What are bus cables and their features? HELUKABEL’s industrial bus cables
Bus cables are the backbone of industrial communication, connecting devices within a network using standard protocols. In this article, let’s explore bus systems, bus cables, and HELUKABEL’s bus cable product lines!
Contents
1. Understanding bus systems
1.1 What is a Bus System?
In computer architecture, the term bus system refers to a system that enables data transmission between different components within a single computer or between multiple computers. This term covers all necessary hardware such as conductors, optical fibers, as well as software—specifically, the communication protocols that control information exchange.
The concept of a computer bus dates back to the early days of computing, when buses were essentially parallel electrical circuits with multiple connection points for hardware components. Over time, the definition has expanded to include any configuration that can perform the same logical function as a traditional electrical busbar.
Today, computer buses have evolved to support both parallel data transmission and bit-serial transmission. They can be organized in various physical structures, including multidrop/parallel connections or daisy-chain serial links. In addition, some bus systems use switched hubs for connectivity, the most well-known example being USB (Universal Serial Bus).

1.2 The role of communication via bus systems
Communication through bus systems forms the backbone of modern mechatronics projects. Bus cables play a key role in Industry 4.0 digital communication networks, connecting devices via standard protocols and enabling all components to share a common cable pathway.
- In mechatronics, components such as sensors, actuators, and microcontrollers must communicate effectively to ensure smooth and reliable system operation. A bus system simplifies this communication, replacing complex point-to-point wiring with structured data transmission protocols.
- In industrial manufacturing, bus systems are used to control production lines, sensors, and actuators. PROFIBUS cables are favored for their stable performance, even in harsh environments. In the automotive industry, they ensure fast and precise coordination between robots and sensors, even under strong electromagnetic interference.
- In modern office buildings, KNX cables enable efficient control of lighting, HVAC, and security systems - enhancing comfort while optimizing energy consumption. In the logistics sector, fieldbus cables are used for conveyor belts and warehouse management systems, helping maintain continuous and accurate operations.
In other words, bus cables are the “nervous system” of modern technology infrastructure.
2. Bus cables for industrial communication
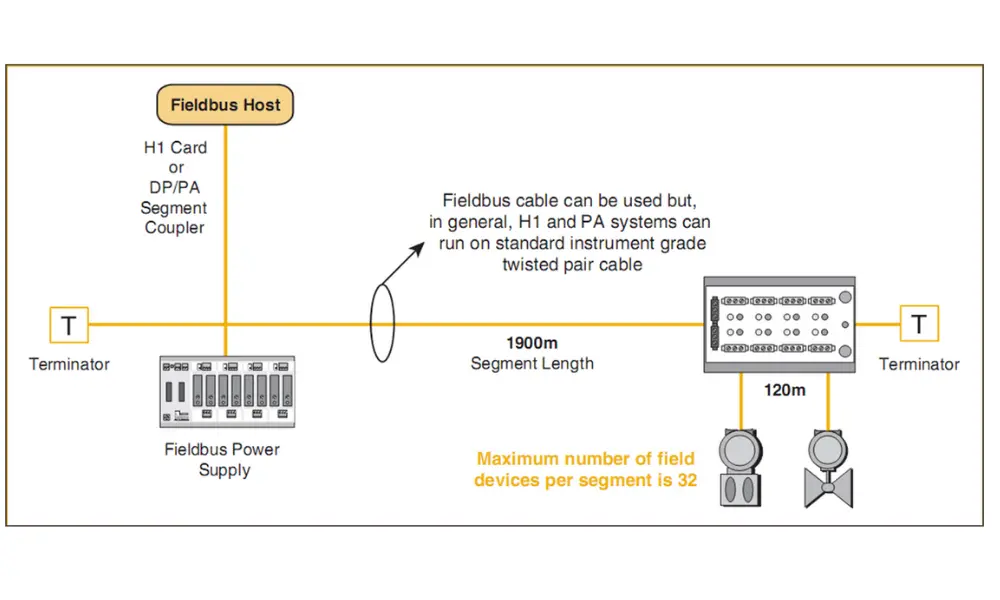
2.1 What is an industrial bus?
An industrial bus is a communication system used to transmit data between components or devices at different levels within a manufacturing plant, including the information level, control level, and field level. Within a bus system, various communication standards may be used, such as DeviceNet, ControlNet, PROFIBUS, or Ethernet.
With the rapid advancement of industrial automation, the role of industrial bus technology has become increasingly important. It is one of the core technologies ensuring efficient communication and data exchange between devices in a production line. Under the control of a master device, information is transmitted from the sending device to the receiving device accurately and synchronously.
2.2 Common industrial applications of bus cables
Bus cables are used to control many functions at the field level. For example, to maintain a stable fluid flow rate, a controller will receive data from a sensor monitoring the fluid volume and send commands to an actuator to adjust the valve opening/closing to meet the required setpoint. All data exchanges between these functions are carried through the bus cable.
Other common applications include connecting a PLC to controllers, switches, sensors, and actuators. Examples include selector switches, pushbuttons, circuit breakers, motor starters, control delay timers, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors.
These industrial automation systems often operate in clean rooms or harsh environments. Conditions such as chemical washdowns, continuous bending motion from robotic arms, high temperatures, or exposure to petroleum-based substances can damage cables. In such conditions, commodity cables are prone to failure - leading to unexpected and unplanned downtime.
3. What is a Fieldbus system?
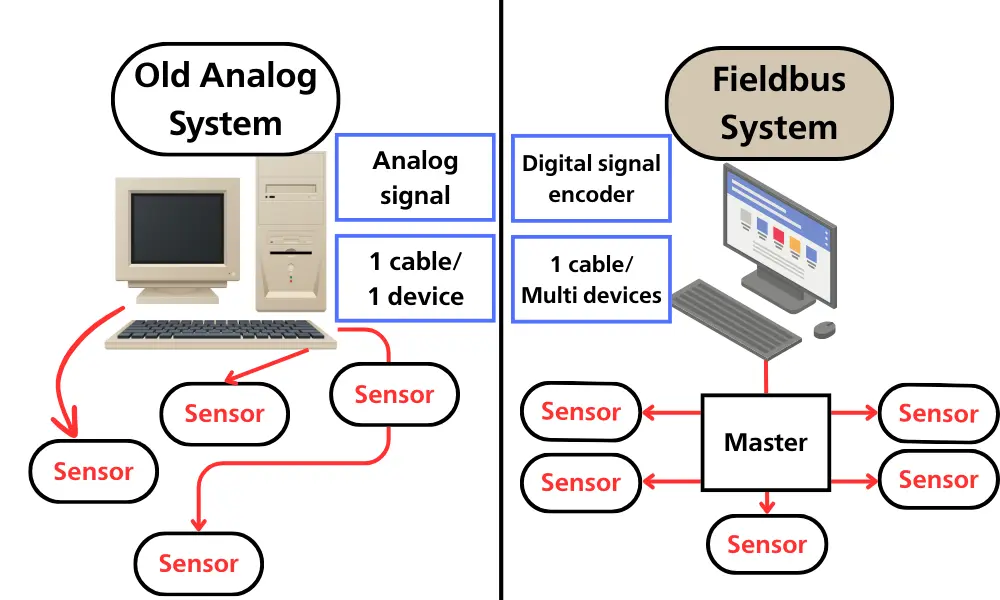
Fieldbus refers to a group of industrial computer networks used for real-time distributed control. The main goals of Fieldbus technology are to reduce installation costs, save time and expenses through simplified planning, and improve system operational reliability thanks to additional features—especially in complex systems with a large number of input/output signals.
In simple terms, Fieldbus is a method of communicating with input devices (sensors, switches, etc.) and output devices (valves, drive motors, indicator lights) without having to connect each device individually to a controller (such as a PLC or industrial PC). It enables two-way communication between field devices and the control system, handling both discrete data (All or Nothing) and more complex analog data (setpoints, alarms).
However, Fieldbus is not a single, specific type of connection. More precisely, it refers to a group of communication protocols used in industrial applications. Today, the standard for Fieldbus protocols is defined in IEC 61158. Below, we will explore some of the most common protocols in the Fieldbus family.
4. Common types of industrial bus cables

Star Quad Topology
4.1 CAN bus cables
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication protocol standardized under ISO, developed by Bosch (Germany) in the 1980s, originally for the automotive industry.
Key characteristics of CAN bus cables include:
- Support for multi-master configurations.
- Data transmission speeds of up to 1 Mbps.
- Can be implemented using twisted pair, coaxial, or fiber optic cables.
- Supports both linear bus and star bus topologies.
CAN bus cables are commonly used in vehicle control systems, industrial machinery, and automated robots.
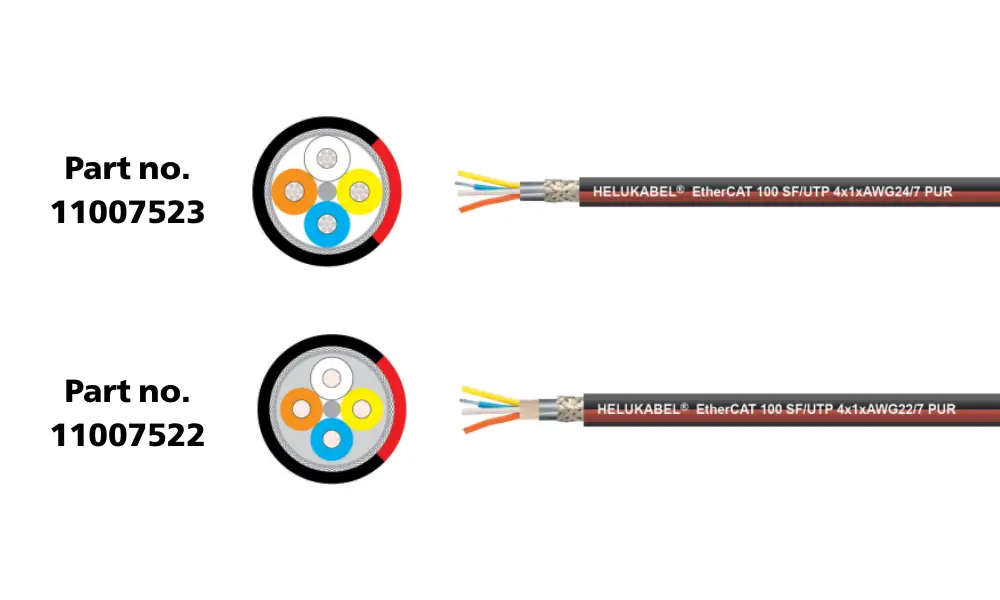
4.2 EtherCAT Bus Cables
EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is a high-performance Ethernet-based protocol for real-time control, introduced by Beckhoff Automation (Germany) in 2003. Data is transmitted in a ring or line topology, where each slave device reads the required data and immediately forwards the remaining data to the next device. Advantages of EtherCAT cables include:
- Ultra-low latency.
- Precise synchronization.
- Flexible network expansion.
Typical applications include high-speed production lines, robot control, and CNC machinery.
4.3 PROFIBUS cables
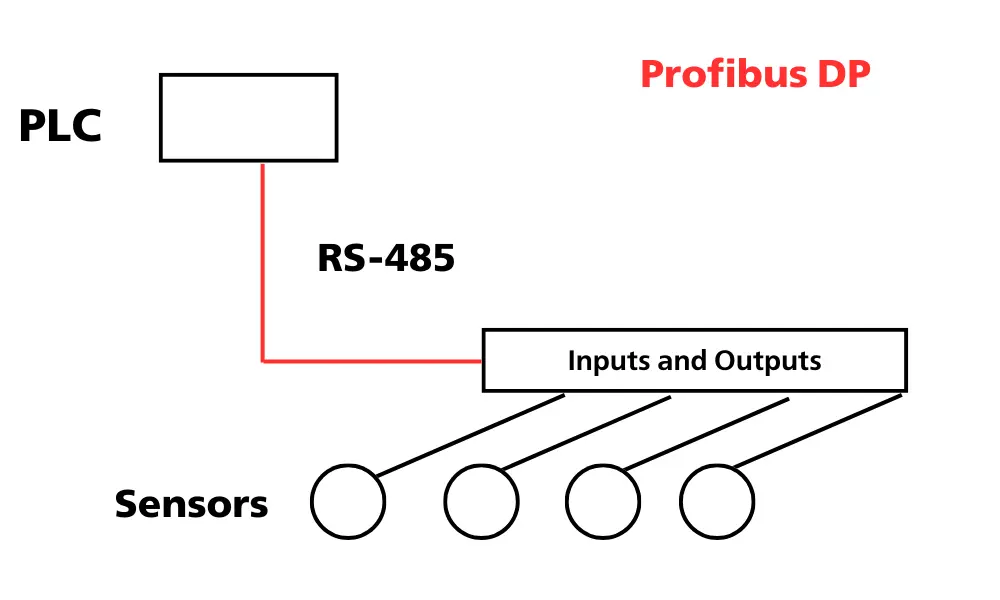
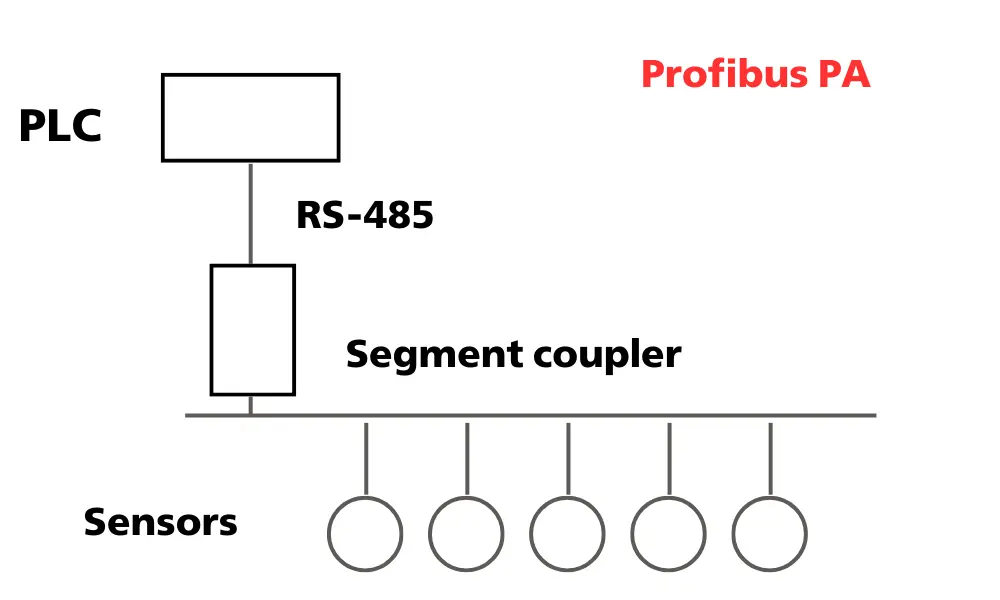
PROFIBUS is a classic serial Fieldbus standard, while PROFINET is an industrial Ethernet protocol. Due to their shared origins, PROFIBUS and PROFINET have some similarities; however, overall, they are quite different. PROFIBUS cables come in two main types: PROFIBUS Decentralized Peripherals (DP) and PROFIBUS Process Automation (PA), each designed for specific applications.
PROFIBUS PA is used in process automation. Its physical layer is Manchester Encoded Bus Powered (MBP), whereas the physical layer for PROFIBUS DP is RS-485.
Although they use different physical layers, PROFIBUS PA and PROFIBUS DP share the same communication protocol.
4.4 PROFINET cables
PROFINET is a distributed communication system developed by Siemens and the PROFIBUS User Organization, combining the strengths of PROFIBUS and industrial Ethernet.
Key characteristics:
- Supports multiple network topologies.
- Compatible with standard Ethernet for easy integration and expansion.
- Enables real-time control while also transmitting data to the Web/Cloud via TCP/IP.
Applications: Factory control system integration, smart manufacturing, and industrial IoT.
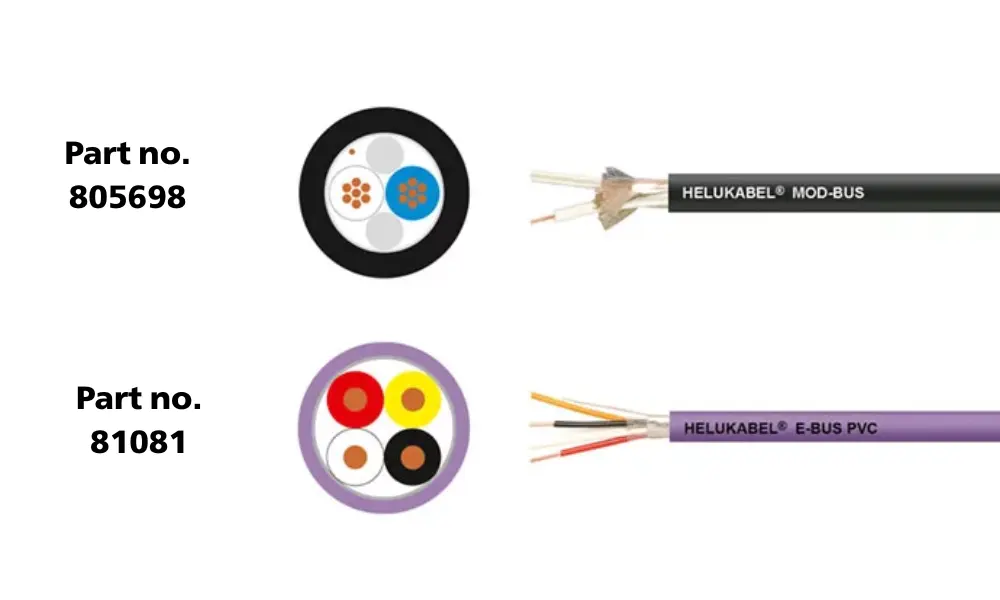
Mod bus and EIB/KNX bus cables
4.5 Modbus bus cables
Modbus is an industrial communication protocol introduced in 1979 by Modicon and is considered the oldest industrial bus standard still in use.
Its advantages include simplicity, ease of implementation, and low cost. Common versions include:
- Modbus RTU – High-speed serial transmission.
- Modbus ASCII – Uses ASCII characters, making it easier to read and debug.
- Modbus TCP – Transmits over Ethernet.
Applications: PLCs, SCADA systems, sensor control, and actuator management.
4.6 EIB/KNX bus cables
EIB (European Installation Bus) cables were the original foundation for building control and automation systems in smart buildings. Developed under the European Installation Bus standard, they enabled integrated management of functions such as lighting, HVAC, and security.
Building on this success, KNX emerged as a unified standard, combining the strengths of EIB, BatiBUS, and EHS. Both standards use the same type of cable; however, KNX supports more protocols, enabling broader device integration while remaining backward-compatible with EIB systems.
| Field bus system | Bus power | Cabling redundancy | Max devices | Synchronization | Cycle time of less than 1 millisecond |
| AS-interface | Yes | No | 62 | No | No |
| CANopen | No | No | 127 | Yes | No |
| ControlNET | No | Yes | 99 | No | No |
| CC-Link | No | No | 64 | No | No |
| DeviceNet | Yes | No | 64 | No | No |
| EtherCAT | No | Yes | 65536 | Yes | Yes |
| Interbus | No | No | 511 | No | No |
| Lon Works | No | No | 32000 | No | No |
| Modbus | No | No | 246 | No | No |
| Profibus DP | No | Optional | 126 | Yes | No |
| Profibus PA | Yes | No | 126 | No | No |
| Profinet IO | No | Optional | Almost unlimited | No | No |
| Profinet IRT | No | Optional | Almost unlimited | Yes | Yes |
| SERCOS III | No | Yes | 511 | Yes | Yes |
| SERCOS interface | No | No | 254 | Yes | Yes |
| Foundation Fieldbus HI | Yes | No | 240 | No | No |
Cabling Redundancy – The capability to maintain system operation even if one cable path fails.
Synchronization – The ability to synchronize timing between the controller (master) and the devices (slaves).
5. HELUKABEL bus cable product lines
HELUKABEL bus cables comply with all relevant standards and deliver multiple outstanding benefits:
- High-quality materials extend service life, while precisely controlled impedance ensures stable signal transmission.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) shielding: Protects transmitted signals from external electromagnetic interference while minimizing the emission of interference into the surrounding environment.
- Exceptional flexibility: Easily installed and routed in confined spaces or narrow cable ducts.
- Proven durability in harsh environments: Our PROFIBUS cables have been tested in food production facilities, withstanding extreme temperatures and high humidity, yet maintaining continuous, uninterrupted data transmission even under the most demanding conditions.
HELUKABEL offers a complete range of cables for the most widely used bus systems:
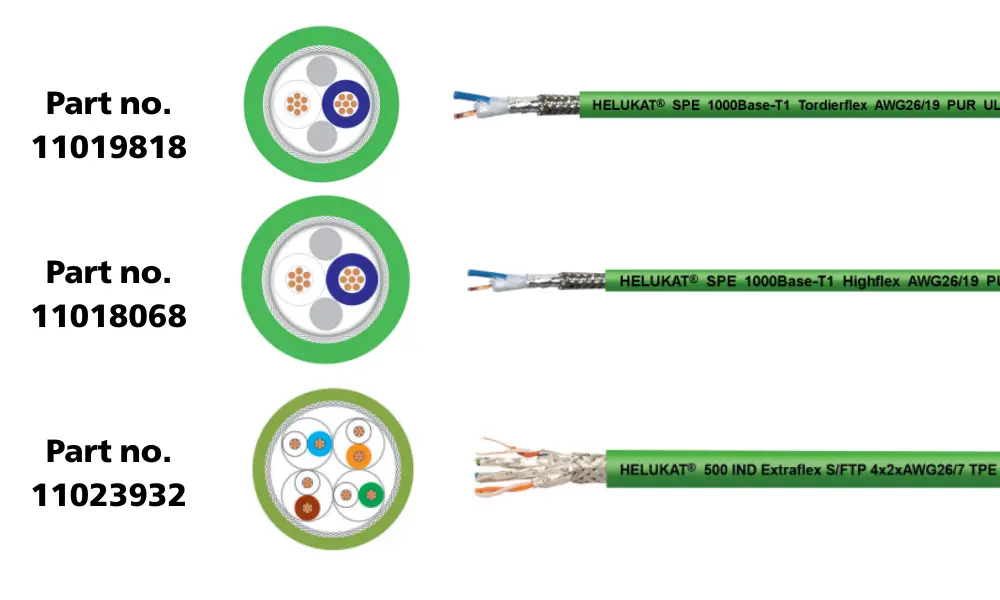
5.1 Industrial Ethernet cables
Industrial Ethernet solutions bring proven Ethernet technology into harsh industrial environments. These networks must withstand wide temperature variations, resist vibration, and operate reliably for many years without failure.
The construction of industrial Ethernet cables is significantly different from office-grade Ethernet cables. Industrial Ethernet cables feature a rugged outer jacket made from special PUR or PVC, offering resistance to oil, heat, and mechanical impact. Two-pair cables are the standard, but four-pair versions are also available for higher data transmission rates.
Some products in this range include:
| IE cables | No. cores x AWG-No | UL standard | Part no. |
| HELUKAT® SPE Type R 1000BASE-T1 SF/UTP PUR ROBOTIC | 1 x 2 x AWG 26 /19 | UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 21223, CSA bzw. cRU AWM I/II A/B | 11019818 |
| HELUKAT® SPE Type C 1000BASE-T1 THICK SF/UTP PUR CHAIN | 1 x 2 x AWG 22 /19 | UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 21223 | 11018068 |
| HELUKAT® 500IND CAT.6A S/FTP LS0H EXTRAFLEX | 4 x 2 x AWG 26 /7 | N/A | 11023932 |
| HELUKABEL® EtherCAT-P100S-M CAT.5e SF/UTP PUR CHAIN | 4 x 1 x AWG 24 /7 | UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 21198 | 11007523 |
| HELUKAT® 600T CAT.7 SF/FTP PUR TORSION | 4 x 2 x AWG 24 /7 | UL-Std. 444 (CMX), CSA-Std. C22.2 No. 214 - CMX, UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 20940 | 805828 |
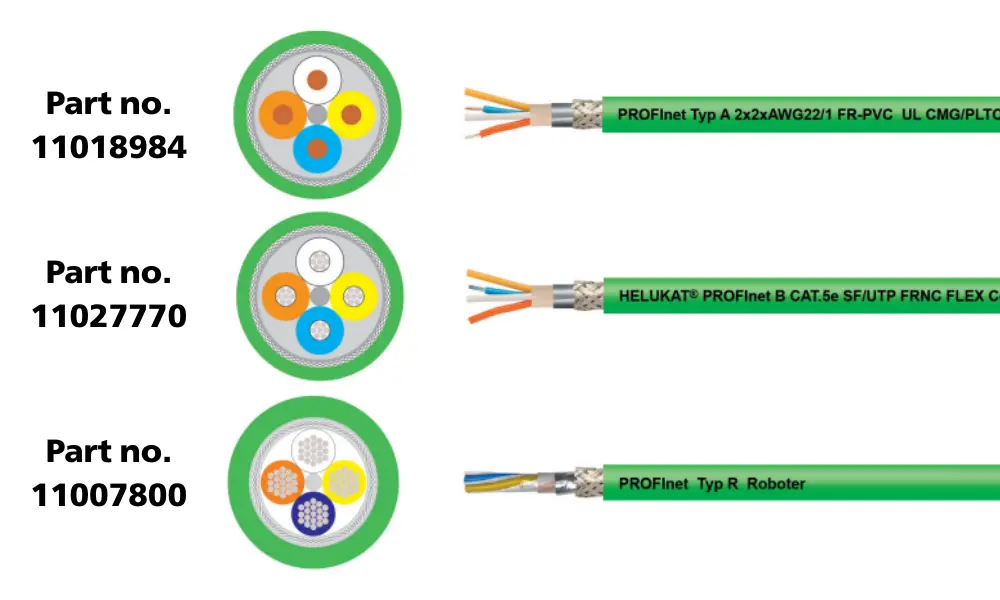

5.2 PROFINET cables
HELUKABEL’s PROFINET cable range includes:
- Type A (Fixed Installation): For stationary installation inside control cabinets.
- Type B (Flexible): For applications where the cable experiences occasional movement.
- Type C (Highly Flexible): For continuous motion applications, such as in cable chains.
- Type R (Torsion-Resistant, for Robots): Designed for applications with high torsional stress, such as robotic arms.
>>See more: What is PROFInet? Top 4 PROFInet cables for industrial networks
| Cables | No. cores x AWG-No | UL | Part no. |
| HELUKAT® PROFInet A CAT.5e SF/UTP PVC STATIC PLTC-ER | 2 x 2 x AWG 22 /1 | UL-Std. 444 (CMG), CSA-Std. C22.2 No. 214 - CMG, UL-Std. 13 (PLTC) | 11018984 |
| HELUKAT® PROFInet B CAT.5e SF/UTP FRNC SHIPLINE | 2 x 2 x AWG 22 /7 | UL-Std. 444 (CM), CSA-Std. C22.2 No. 214 - CM, UL-Std. 13 (PLTC) | 802185 |
| HELUKAT® PROFInet B CAT.5e SF/UTP FRNC FLEX Cca | 2 x 2 x AWG 22 /7 | UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 22375, CSA-Std. C22.2 No. 210 - AWM I A/B | 11027770 |
| HELUKAT® PROFInet R+ CAT.5e SF/UTP PUR ROBOTIC | 2 x 2 x AWG 22 /19 | UL-Std. 758 (AWM) Style 21209 | 11007800 |
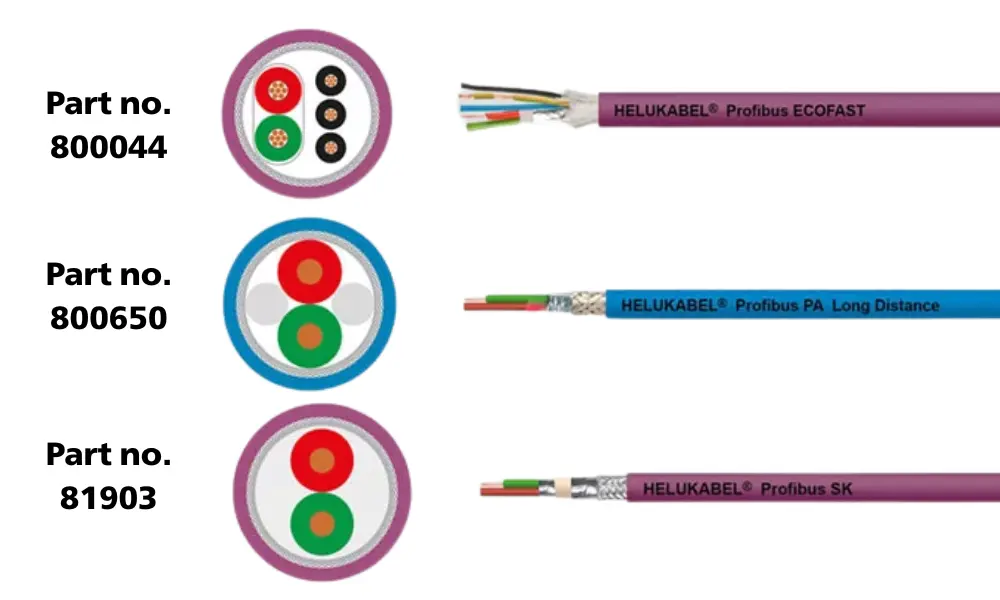
5.3 PROFIBUS DP, PA, SK cables
HELUKABEL’s PROFIBUS cable range:
- Manufactured from a variety of materials such as PE, PVC, PUR, FRNC, and FEP.
- Available for a wide range of applications including STATIC installations, cable drag chains, torsion applications, direct burial, festoon systems, maritime/offshore use (SHIPLINE series), and hybrid cables such as ET200X + Ecofast.
>>Read more: Top 3 Profibus PA cables from HELUAKBEL and their features
| Type | Cable | UL | Part no. |
| Profibus DP | Profibus L2 ECOFAST PUR DRAG CHAIN | AWM Style 20236 AWM I/II A/B 80°C 30V; UL Style 20233 FT1 | 800044 |
| Profibus L2 PUR TORSION | CMX 75°C (shielded); CMG 75°C FT4 or CL2 or AWM 21694 600V SUN RES | 800109 | |
| Profibus PA | PVC STATIC | UL Style 2571 | 82835 |
| LONG DISTANCE PVC STATIC | UL Style 2571 | 800650 | |
| Profibus DP SK | Profibus SK fixed installed Indoor + Outdoor | CMG 75°C or CL3 or AWM 21694 600V | 81903 |
| Profibus SK drag chain | CMX 75°C (shielded) | 801659 |
5.4 CAN bus cables
| CAN bus | UL | Part no. |
| CAN-BUS 0,50mm² 1-PAIR PVC STATIC | UL Style 2571 | 800571 |
| CAN-BUS 0,25mm² 2-PAIR 105°C PUR STATIC | UL/CSA 21223 80°C, 600V | 801982 |
| CAN-Bus 0,34mm² QUAD PUR DRAG CHAIN | CMX 444 | 802339 |
| CAN-BUS 0,75mm² QUAD PVC STATIC | UL Style 2571 | 803384 |

5.5 Other types of bus cables from HELUKABEL
In addition to the bus cable types mentioned above, HELUKABEL also offers various other bus cable ranges, such as:
- FOUNDATION™ Fieldbus
- HMCB bus cables for digital encoder cable
- USB
- CAN BUS
- Multibus
- AS-Interface
- DeviceNet™
- CC-Link
- Safety BUS
- LON
- MOD-Bus
- EIB / E-BUS / KNX
- Bus Cables for Patient Communication Systems
| Bus cables | UL | Part no. |
| DeviceNet™ THICK FRNC STATIC | CL2 CMG | 800681 |
| FOUNDATION™ Fieldbus flexible Basic | CMG 75°C PLTC FT4 | 803354 |
| A-BUS LONG DISTANCE PUR DRAG CHAIN | AWM Style 20549 | 804410 |
| CC-Link BUS PVC STATIC | CM 75°C or PLTC | 800497 |
| SafetyBUS p PUR DRAG CHAIN | CMX 75°C (shielded) | 800652 |
| HMCB500S DRIVE CLIQ™ PVC CHAIN | AWM Style 2502 AWM I/II A/B 80°C 30V FT1 | 803672 |
6. How to select the right bus cable – 4 essential principles
Choosing the correct type of bus cable not only ensures stable operation of industrial systems but also minimizes the risk of signal loss and extends the service life of equipment. Below are four key principles to remember.
6.1 Select the right cable type for the operating frequency
- Do not use low-frequency data cables for high-frequency Ethernet applications.
- Ethernet requires a twisted-pair construction with varying twist lengths between pairs to reduce interference and maintain high transmission speeds.
- For high-speed applications (e.g., PROFINET, EtherCAT), ensure the cable meets Cat5e, Cat6, or higher specifications.
6.2 Use the correct core pairing structure
- Industrial standards such as PROFINET and EtherCAT often use a star quad configuration to ensure uniform transmission times and minimize signal skew.
- Avoid using regular twisted-pair cables or 4-core sensor cables, as they do not meet the impedance and EMI shielding requirements of these systems.
6.3 Ensure cable length and conductor cross section meet standards
- For Ethernet: maximum length is 100 m for standard cables.
- Thinner cables (e.g., AWG26) should be limited to 60–70 m to avoid signal attenuation.
- Excessive length or undersized conductors will weaken signals and increase the risk of transmission errors.
6.4 Choose compatible connectors
- Use the correct type of industrial-grade Ethernet connectors: RJ45, M8, M12, Ix Industrial, SPE, etc.
- Avoid non-standard or unverified connectors, as they may degrade transmission quality and speed.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |