lugs is high reliability—because of the closed-loop design, the lug cannot slip off a bolt or terminal block unless fully removed, enhancing both safety and connection stability. Ring lugs are typically used at bolt-and-nut connection points.
7.2 Pin lugs and blade lugs
Pin lugs have a cylindrical, pin-like shape and are primarily used in industrial applications, especially for connecting cables to relays, measuring devices, and other electrical instruments. The lug is typically straight (I-shaped), making connection and disconnection quick and easy, particularly when inserted into terminal sockets.
Pin lugs are commonly used in control and signal circuits operating at low voltage, such as in industrial control panels, automation control boards, and equipment monitoring systems.
Blade lugs are similar in design to pin lugs, but the connecting end is flat (blade-shaped). This design allows the lug to be directly inserted into specialized slots or connectors in terminal blocks or compatible connectors.
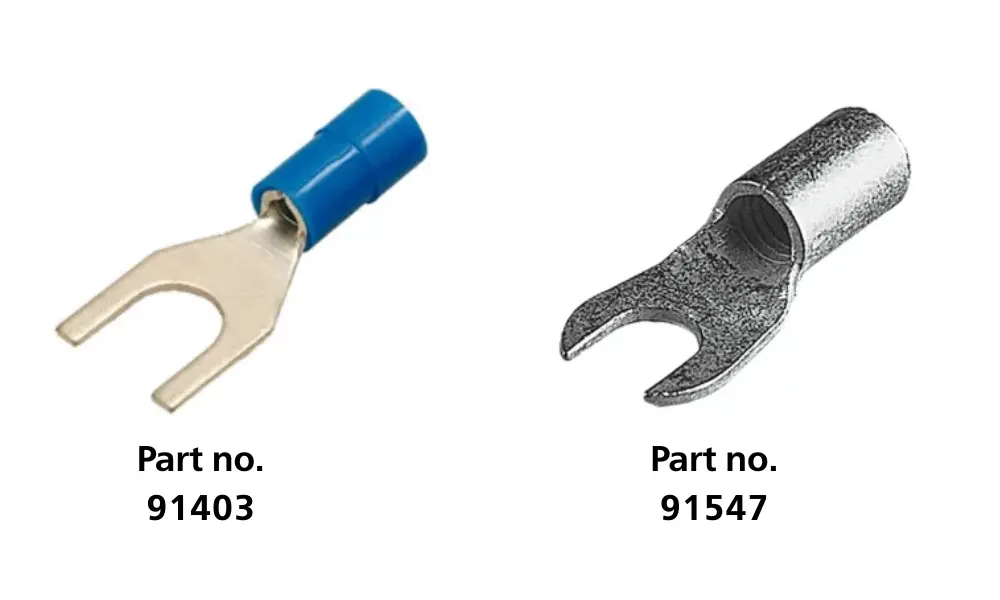

Y-type cable lugs
7.3 Y-type cable lugs
Y-type lugs have an open Y-shaped design at the end. This shape allows the lug to be installed or removed easily by loosening the bolt or nut at the connection point, without fully detaching the connection.
Thanks to their quick and convenient installation, Y-type cable lugs are commonly used in:
- Electrical control panels, switchgear, relays, and control switches
- Industrial and residential electrical systems that require frequent assembly, disassembly, or maintenance
Some HELUKABEL products include: ST-PS / FS (91403), B-FT (91547)
8. Other classification methods for cable lugs
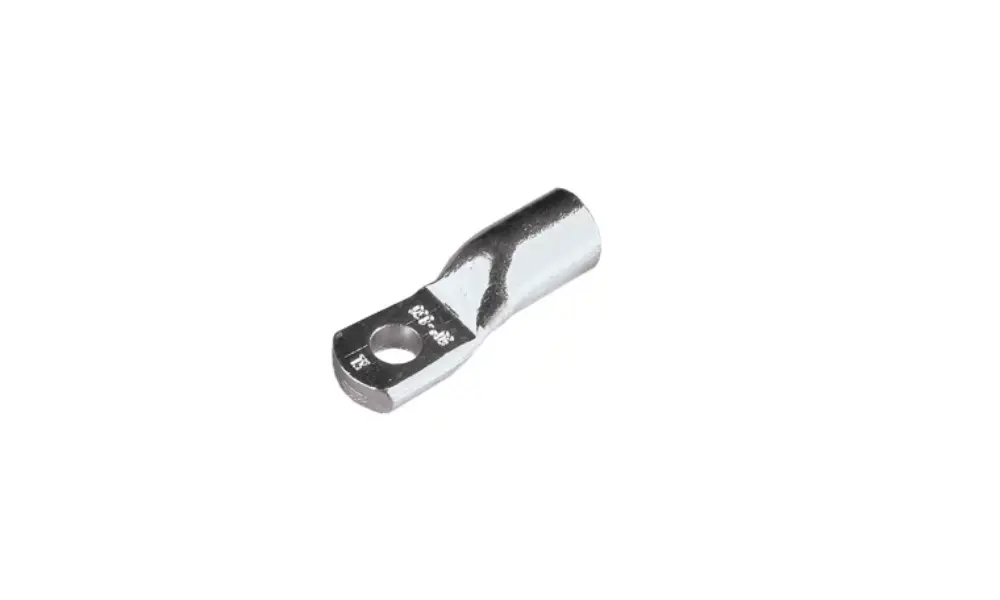

UL-certified cable lug HELU-S-RK-S-CU-UL
8.1 Insulated vs non-insulated cable lugs
- Non-insulated lugs: This is the standard type made entirely of conductive metal without any insulation layer. Non-insulated lugs typically offer higher current-carrying capacity and are more cost-effective, making them suitable for industrial applications and high-power electrical systems.
- Insulated Lugs: These lugs are equipped with an integrated insulating sleeve, usually made of PVC or nylon, and are commonly used with small-gauge wires in control panels, automotive systems, and low-voltage circuits. Insulated cable lugs provide enhanced safety and protection against accidental short circuits, making them ideal for residential and commercial electrical installations.
8.2 Classification by technical standards
- DIN 46235 standard: This standard defines the application, dimensions, and marking of compression cable lugs for crimping solid, stranded, fine-stranded, and extra-fine-stranded copper conductors. It also specifies the required number of crimps for each conductor type.
For installation, DIN recommends using crimping dies according to DIN 48083, Parts 1, 3, and 4, ensuring proper crimping for solid, multi-stranded, and fine-stranded wires. - EN 13600 standard: In addition to DIN compression lugs, some manufacturers offer standard tubular cable lugs made from electrolytic copper in compliance with EN 13600. Compared to DIN lugs, tubular lugs are generally shorter and have different tube dimensions, making them suitable for specific installation configurations.
- Cable lugs may also comply with other standards such as UL 486A-486B, IEC 61238-1.
| Type of cable lugs | Representative products |
| Ring cable lug | B-ET, ST-ET |
| Y-type cable lug | ST-PS / FS |
| Straight cable lug | HELU-S-PV-CU-DIN, HELU-S-SV-CU |
| Copper cable lug | HELU-S-RK-CU, HELU-S-SV-CU |
| Aluminum cable lug | HELU-S-PK-AL-DIN, HELU-S-PV-AL-DIN |
| Bimetallic cable lug | HELU-S-PK-AL/CU, HELU-S-PV-AL/CU |
| Compression cable lug | HELU-S-PK-AL/CU, HELU-S-PK-AL-FG-VZN |
| Type of cable lugs | Representative products |
| Tubular cable lug | HELU-S-RK-N, HELU-S-RK-CU-UL |
| DIN cable lug | HELU-S-PK-CU-DIN, HELU-S-PV-CU-DIN |
| UL cable lug | HELU-S-RK-90-CU-UL, HELU-S-RK-45-CU-UL |
| Insulated cable lug | ST-ET, ST-PS / FS, ST-PR / FP, ST-RP |
| Non-insulated cable lug | HELU-S-RK-CU, HELU-S-PK-AL-DIN |
| Halogen-free cable lug | ST-ET, ST-PR / FP, ST-RP |
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |



