Copper vs aluminum: How to select the right conductor material?
Copper, aluminium, or CCA? When selecting cables, the decision between conductor materials is an import one, involving conductivity, weight, mechanical strength, and price. Get an overview of how these materials differ from one another.
1. Characteristics of some conductor materials
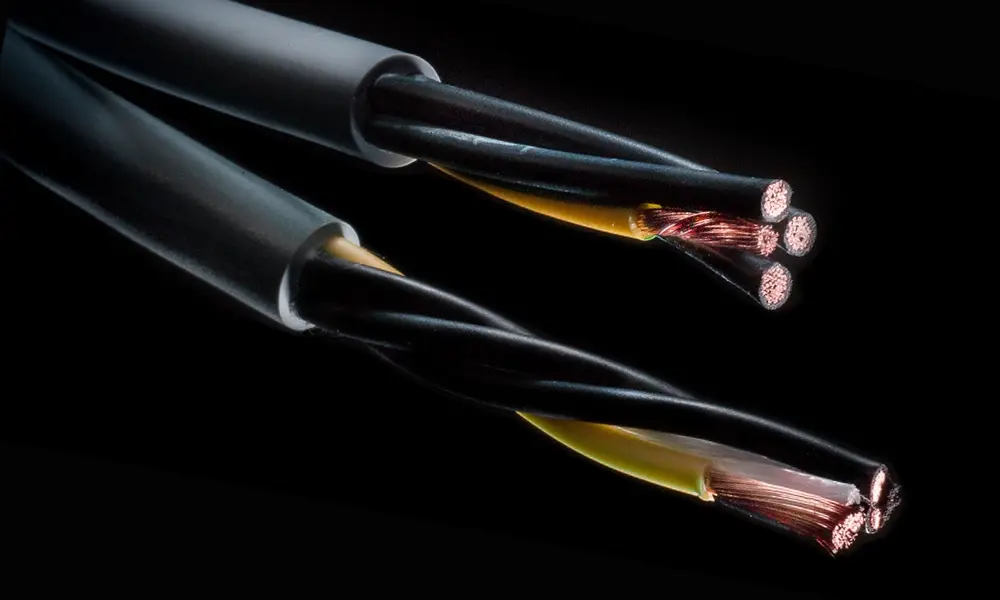

Copper is suited for a large number of applications in industry, building automation, mobility, and energy supply
1.1 Copper: The reliable standard
For most cables and wires, copper is the industry standard, and for good reasons. The material exhibits very high electrical conductivity, is tension resistant, flexible, easy to work with, and recyclable. Because of these characteristics, it is suited for a large number of applications in industry, building automation, mobility, and energy supply. Even in demanding environments with mechanical stresses such as bending or vibrations, copper proves to be operationally reliable.

Aluminium is primarily used when weight is a deciding factor
1.2 Aluminum: A slight cost advantage
Inner conductors made of aluminium are primarily used when weight is a deciding factor, e.g., in long transmission cables, in wind turbines, or as battery cables in vehicles. Aluminium is significantly lighter than copper but is only 63% as conductive as copper. Larger cross-sections are needed to achieve the same current carrying capacity. Additionally, aluminium is more brittle, more susceptible to corrosion, and less mechanically resilient. The use of aluminium requires special know-how and appropriate connection technology & tools.
>>See more: What are aluminum cables, their features and applications?

1.3 CCA—Copper-Clad Aluminium: A deceptive compromise?
CCA conductors are aluminium conductors that are covered in a thin layer of copper. This technology originates in antenna technology and the "skin effect" where the densest AC currents travel along the surface of the conductor. When it comes to electricity, CCA should be viewed critically, as it is significantly less conductive than pure copper.
Nevertheless, CCA cables are being offered more and more commonly by Asian manufacturers and are often marketed as a low-price alternative in the following applications:
- Speaker cables
- Power cables for HiFi car audio
- Network cables (patch cables)
2. Comparing technical data
When selecting cables, in addition to cost, it is important to compare technical parameters such as chemical composition, tensile strength, and electrical conductivity to ensure transmission efficiency and operational durability.
| Alloy | Chemical composition | Tensile strenghth | Conductivity IACS 20°C (68°F) | |
| Aluminum | 1350 | 99,5% Al | 82,7 Mpa (12,0 ksi) | 61,2 |
| 8176 | 98,5% Al | 117 Mpa (17,0 ksi) | 65,2 | |
| Copper | CDA 10100 | 99,99% | 379 Mpa (55,0 ksi) | 100 |
| CDA 10200 | 99,5% | 379 Mpa (55,0 ksi) | 100 | |
| CDA 1100 | 99,99% | 379 Mpa (55,0 ksi) | 100 | |
| CCA | 10% CCA | 10% copper by volume | 82.7 Mpa (12,0 ksi) | 62,9 |
| 15% CCA | 15% copper by volume | 117 Mpa (17,0 ksi) | 64,4 |

2.1 Technical data of aluminum cables
Aluminum cables typically contain 98,5–99,5% pure aluminum. Their tensile strength ranges from 82,7 to 117 MPa, which is significantly lower than that of copper. Electrical conductivity reaches only 61–65% IACS, meaning that to transmit the same current, aluminum cables require a larger cross-sectional area.
The main advantages of aluminum are its lightweight and low cost, making it suitable for applications where cost optimization or weight reduction is essential, such as long-distance transmission cables or cables in wind turbines.
2.2 Technical data of copper cables
Copper conductors (CDA 10100, 10200, 1100) have a purity of ≥ 99,5% and are considered the global industry standard. These conductors feature a very high tensile strength, averaging 379 MPa, which is several times greater than that of aluminum and CCA. Their electrical conductivity reaches 100% IACS, serving as the benchmark in the electrical industry.
With outstanding transmission performance and excellent mechanical strength, copper cables are suitable for nearly all applications in industry, construction, energy, and automation.
Example comparison of two conductor cross-sections with similar conductance (IEC 60228, Class 2):
- Copper conductor 150 mm²: approx. 1341 kg/km
- Aluminium conductor 240 mm²: approx. 723 kg/km
- A 30-40% reduction in weight
This demonstrates that although aluminum conductors have only about 63% of the conductivity of copper, increasing their cross-sectional area allows them to achieve a comparable current-carrying capacity. The key difference is that aluminum is significantly lighter, helping reduce the overall weight of the cable system.
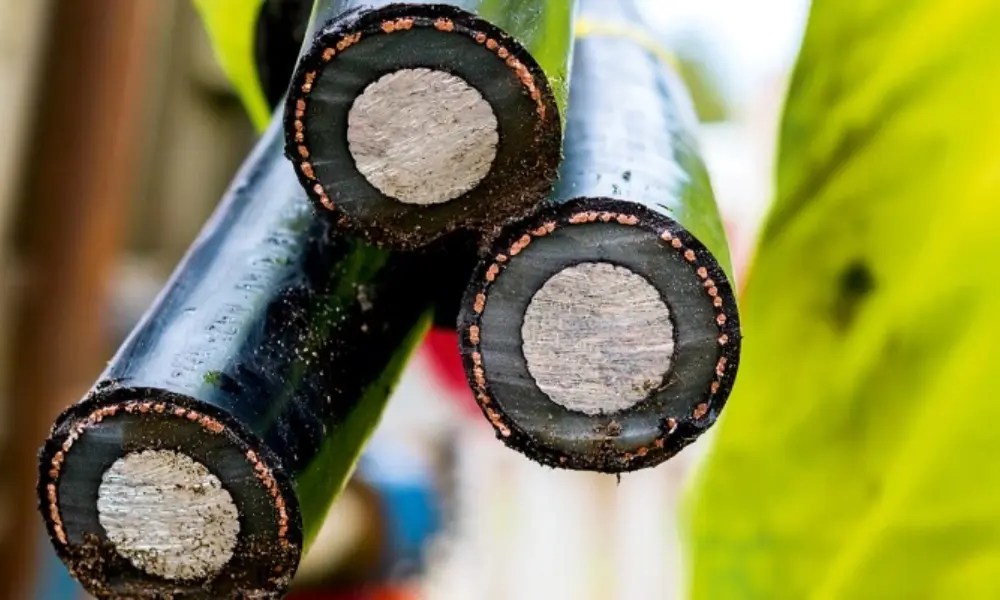

CCA has weaker conductivity and requires a larger cross-sectional area to achieve the same performance as copper
2.3 Technical data of CCA cables
CCA conductors are a combination of an aluminum core coated with a thin layer of copper, typically containing 10–15% copper by weight. Their tensile strength is comparable to aluminum (82.7–117 MPa), while electrical conductivity is only 62.9 - 64.4% IACS, far below that of pure copper.
The advantages of CCA are low cost and lightweight, but it has major limitations in terms of electrical performance and mechanical durability. For this reason, CCA cables should not be used in applications that require high-power transmission.
Limitations of CCA conductors:
- Lower electrical performance: A CCA conductor with a cross-section of 2.5 mm² is roughly equivalent to a 1.5 mm² copper conductor. This shows that CCA has weaker conductivity and requires a larger cross-sectional area to achieve the same performance as copper.
- Higher voltage drop and heat generation: When used in Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, CCA cables are prone to significant voltage drops and increased heat generation, which can reduce both efficiency and device lifespan.
- Fire risk in car audio systems: In automotive HiFi systems, if fuses are not properly protected, using CCA can lead to cable overload and potentially cause fires or explosions.
- Non-compliance with international standards: CCA network cables do not conform to TIA or IEC standards, meaning they are prohibited in enterprise network installations.
3. Choosing copper or aluminum conductors? HELUKABEL’s conclusion

Copper is used when performance, reliability are required, while aluminum cables are suitable for lower weight applications.
Copper remains the best electrical conductor and is considered the most reliable standard for the majority of electrical connections.
Aluminum, when used correctly, is a practical option in cases where long cable lengths or reduced system weight are required.
In contrast, CCA conductors are not recommended for power supply or energy transmission systems. Their lower conductivity, higher heat generation, and greater voltage drop present significant safety risks. In practice, many CCA products on the market lack clear labeling or complete information, leading to uninformed use and increased operational hazards.
In summary:
- Choose copper when performance, reliability, and long service life are required.
- Choose aluminum when cost reduction or lower weight is the priority in suitable applications.
- Avoid CCA in electrical and network systems, especially where safety and compliance with technical standards are essential.
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |