What are drag chains and why are they used?
Drag chains are gradually becoming an indispensable part in the field of automation. So what are drag chains and how they are applied in industries?
1. What are drag chains?
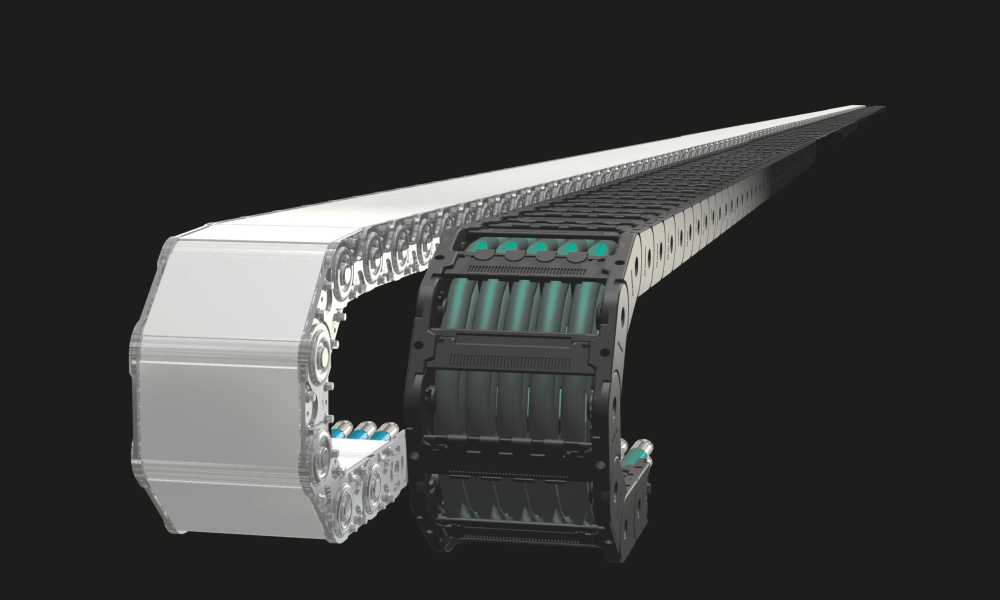
Electric cables fulfill the function of supplying energy to production equipment and technical machinery, as well as interconnecting the entire power supply system within buildings and factories. Any damage to these cables can be detrimental to businesses. For instance, partial or entire damage to an electrical cable system can cause adverse effects throughout the entire production line.
Hence, the necessity for drag chain solutions arises to safeguard these intricate structures. Resembling a robotic arm in appearance, drag chains manifest in various configurations, including flexible structures designed to encase power cables, thereby shielding them from damage.
>>See more: How to identify the quality of control cables?
Drag chain, alternatively referred to as cable chain, energy chain, cable carriers, or energy supply chain, constitutes a flexible cable and hose management system employed for transmitting power and signals from a stationary source to terminal equipment and continuously moving machinery. These drag chains serve to safeguard cables and hoses against wear and damage induced by motion, vibration, or environmental elements, while also orchestrating them into a structured system to enhance the efficiency of machinery and equipment operation. Widely adopted in industrial sectors including mechanical engineering, automation technology, robotics, and material handling, drag chains are integral components of various industrial applications.
2. Benefits of using drag chains
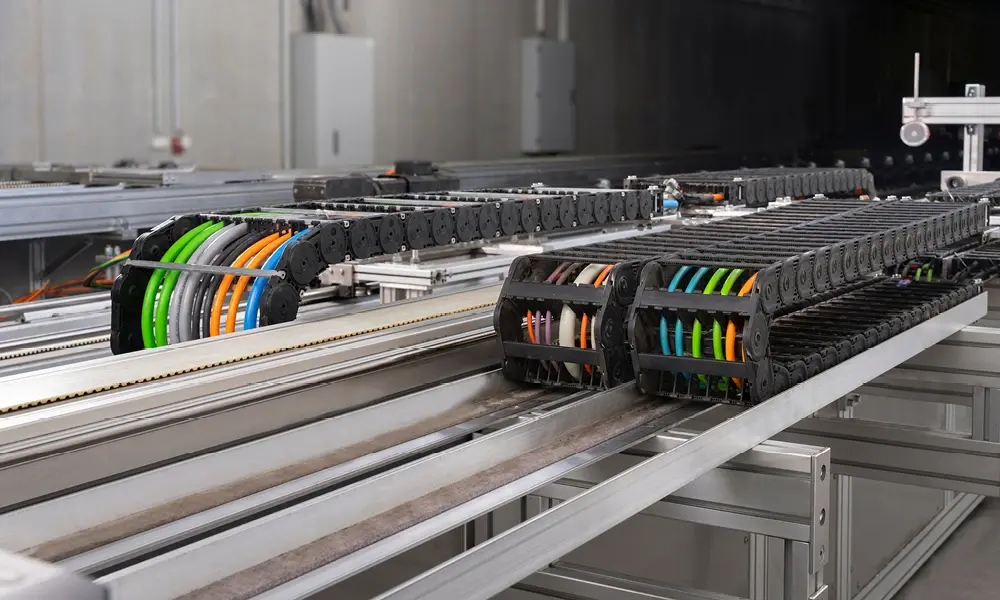

Using drag chains offers numerous benefits as follows:
2.1 Prolonged lifespan of electric cables
Drag chains are crafted from high-quality materials such as plastic, iron, or stainless steel, engineered to endure challenging industrial settings. Consequently, they provide a protective enclosure for electric cables, mitigating mechanical factors such as bending, twisting, abrasion, and impact.
2.2 Space optimization during installation
By securely keeping cables within the drag chain system, unnecessary cable length is minimized, reducing the likelihood of tangling and entanglement. This ensures that cables are only extended to the required length, thereby enhancing overall cable management. By directing cables along predetermined paths, drag chains prevent cable sprawl, thus optimizing the installation area, a particularly advantageous feature in space-constrained environments.
2.3 Enhanced safety in electrical system
Safety within the working environment is heightened thanks to the application of drag chains. By containing cables and hoses within their confines, drag chains mitigate the risks of collisions, slips, and workplace accidents. Moreover, the flexible and easy-to-install design of drag chains facilitates expedited maintenance and repair tasks, thereby reducing downtime and effort expenditure.
2.4 Downtime minimization
Unplanned downtime can incur significant losses for businesses. The utilization of drag chains helps diminish the likelihood of damage and unwanted machine downtime, thus enabling continuous and efficient production operations.
2.5 Versatility in applications, flexibility in design
Drag chains find widespread application across various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy sectors. Their adaptability stems from their capacity to accommodate diverse cable types, hose configurations, and operational requirements. For instance, drag chains can be tailored to meet specific bend radii, travel distances, and environmental conditions, rendering them suitable for diverse industrial contexts. This customization ensures compatibility with different devices and machinery, thereby enhancing overall performance and efficiency.
>>See more: 6 factors affecting the design of drag chains
3. Applications of drag chains
The application spectrum of drag chains is extremely diverse. Some of the typical ones include:
- Railway and transportation: This industry necessitates flexible and continuous movement, particularly in scenarios involving heavy loads. Drag chains serve to organize cables and hydraulic hoses systematically, shielding them from damage and wear induced by constant motion.
- Robotics: Robots rely on electrical or hydraulic cables to power their components, requiring seamless movement alongside the machine. Drag chains aid in safeguarding cables and hydraulic hoses from entanglement, ensuring unhindered robot operations.
- Food and Beverage (F&B): Automated assemblies are gradually becoming an indispensable part of the F&B industry. The employment of drag chains not only facilitates the optimal operation but also reduces labor-intensive jobs.
- Marine and offshore: Crane is a typical example where drag chains are utilized in this sector. This type of machine demands components capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to sea salt corrosion. Furthermore, drag chains simplify the utilization of electrical cables and hydraulic hoses on offshore oil rigs, protecting the cable systems during equipment movement.
- Mining: Conveyors use drag chains to transport coal from mining sites to collection points. These conveyors tackle the problems confronted by alternative transportation modes.

