What are cable insulations? Common types of insulation materials
Insulation materials prevent current leakage and isolate electrical conductors from one another. Learn more about the role of cable insulation and the most common types of insulation materials in the article below!
The concept of insulation materials is entirely different from that of conductive materials. Conductive materials allow electricity to pass through them easily, facilitating the flow of electric current or charges. In contrast, insulation materials resist the flow of electric current and do not allow charges to move freely through them.
1. What are cable insulations?
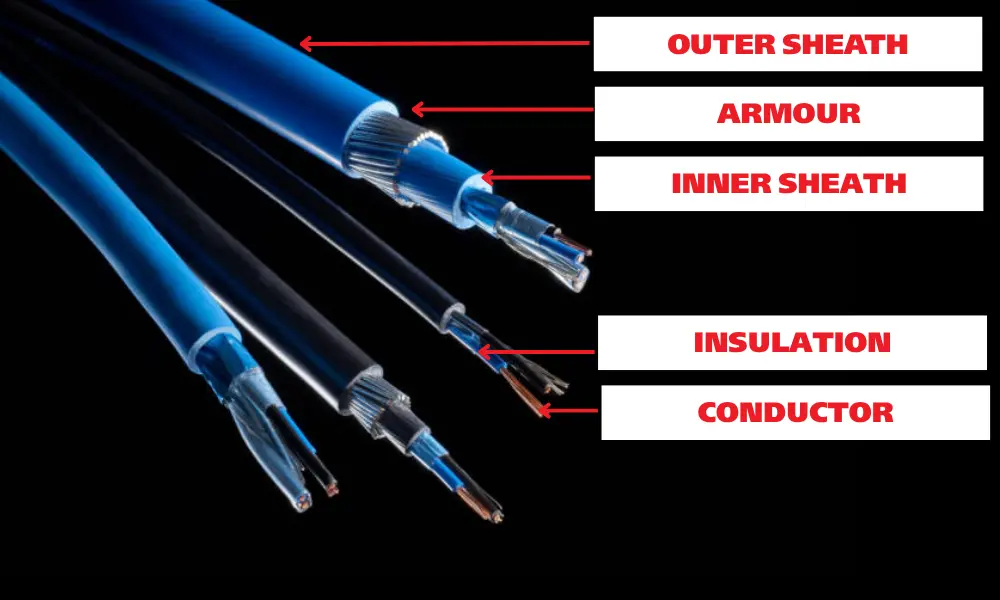
Components of electrical cables
The insulation layer in an electrical cable is the protective sheath wrapped around the conductor, designed to prevent direct contact and ensure safe operation in power and data transmission systems. It is a critical structural component of the cable, protecting the core from environmental factors and maintaining the stability of the current flow.
The composition of the insulation layer may vary depending on its intended use, but its primary function is to provide a reliable electrical barrier that allows the cable to perform safely and efficiently in various environments. In RF (radio frequency) cables, this layer is often referred to as the dielectric material.
The lifespan and performance of a cable are closely tied to the type of insulation material used. These materials protect the conductor from environmental hazards such as moisture, high temperatures, chemicals, and mechanical stress. Additionally, insulation prevents electrical leakage, ensuring that the current stays within the cable and does not come into contact with nearby conductors - thus maintaining safety and system integrity.
2. The role of insulation in electrical cables
Nearby electrical equipment like motors, transformers, or broadcasting devices can emit electromagnetic waves that interfere with cable signals
Insulation plays a vital role in ensuring the performance, safety, and durability of electrical systems. Key roles of cable insulation include:
2.1 Electrical isolation
The insulation layer effectively separates conductors, preventing current leakage or unwanted transmission between cores. This avoids short circuits and ensures that current flows according to the circuit design - especially important in multi-core cables used in complex systems.
2.2 Reducing crosstalk
Crosstalk occurs when electrical signals from one conductor interfere with adjacent conductors, which is critical in high-speed signal transmission. The insulation layer acts as a barrier, minimizing interference between cores and helping to maintain clear, stable, and accurate signal transmission.
2.3 Reducing EMI
Nearby electrical equipment like motors, transformers, or broadcasting devices can emit electromagnetic waves that interfere with cable signals. High-quality insulation materials can block or reduce these external fields, protecting signal integrity - crucial for sensitive data transmission and automated control systems.
2.4 Protecting workers from electric shock
One of the most important functions of insulation is to prevent direct contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electric shock. This is essential in public areas or industrial environments where workers are frequently exposed to electrical installations.
2.5 Environmental resistance
Cables may be exposed to moisture, corrosive chemicals, temperature changes, or UV radiation. Insulation materials are engineered to withstand these conditions, extending cable life and maintaining stable performance in both indoor and outdoor settings.
2.6 Mechanical protection
In addition to electrical insulation, the layer provides mechanical protection. It helps resist impacts, abrasion, tensile stress, or bending during installation and operation - safeguarding the conductors and ensuring continuous, safe power transmission.
3. Common types of cable insulations

PVC-insulated cables from HELUKABEL
Electrical cable insulations vary widely, each with specific properties and advantages. Below are some of the most commonly used materials:
3.1 PVC (Polyvinyl Clorua) insulation
PVC provides good electrical insulation, abrasion resistance, and can withstand temperatures from -30°C to 70°C, and up to 100°C–120°C for short periods.
Key advantages:
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Strong chemical resistance against acids, solvents, and oils
- Excellent flame retardancy for enhanced safety
Applications: Used in residential wiring, power distribution, signal, and telecommunication cables. However, PVC is not ideal for harsh environments or high-performance transmission systems.
| Cable | Properties and applications | Datasheet |
| JZ-HF control cable | Oil-resistant, for use in drag chains | Datasheet |
| HELUDATA® EN-50288-7 PVC/PVC IOS 500 instrumentation cable | Signal measurement cable for oil & gas, petrochemical industries | Datasheet |
| HELUWIND® WK POWERLINE ALU 0,6/1 kV single core cable | Highly flexible, for use in wind power applications | Datasheet |
| HELUSOUND® 450 EXTREME FLEX PVC audio cable | Finely stranded conductor (class 6), extremely flexible, used for stage/studio audio systems | Datasheet |

3.2 PE (Polyethylene) and PP (Polypropylene) insulation
PE is widely used in coaxial and low-capacitance cables due to its excellent dielectric properties. It’s ideal for high-performance transmission and can be foamed to reduce dielectric constant to around 1.50.
Key specifications:
- Temperature range: -45°C to +70°C
- High insulation performance for stable, high-speed signal transmission
- Common in signal, data, LAN, and measurement cables used in dry or low-capacitance applications
However, PE is stiff and brittle, making it less suitable for bending or flexible applications.
PP shares similar properties but offers a wider temperature range (-10°C to +90°C) and can temporarily withstand up to 140°C.
| Cable | Properties and applications | Datasheet |
| TOPFLEX®-EMV-3-PLUS-2YSLCY-J | PE insulation, double screened | Datasheet |
| HELUKAT® PROFInet C CAT.5e SF/UTP PUR CHAIN | PE insulation, FRNC, compatible with drag chains | Datasheet |
| HELUCHAIN® MULTIFLEX 512®-C-PUR UL/CSA | Special PP insulation, special PUR outer sheath, suitable for high mechanical stress applications (drag chains, robots…) | Datasheet |
| HELUPOWER® ROBOFLEX®-D PUR UL/CSA UV | PP insulation, resistant to bending and torsion movements in robots | Datasheet |
3.3 PUR (Polyurethane) insulation
PUR is known for its exceptional toughness, flexibility, and long flex life, even at low temperatures. It resists chemicals, moisture, and abrasion - ideal for harsh industrial environments.
However, PUR has poor dielectric properties and is typically used as an outer sheath rather than primary insulation.

3.4 XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) insulation
XLPE excels in high-temperature resistance and mechanical strength.
Key characteristics:
- Operating temperature up to 90°C, short-term up to 130°C
- Resistant to heat and chemicals
- Low moisture absorption, stable insulation performance
Applications: Power transmission and distribution in industrial, outdoor, chemical, or high-temperature environments.

3.5 TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) insulation
TPE combines rubber and plastic features, offering high flexibility and elasticity.
Advantages:
- UV and ozone resistance for outdoor use
- Excellent abrasion resistance
- Highly flexible - ideal for tight installation spaces
Applications: Automotive, mobile electrical devices, or confined-space installations.
| Cable | Properties and applications | Datasheet |
| MULTISPEED® 500-C-TPE | Bend-resistant, low torsion, halogen-free | Datasheet |
| HELUEVENT® LOAD CABLE TPU | Used in lighting and stage technology | Datasheet |
| UNIPUR®-CP1 | Abrasion-resistant, flexible in low temperatures | Datasheet |
| PUR spiral cables | Shielded, for measurement/medical/low-current applications | Datasheet |

3.6 Rubber insulation
Rubber insulation - both natural and synthetic - is one of the most flexible and durable types of insulating materials available today. Several types of rubber are commonly used, each offering unique advantages:
- Ethylene Propylene Rubber (EPR): EPR is highly regarded for its excellent thermal and electrical insulating properties. It has a wide operating temperature range, typically from -30°C to +160°C.
- Neoprene (Polychloroprene): Neoprene is a thermoset synthetic rubber that requires vulcanization to achieve its desired properties. It stands out for its abrasion resistance, puncture resistance, and strong resistance to oils and solvents. These features enhance the durability and service life of cables used in harsh environments.
- Silicone: Silicone is one of the best temperature-resistant insulating materials available, with high fire resistance and stable performance at temperatures of up to +180°C. Thanks to its outstanding flexibility, it is ideal for applications requiring frequent bending, confined space installations.
| Cable | Properties and applications | Datasheet |
| NSHTÖU reeling cable | Oil-resistant; suitable for applications involving simultaneous reeling and pulling stress such as conveyors, lifts, and cranes | Datasheet |
| HELUPOWER® SJOOW | EPR insulation, oil-resistant, water-resistant | Datasheet |
| NEO-Flat-C flat cable | Special rubber insulation, trailing cable for festoon applications | Datasheet |
| THERMFLEX® 180 EWKF | Silicone insulation, halogen-free, temperature-resistant | Datasheet |
3.7 Fiberglass insulation
This is a type of glass fiber insulation material, known for its exceptionally high temperature resistance, with a continuous operating temperature of up to +400°C, and even up to +700°C for short durations. It is an ideal choice for applications in extreme temperature environments.
Several HELUKABEL cable series use glass fiber as insulation, such as: HELUTHERM® 400, HELUTHERM® 400-MULTI, HELUTHERM® 400-MULTI-ES, HELUTHERM® 600, HELUTHERM® 600-ES.
3.8 Other types of insulations
In addition to the insulation materials mentioned above, several other materials are also commonly used for cable insulation:
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): A thermoplastic insulation material with an exceptionally wide operating temperature range from -190°C to +260°C. PTFE offers excellent flexibility, along with outstanding resistance to water, oil, chemicals, and heat.
- FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene): Known for its thermal and chemical stability, FEP has an operating temperature range from -100°C to +205°C.
Some HELUKABEL cable series that use PTFE or FEP insulation include: HELUFLON®-FEP-6Y MULTI, HELUFLON®-FEP-6Y, HELUFLON®-PTFE-5Y.
4. FAQs about cable insulations
4.1 What is the difference between insulation and outer sheath?
The insulation is wrapped around the conductor and serves to prevent electrical leakage and electrical contact between cores (in multi-core cables), ensuring safe energy transmission.
In contrast, the outer sheath (also called the jacket) surrounds the entire cable construction. It protects against mechanical impact, moisture, chemicals, UV radiation, and other environmental influences.
While they serve different purposes, both layers are typically extruded and made of plastic materials, with thicknesses varying depending on cable specifications and installation conditions.
4.2 What are thermoplastic and thermoset insulation materials?
- Thermoplastic materials: These can be melted and reshaped multiple times upon heating. Common thermoplastics used for cable insulation include PVC, PE, PP, and PUR, offering flexibility and recyclability.
- Thermoset materials: Once cured, these cannot be remelted. Thermosets like XLPE and EPR offer superior heat resistance, chemical resistance, and durability, making them ideal for demanding or high-temperature environments.
4.3 What are the advantages of halogen-free insulation materials?
Halogen-free insulation emits low smoke and non-toxic gases when exposed to fire, reducing the risk of respiratory hazards during emergencies. These materials are essential for use in residential buildings, hospitals, schools, and office complexes, where fire safety and air quality are critical.
4.4 What are key factors in selecting an insulation material?
When choosing insulation for electrical cables, it's important to consider the application's specific technical and environmental requirements:
- Temperature resistance: In high-temperature environments, materials like XLPE or silicone rubber are ideal due to their thermal stability and insulation integrity.
- Chemical resistance: For use in chemical plants, oil and gas, or marine applications, choose insulation materials with strong chemical and corrosion resistance.
- Flexibility: In applications involving frequent bending or movement - such as robotics or machinery - opt for flexible materials like PVC or EPR, which provide long-lasting performance.
- Compliance with safety standards: Select insulation materials that meet international safety standards (ISO, IEC) to ensure compliance in industrial, commercial, and residential installations. These standards confirm performance in dielectric strength, fire resistance, and long-term reliability.
4.5 Why does insulation thickness matter?
The thickness of the insulation layer directly correlates with the voltage rating of the cable. Higher voltage applications require thicker insulation to prevent dielectric breakdown and ensure safe operation.
Additionally, the dielectric strength of the insulation material affects how thick the insulation needs to be. Materials with high dielectric strength can maintain safety and performance with thinner insulation, which helps to reduce cable size and environmental impact through lower material consumption.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Ward 3, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |



