What are solar storage batteries? Common types of solar batteries
Solar storage battery systems stabilize the power supply by storing surplus energy during periods of high generation and releasing it when electricity demand increases. This enables continuous, efficient, and flexible system operation.
As more households and businesses transition to renewable energy, solar storage battery has become a key solution for maximizing the performance and efficiency of solar power systems. However, how do solar battery storage systems work, and why do they play such an important role in clean energy solutions?
This article will provide a clear overview of the fundamentals of solar storage battery, the benefits it offers, and why investing in a reliable energy storage system is a smart and future-ready decision.
1. What is a solar storage battery?
A solar storage system uses batteries or energy storage units to store electricity generated by photovoltaic (PV) solar panels for use at a later time. This technology enables more efficient utilization of solar power by ensuring a stable electricity supply even when sunlight is unavailable or during peak energy demand periods.
By integrating battery storage, households and businesses can increase energy independence, reduce electricity costs, and minimize reliance on the national power grid. Energy storage systems allow users to maximize the performance of their solar installations, ensuring more stable, reliable, and sustainable operation.
In practice, the timing of solar power generation does not always align with actual electricity consumption. Household energy demand is typically higher in the early morning and evening, when solar output is low or unavailable. Any excess electricity generated during the day that is not consumed on-site is usually exported to the grid.
Although homeowners may receive compensation for feeding surplus electricity back into the grid, this value is often lower than the savings achieved by storing the energy and using it directly within the home. As a result, a solar storage battery offers a more economical and efficient way to fully capitalize on solar energy generation.
2. How does a solar storage battery work?

The electrical energy generated by the PV panels will be fed into the storage battery system.
A solar storage battery system operates on the principle of generation – conversion – storage – distribution of electricity. This integrated process optimizes the use of solar power while ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply for households or businesses.
2.1 Electricity generation from solar panels
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) modules, absorb sunlight and convert solar radiation into direct current (DC) electricity. These panels are typically installed on rooftops, ground-mounted structures, or other suitable locations to maximize solar exposure.
2.2 Charge control and battery protection
The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is routed through a charge controller. This device regulates the flow of electricity between the solar panels, the battery storage system, and the inverter. It prevents overcharging, overcurrent, and overvoltage, thereby protecting the batteries and extending their service life.
2.3 Energy storage (Battery storage system)
Any excess electricity that is not immediately consumed is stored in the battery storage system. This system may consist of one or multiple batteries, using technologies such as lead-acid, lithium-ion, or other advanced energy storage solutions. The stored energy is reserved for use when solar generation is insufficient.

An inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
2.4 Power conversion (Inverter)
Since most household and commercial electrical appliances operate on alternating current (AC), the DC electricity generated by the solar panels or stored in the batteries must be converted into AC. This conversion is performed by an inverter, making the electricity suitable for everyday use.
2.5 Power distribution
Once converted, AC electricity is distributed to power electrical loads within the home or facility. During periods of low solar output or high electricity demand - such as at night or during peak hours - the system automatically draws energy from the battery storage to supply the loads.
2.6 Grid connection
In grid-tied solar systems, when solar generation exceeds consumption and the batteries are fully charged, surplus electricity is exported to the national grid. Depending on local net metering or feed-in tariff policies, this exported energy may be credited and offset against the user’s electricity bill.
3. Benefits of solar storage batteries
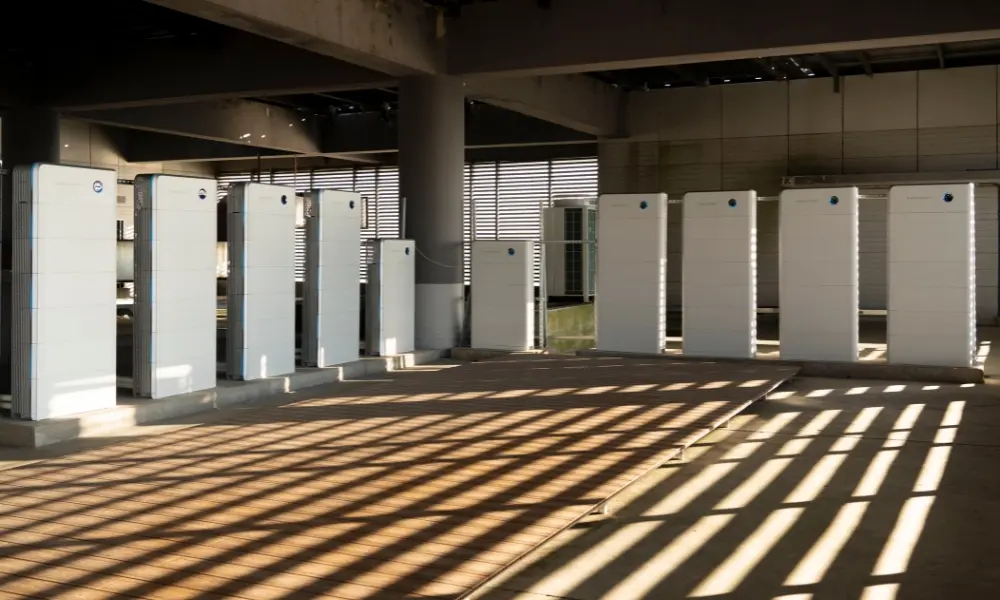

Battery storage systems enhance energy independence for both residential and commercial/industrial applications.
Solar storage battery systems offer a wide range of advantages:
- Enhanced energy independence: Solar battery storage enables households and businesses to store electricity generated by their solar power systems for later use, significantly reducing dependence on grid-supplied electricity.
- Backup power supply: Battery storage systems can provide reliable backup power during grid outages or when solar generation is limited due to unfavorable weather conditions. This ensures that critical loads and essential equipment remain operational, offering safety, continuity, and peace of mind during emergencies or natural disasters.
- Electricity cost savings: By storing and consuming self-generated solar electricity instead of purchasing power from the grid, users can substantially reduce monthly electricity expenses.
- Optimization of net metering and load shifting: In regions where net metering policies are in place, excess solar energy can be exported to the grid in exchange for bill credits.
- Grid support and stability: Solar energy storage systems contribute to grid stability by supplying stored electricity during peak demand periods or when the grid is under stress. This helps alleviate grid congestion and can potentially delay or reduce the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades.
- Environmental benefits: By maximizing the utilization of solar-generated electricity, battery storage systems help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and support the broader transition toward clean, renewable, and sustainable energy sources.
4. Common types of solar storage batteries
Currently, there are various types of solar storage batteries available on the market. Each battery type has its own advantages and limitations, making it suitable for different applications and usage requirements. Below are the most commonly used solar battery types and their key characteristics.
4.1 Lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries are widely used in vehicles and applications that require high discharge currents. Their main advantages include low initial investment cost, mature and well-established technology, and efficient recyclability.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Low cost and simple manufacturing process | Low energy density, poor weight-to-energy ratio |
| Low cost per watt-hour (Wh) | Slow charging time: a fully saturated charge typically takes 14–16 hours |
| High specific power, capable of delivering high discharge currents | Must be stored in a charged state to prevent sulfation |
| Reliable performance in both low and high temperature environments | Limited cycle life; frequent deep discharging significantly reduces battery lifespan |
| No block-level or cell-level Battery Management System (BMS) required | Requires periodic water replenishment for flooded (open-type) batteries |
| Transportation restrictions apply to flooded batteries | |
| Negative environmental impact |
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used
4.2 Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in electronic devices such as cameras, calculators, laptop computers, and mobile phones, and are increasingly adopted in electric mobility applications. Among them, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄) batteries are highly regarded and have become increasingly popular in residential and commercial solar energy storage systems.
Other lithium-ion battery chemistries used in energy storage include Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC – LiNiMnCoO₂), Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO₂), and several other variants.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High specific energy and high load capability, particularly with power cells | Requires a protection circuit to prevent overheating and thermal runaway when the battery is stressed or operated beyond its limits |
| Long cycle life and extended shelf life; maintenance-free | Performance and lifespan degrade when operating at elevated temperatures |
| High capacity, low internal resistance, and high coulombic efficiency | Rapid charging is not possible at freezing temperatures (below 0 °C / 32 °F) |
| Simple charging algorithm with relatively fast charging times | Subject to strict transportation and safety regulations when shipped in large quantities |
4.3 Sodium–Sulfur batteries
Sodium-Sulfur (Na-S) batteries, also known as liquid metal batteries, are a type of high-temperature battery composed of molten sodium and sulfur. These batteries feature high energy density, high charge-discharge efficiency (approximately 89-92%), and a long cycle life, while being manufactured from relatively low-cost materials. Na-S batteries are mainly used in large-scale energy storage systems and are less commonly applied in residential applications.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Liquid-state electrodes enable the battery to withstand a high number of charge-discharge cycles | Must be operated at temperatures above 300 °C |
| Low-density active materials combined with high cell voltage provide good energy and power density | Metallic sodium is highly reactive and combustible when exposed to water |
| Stable operation across a wide range of conditions, including charge/discharge rates, depth of discharge, and temperature | Additional costs are required for robust containment structures to prevent material leakage |
| 100% coulombic efficiency with reasonable internal resistance | Stringent operational and maintenance requirements |
4.4 Redox flow batteries
Redox flow batteries are charged and discharged through oxidation–reduction reactions of metal ions, most commonly vanadium or similar materials. This type of battery offers several outstanding characteristics, including a very long operating life with minimal degradation of electrodes and electrolytes, high safety due to the absence of combustible materials, and stable operation under normal ambient temperature conditions.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Very long service life | Large size |
| Low capacity degradation over time | Complex system configuration |
| Power and energy capacity can be scaled independently by adjusting the size of the electrolyte tanks | More suitable for large-scale energy storage applications rather than residential use |
5. Lithium batteries – The preferred solar energy storage solution in the Vietnamese market
Amid increasingly volatile electricity prices, growing demand for energy independence, and the rapid expansion of solar power in Vietnam, lithium battery storage - especially Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries - is being widely adopted. From residential systems to commercial and industrial (C&I) solar installations, LFP lithium batteries help optimize solar energy utilization, reduce reliance on the power grid, and improve long-term investment efficiency.

5-in-1 integrated storage battery
5.1 Solar storage batteries for residential use
The Sigentor BAT battery uses high-reliability LFP cells and integrates industry-leading protection systems. Key technical features include:
- Premium 314 Ah battery cells with up to 10,000 charge–discharge cycles, delivering durability and long-term reliability
- Five-layer battery safety protection, setting a new benchmark for system safety
- Integrated battery optimizer, allowing flexible system expansion and seamless combination of existing and new battery modules
- High energy density for efficient storage in a compact, space-saving design
- 100% depth of discharge (DoD), maximizing usable energy capacity
One of the key reasons this battery storage solution is increasingly trusted lies in its advanced five-layer protection architecture, which includes:
- Individual cell-level temperature monitoring
- Integrated internal fire suppression system
- High-temperature-resistant thermal insulation layers
- Aerogel thermal insulation panels
- Pressure relief valve
In addition, users can accurately monitor real-time energy flow through the mySigen application, which is deeply integrated with artificial intelligence. The intuitive interface provides transparent insights into how different renewable energy sources charge the battery, ensuring efficiency and visibility in every charging cycle. With mySigen, energy management becomes smarter, more precise, and significantly easier.



Storage battery solutions for C&I
5.2 Solar storage batteries for C&I
In commercial and industrial (C&I) solar power systems, Sigentor BAT energy storage batteries play a central role in energy flow management, cost optimization, and ensuring a reliable power supply.
- Battery storage in grid-tied PV + ESS systems: In grid-connected operation, battery storage maximizes solar self-consumption by storing surplus electricity during the day and discharging it during peak-demand periods or when PV generation declines. This allows businesses to reduce grid electricity purchases, mitigate peak-hour electricity costs, and improve the return on investment of their PV systems. In addition, battery storage helps smooth power output, reduce load fluctuations, and support stable system operation.
- Battery storage in microgrid systems: In microgrid configurations, battery storage acts as an “energy buffer” that ensures continuous and independent system operation. The ESS stores solar energy to supply loads during grid outages or nighttime hours, while seamlessly coordinating with diesel generators when required. This enables businesses to maintain operations, protect critical equipment, and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
6. Electrical cables – A critical link in solar storage battery systems
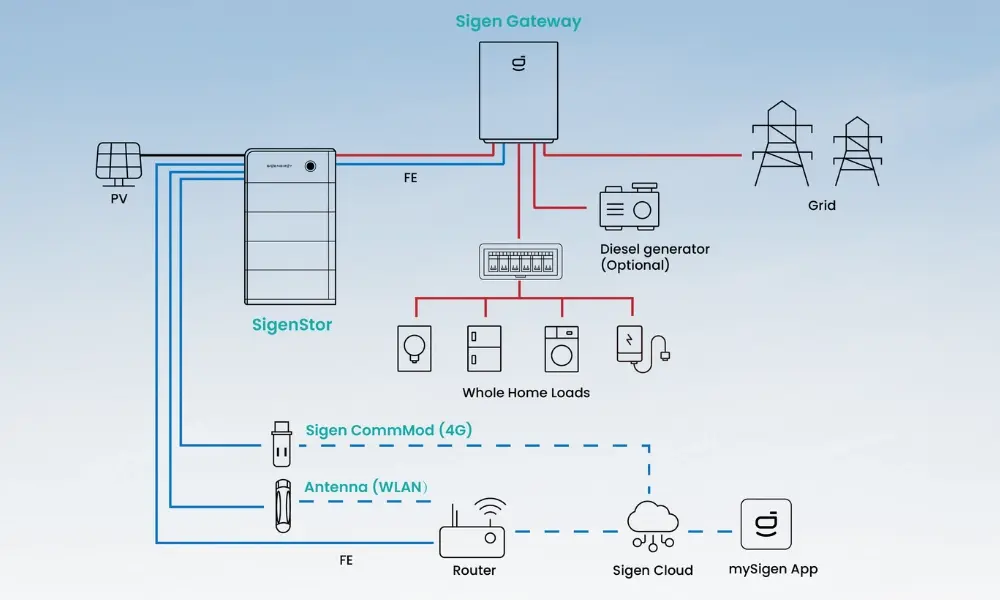
Electrical cables connect various components within the solar power storage system.
6.1 The role of cables in solar storage battery systems
Solar storage battery systems stabilize the power supply by storing surplus energy during periods of high generation and releasing it when electricity demand increases. This enables continuous, efficient, and flexible system operation.
However, system safety and performance depend not only on the batteries and inverters, but also directly on the quality of all system components - especially electrical cables.
In a battery energy storage system (BESS), electrical cables are responsible for transmitting power between key functional blocks, including:
- Battery storage units (battery modules, battery racks)
- Power conversion systems (PCS / inverters)
- Distribution cabinets, transformers, and the utility grid
Selecting cables that can withstand high current loads, elevated voltage levels, and continuous charge-discharge operation is a decisive factor in:
- Energy transmission efficiency by minimizing electrical losses
- Long-term operational stability of the system
- Overall system safety
6.2 Types of cables used for solar storage battery systems
Each section of a battery energy storage system requires specialized cables designed to handle high current, high voltage, industrial operating conditions, and stringent safety requirements.
| Cable type | Application | Typical products |
| DC cables | Connections between battery cells and battery modules Connections from battery storage to PCS / inverter | SOLARFLEX®-X H1Z2Z2-K, HELUPOWER® SOLARFLEX®-X PREMIUM, SOLARFLEX®-X H1Z2Z2-K NTS |
| AC cables | Connection between inverter/PCS and AC distribution panels Connection from ESS to transformer or utility grid | NYY-J / NYY-O, HELUPOWER® 1000 RV-K |
| Communication, network, bus cables | Interconnection of BMS, EMS, SCADA systems Data transmission for monitoring, measurement, and control | PAAR-TRONIC-Li-2YCYv, HELUKAT® 600A CAT.7e S/FTP PVC STATIC, E-BUS / KNX PVC + FRNC STATIC, CAN-BUS 0.50 mm² 2-PAIR PVC STATIC |
| Earthing/Grounding | Grounding for battery cabinets, inverters, and ESS containers Electrical safety and overvoltage protection | HELUPOWER® CU-CONDUCTOR-CL2 TINNED, HELUPOWER® CU-CONDUCTOR-CL5 TINNED |
| Accessories | Cable conduits, cable lugs, cable glands, RJ45 connectors, cable ties… |
Explore our cable and accessories for solar energy
If you still have questions, don't hesitate to contact the HELUKABEL Vietnam engineering team for detailed answers.
Contact Information HELUKABEL Vietnam
| HELUKABEL Vietnam 905 Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam | Phone:
+84 28 77755578 Email: info@helukabel.com.vn | Connect with us on |
| Order through our online channels Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder | ||