4. Common types of drag chains
4.1 Open drag chains and closed drag chains
Closed drag chains are favorable in dusty, abrasive environments, requiring a high level of protection and sealing performance. This type of drag chain is used in power plants and coal mining enterprises, where specialized transportation systems are essential.
On the other hand, open drag chains feature an open-link structure comprising horizontal bars that accommodate electric cables and hoses. Each link incorporates a latch mechanism that facilitates convenient insertion of power cables into the cable chain.
4.2 Plastic drag chains
Plastic drag chains can be made from polyamide material or combined with other materials such as aluminum, iron, or steel, depending upon the intended usage purpose as well as environmental conditions.
The highlight of plastic drag chains encompass the following:
- Excellent resistant to abrasion and impact, rendering them sufficient in diverse conditions such as acid, salt, or grease settings.
- Operating temperature ranges from -20℃ to 100℃, owing to the utilization of polyamide 6 material reinforced with 35% glass fiber.
- Compact and lightweight design facilitates easy installation and removal for maintenance and repair purposes.
- Endures high pressure and heavy loads.
- Cost savings in comparison to iron or stainless-steel drag chains.
>>>See more: A thorough look into 3 types of plastic drag chains by EKD Systems
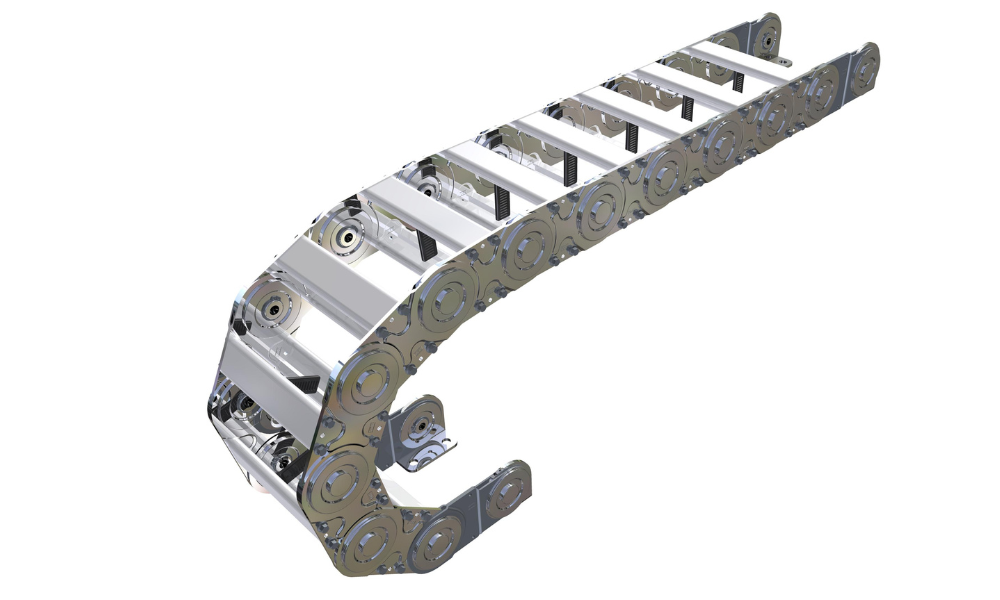

Steel link chain SLE
4.3 Steel drag chains
Steel drag chains are crafted from robust materials, abrasion-resistant, making it suitable for operation in rigorous environments. They find widespread application in heavy industries such as mining, metallurgy, oil production… Steel drag chains exhibit resilience against high temperatures and severe abrasion conditions, making them ideal for applications like hot clinker and hot lime conveyors, where temperatures can soar up to 1000°F. Notable characteristics of steel drag chains include:
- High flexibility and durability, ensuring resistance to bending or breakage.
- The maximum operating temperature of steel drag chains is higher than that of plastic ones, ranging from -20°C to 600°C (as opposed to -40°C to 600°C for stainless steel).
- Fabricated from steel or stainless steel, drag chains have prolonged lifespan and are less susceptible to wear in comparison to plastic drag chains.
- The ability to lengthen or shorten steel drag chains not only facilitates flexible adaptation to specific applications, but also streamline maintennace and repair when needed.
5. Important notes prior to the selection of drag chains
Selecting drag chains for a specific application stem from a few notes as follows:
5.1 Bending radii
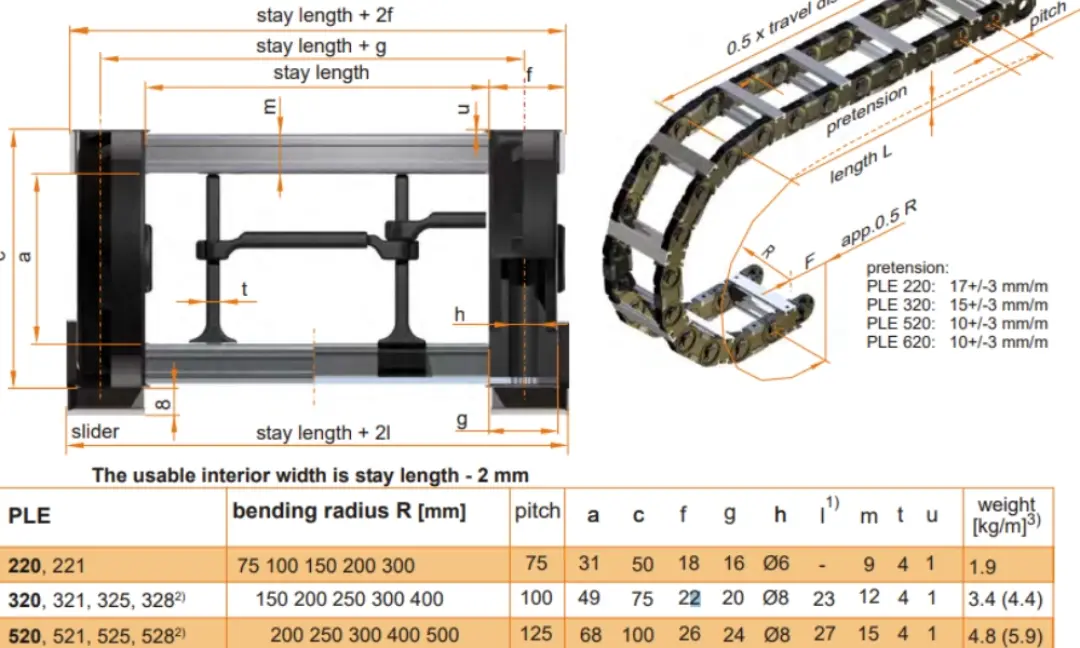
Bending radius should be the top consideration when opting for drag chains. Bending radius is gauged from the center of the curve loop to the center of the pivot pin on the side link. The greater the bending radius is, the greater the tension on cables is reduced, thus the lifespan is extended. Apart from space-constrained applications, it is of great significance that the bending radius outweighs the recommended bending radius of cable manufacturers.
All cables offer a range of bending radius options, with each cable manufacturer specifying a minimum bending radius. The bending radius chosen for the drag chain will hinge upon the largest diameter cable or hose. Opting for a bending radius significantly larger than what is necessary for the buffer package will enhance the longevity of the cables and hoses.
5.2 Cable access
Drag chains are available in various configurations that facilitate different cable access methods.
Closed type drag chains are most suitable for small-scale applications since cable access from the middle of the channel is unfeasible. The alternative type employs hinged crossbars to enable cable access. Generally, these hinges necessitate a specialized tool for opening, thereby preventing inadvertent opening of the horizontal bars during operation.
Open-rail types also offer alternatives that do not mandate tools for cable insertion into the rail. Nonetheless, they are most effective over short distances, as prolonged usage may exert strain on the cable.
5.3 Environmental conditions
Environmental conditions directly impact the longevity of drag chains. For instance, carriers utilized on offshore oil rigs must endure severe environmental conditions while retaining functionality for extended periods, given their remote location and the challenges associated with frequent replacement.
Additional factors influencing durability include the necessity for heat-resistant drag chains fabricated from steel or fire-resistant plastic. Both variants of drag chains are designed for operation in environments characterized by high temperatures and the potential for fire and explosion hazards.

If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam
Tel. +84 28 77755578 | info@helukabel.com.vn | www.helukabel.com.vn






