What are ATEX and IECEx standards? Cables and accessories for hazardous areas
Ensuring safety in environments with a high risk of explosion is critical in many industries such as oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. Two prominent international safety standards regulate the design, production, and use of equipment in hazardous areas: ATEX and IECEx. Let’s explore and distinguish these two standards in the following article!
1. How are hazardous areas classified?

Explosion risks are a major concern in many industrial environments, requiring a comprehensive risk-management approach. A key element of this approach is the hazardous area classification system, which is essential for establishing strict safety procedures and complying with relevant standards. Proper classification protects both personnel and equipment from the dangers posed by flammable gases, vapors, combustible dust, and easily ignitable fibers.
Two primary standards guide this classification:
- National Electrical Code (NEC – United States): Defines and regulates Hazardous Locations (HAZLOC).
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards: Widely recognized in the United Kingdom, European Union, and many other regions.
In the U.S., these environments are commonly referred to as Hazardous Locations (HAZLOC), whereas in the U.K., EU, and other parts of the world, the more common term is Hazardous Areas.
>>Related articles: Cables used in the harsh environment of the mining industry
NEC hazardous area classification
1.1 NEC hazardous area classification
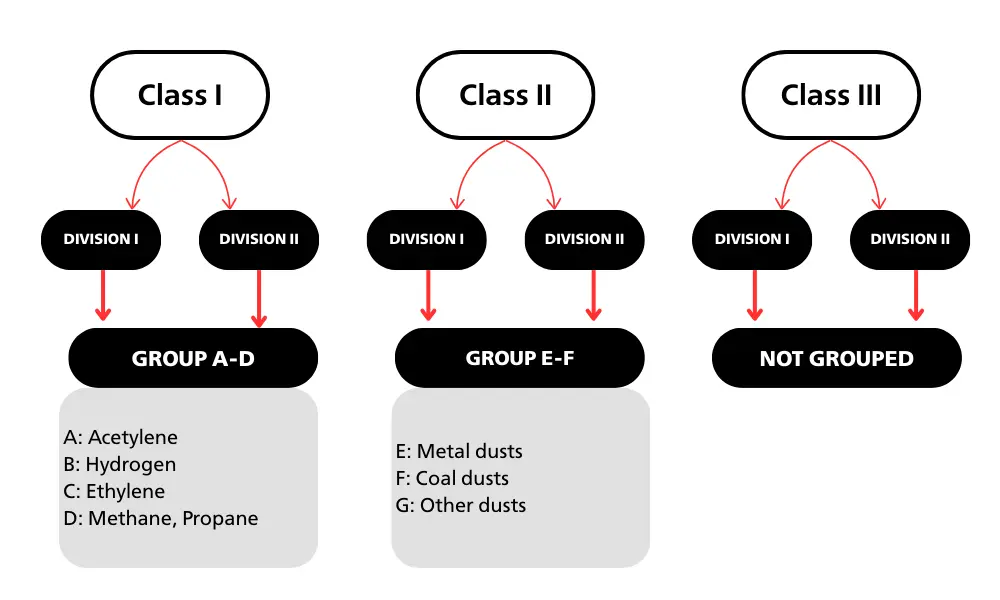
The National Electrical Code (NEC), issued by the U.S. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), is the foundational document that provides detailed guidelines for electrical installations in the United States. NEC classifies hazardous locations using a Class–Division–Group system:
- Classes identify the type of hazardous material: Class I (Flammable gases or vapors), Class II (Combustible dust), Class III (Easily ignitable fibers or flyings).
- Divisions indicate the level of risk:
Division 1: High likelihood of the hazardous substance being present during normal operations
Division 2: Hazardous substance is present only under abnormal conditions
In addition, NEC categorizes hazardous substances into Groups A through G based on ignition temperature, minimum ignition energy (MIE), and flame-propagation characteristics, helping engineers select equipment with the appropriate protection level:
- Group A: Acetylene – extremely low ignition temperature and energy
- Group B: Hydrogen – very low ignition temperature and energy
- Group C: Ethylene – low ignition temperature and energy
- Group D: Methane, Propane – relatively low ignition temperature and energy
- Group E: Metal dusts – variable ignition temperatures and MIE
- Group F: Coal dust – high ignition temperature but low MIE
- Group G: Fibers and flyings – variable flammability characteristics
1.2 IEC hazardous area classification
Unlike the Class–Division–Group system used in the NEC, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) adopts a Zonal Framework to classify hazardous areas. This approach focuses on the likelihood and frequency of the presence of explosive substances, making it simpler but generally less granular than the NEC system.
| Gas | Dust | Description |
| Zone 0 | Zone 2 0 | An area where explosive gas or dust is present continuously or for long periods. |
| Zone 1 | Zone 1 0 | An area where explosive gas or dust is likely to occur during normal operation. |
| Zone 2 | Zone 2 2 | An area where explosive gas or dust is unlikely during normal operation, but may occur occasionally due to equipment failure or abnormal conditions. |
2. ATEX and IECEx standards for cables and accessories in hazardous areas

ATEX logo
Operating in high-risk industries requires a deep understanding of international safety standards and certification systems. Among these, ATEX and IECEx are the two leading global frameworks for explosive atmospheres, forming the foundation for both safety and regulatory compliance.
Compliance with either ATEX or IECEx demonstrates a company’s strong commitment to protecting workers and production systems. These certifications are recognized worldwide, serving not only as a legal requirement but also as proof of excellence in explosion protection.
2.1 ATEX standard
ATEX (short for ATmosphères EXplosibles) is a European Union directive that specifies the requirements equipment must meet to be considered safe for use in explosive atmospheres.
This standard applies to both electrical and non-electrical equipment capable of generating an ignition source. ATEX certification confirms that a product is designed and manufactured to the highest levels of explosion-proof safety.

IECEx logo
2.2 IECEx standard
The IECEx (International Electrotechnical Commission System for Certification to Standards Relating to Equipment for Use in Explosive Atmospheres) is a global certification system that harmonizes the assessment and management of equipment intended for hazardous environments.
IECEx simplifies international trade by providing a single, globally accepted certification process, ensuring that equipment meets recognized international safety standards.
Electrical cables and accessories with IECEx certification can be sold and used across participating countries without the need for separate national testing or re-certification.
Because individual countries often maintain their own safety requirements, equipment exported from one nation to another typically must undergo additional testing and approval to be used in hazardous areas.
With IECEx, member nations agree on a common set of safety standards, significantly reducing inspection costs and certification time for manufacturers. Participating countries include most of Europe, as well as Canada, Australia, Russia, China, the United States, and South Africa, among others.
3. Differences between ATEX and IECEx standards
| ATEX | IECEx | |
| Scope | Valid only in European Union member countries | Recognized globally, widely accepted in multiple regions |
| Legal and standard basis | Legally mandated; the manufacturer is fully responsible for the certification process | Standard-driven; certification is carried out by an independent, approved certification body |
| Components | 2 directives | 4 schemes |
| Certification body | Notified Body (NB) – EU-designated organization | ExCB (Approved Certification Body) – IECEx-approved certification body |
| Marking | CE marking required, “Ex” symbol, equipment group & category, Notified Body (NoBo) number | Certificate of Conformity (CoC) number, ExCB number, and protection level description |
ATEX certification directives:
- ATEX 95: Requirements for explosion-proof equipment and systems
- ATEX 137: Requirements for worker safety in hazardous environments
IECEx certification schemes:
- IECEx Equipment Scheme: Certification for explosion-protected equipment
- IECEx Conformity Mark License: Authorization to use the IECEx compliance mark
- IECEx Services Scheme: Certification for services related to explosion-protected equipment
- IECEx Certified Persons Scheme: Certification of personnel competence for working with explosive atmospheres
4. Marking system for ATEX and IECEx certified cables and accessories
In hazardous areas, quickly identifying the safety certification of equipment is crucial. Understanding the marking systems for ATEX and IECEx ensures proper compliance and safe operation.
4.1 Marking for ATEX-compliant cables and accessories
ATEX labels provide essential information to select and use equipment safely in explosive atmospheres. However, reading these labels can sometimes be confusing, as labeling conventions are not fully standardized and may not always match the classification system described in the ATEX directives. Detailed guidance is usually provided in the product’s user manual.
Key elements commonly found on an ATEX label include:
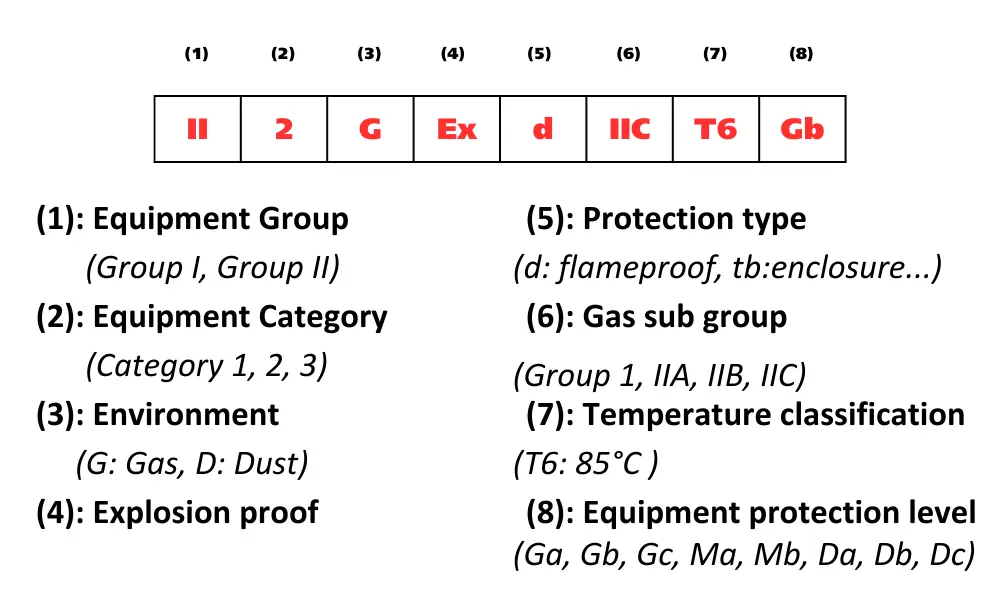
Key elements commonly found on an ATEX label
- CE Marking: Confirms compliance with EU requirements.
- Explosion protection symbol: The letter “E” inside a hexagon indicates explosion protection capability.
- Equipment group:
According to ATEX directives: Group I (mines), Group II (surface industries)
According to EN 60079-0: I, II, III (I: mines, II: gas, III: dust)
- Equipment category: 1, 2, or 3, indicating the protection level (1 = highest, 3 = lowest).
- Environment type: G / D / DG (G: Gas, D: Dust, DG: Both gas and dust)
- “Ex” symbol and protection code: e.g., Ex tD A21 indicates dust-protected equipment with a specific protection method.
- Gas or dust group: e.g., IIC denotes the gas group with the highest flammability (hydrogen, acetylene, etc.).
- Maximum surface temperature: Indicated via T-code (T1–T6) or °C (e.g., T4 or T80 °C).
- Protection level: e.g., Gb (Gas, high protection level).
4.2 Marking for IECEx-compliant cables and accessories
IECEx labels are visually similar to ATEX labels but have some notable differences. Unlike ATEX:
- IECEx does not use the “Ex” equipment symbol
- There is no CE marking
- Equipment groups and categories are not displayed
4.3 How to read markings on HELUKABEL cable glands
For example, a HELUKABEL cable gland like HELUTOP® HT-MS-EX-d 1 EMV includes the following marking: Ex-d, Ex-e EX II 2GD Ex d IIC Gb, Ex e IIC Gb, Ex tb III CDb

| Marking | Meaning |
| Ex II 2GD |
|
| Ex d IIC Gb |
|
| Ex e IIC Gb |
|
| Ex tb IIIC Db |
|
5. HELUKABEL ATEX/IECEx certified cables and accessories
5.1 ATEX/IECEx bus cables
HELUKABEL offers ATEX-certified bus cables in various versions, including:
- Profibus PA: Designed for process automation applications.
- Profibus PA Armoured: Ideal for areas where protection against rodents is required.
- Profibus PA Long Distance: Suitable for exceptionally long transmission distances.

| Name | Standard | Application | Part no. |
| Profibus PA | ATEX/ Class II, EX-i/ EN 60079-14 | is used for normal requirements in the process automation field (chemical industry) | 82835 |
| Profibus PA Armoured | ATEX/ Class II, EX-i/EN 60079-14 | finds use in areas with rodent such as rats, nutria etc. but also offers additional protection against all other outside mechanical influences thanks to it steel tape armouring | 802180 |
| Profibus PA Long Distance | ATEX/Class II, EX-i/EN 60079-14 | is used for especially long transmission distances in process networks. It uses a larger conductor cross-section to satisfy the attenuation requirements. | 800650 |

5.2 Other cables for use in hazardous areas
- Instrument cables: Installation in hazardous areas acc. to IEC 60079-14 ANNEX E but only with the correct ATEX conform accessories
- HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 PVC/PVC OS 300
- HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 PVC/PVC IOS 300
- HELUDATA® PLTC UL13 XLPE/LS0H OSA 300
- Bus cables: This cable is flame retardant and is designed for usage and installation in cable trays, ducts and / or armored tubes (reinforced tubes) such as Zone 1 & Zone 2 respective IEC 60079-14 ANNEX E, but only using the correct ATEX accessories.
5.3 Cables for intrinsically safe systems in explosion-endangered areas
In addition to the ATEX- and IECEx-certified cables mentioned above, HELUKABEL also supplies specialized cables for intrinsically safe systems. While these cables are not ATEX/IECEx certified, they are commonly used in intrinsically safe measurement and control technology.
The three available versions are:
- OZ-BL cable : Standard version | Part No. 14001
- OZ-BL-CY cable : Shielded version | Part No. 14028
- OB-BL-PAAR-CY cable : Shielded, twisted-pair version | Part No. 14077

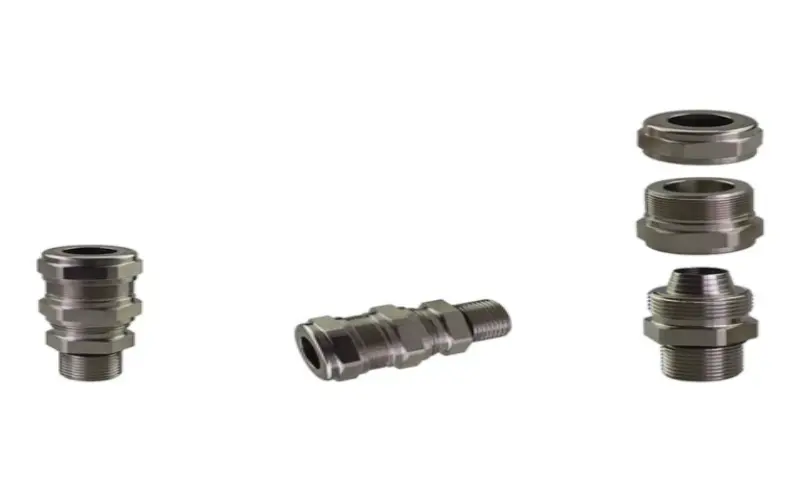
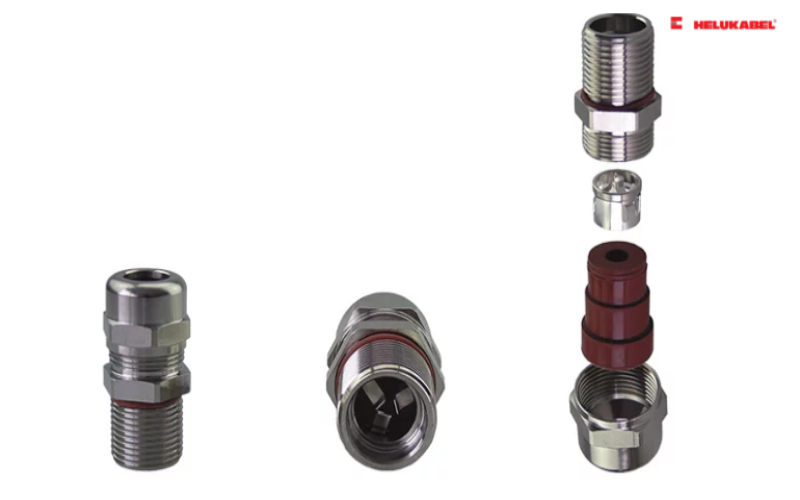
5.4 ATEX/IECEx cable glands from HELUKABEL
| Cable gland | Temperature range | Applications | Part no. |
| HELUTOP® HT-PA-EX | -40°C to +80°C |
| 906691 |
| HELUTOP® HT-PA-EX-Plus | -40°C to +70°C | 908080 | |
| HELUTOP® HT-PA-EX-Plus Silicone | -60°C to +70°C | 908105 | |
| HELUTOP® HT-MS-EX-d | -40°C to +80°C | 906941 | |
| HELUTOP® HT-MS-EX-d / e4 | -40°C to +100°C | 906965 | |
| HELUTOP® HT-MS-EX-d 1 EMV (copper) | -40°C to +80°C | 906959 | |
| Copper cable gland HSK-MS-EX / HSK-MS-EX-E | -20°C to +95°C | 98045 / 92880 |
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |