What are cable conduits? Types of conduits and applications
In modern electrical systems, cable conduit is an essential component that protects electrical cables, meets safety standards, and ensures long-term operational durability for applications ranging from residential to industrial projects.
Electrical cables must be routed through a wide variety of environments and installation conditions. From inside the walls of residential and office buildings to heavy-duty industrial systems or underground installations, electrical conduit plays a critical role in protecting wires and cables from a wide range of potential hazards. Selecting the right conduit material helps safeguard cables against corrosion, mechanical impact, UV radiation, moisture, and other risks that could negatively affect system performance.
1. What are cable conduits?

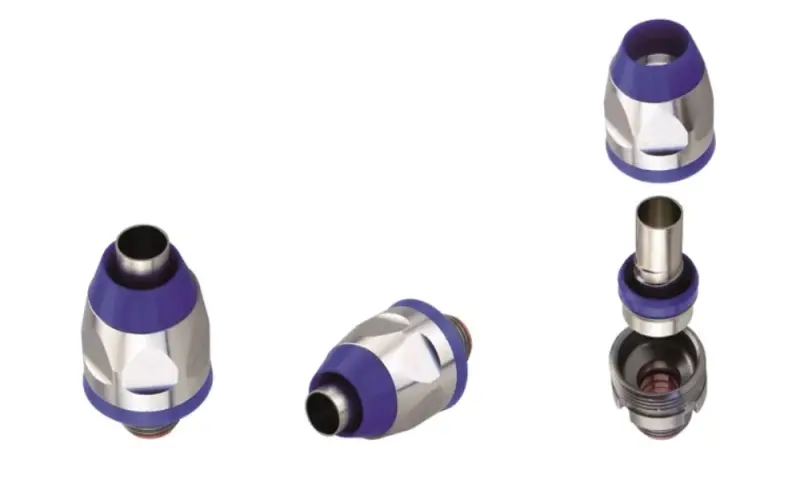
Cable conduit accessories help protect electrical cables in various installation environments.
Cable conduit, also known as electrical conduit, is a type of plastic or metal tubing used to contain and protect electrical wires or cables. It is available in rigid or flexible forms and can be used in a wide range of installation conditions, from indoor spaces to outdoor environments.
To meet diverse installation requirements and system configurations - including concrete-embedded installations and underground applications - electrical conduit is manufactured in various types and sizes.
Electrical conduit must be properly terminated at an electrical box or an equivalent enclosure. Together with electrical boxes and conduit accessories such as connectors and fittings, conduit forms a critical part of the electrical raceway system. When made of metal, the conduit itself can also function as a grounding conductor for the electrical system.
2. The role of cable conduits
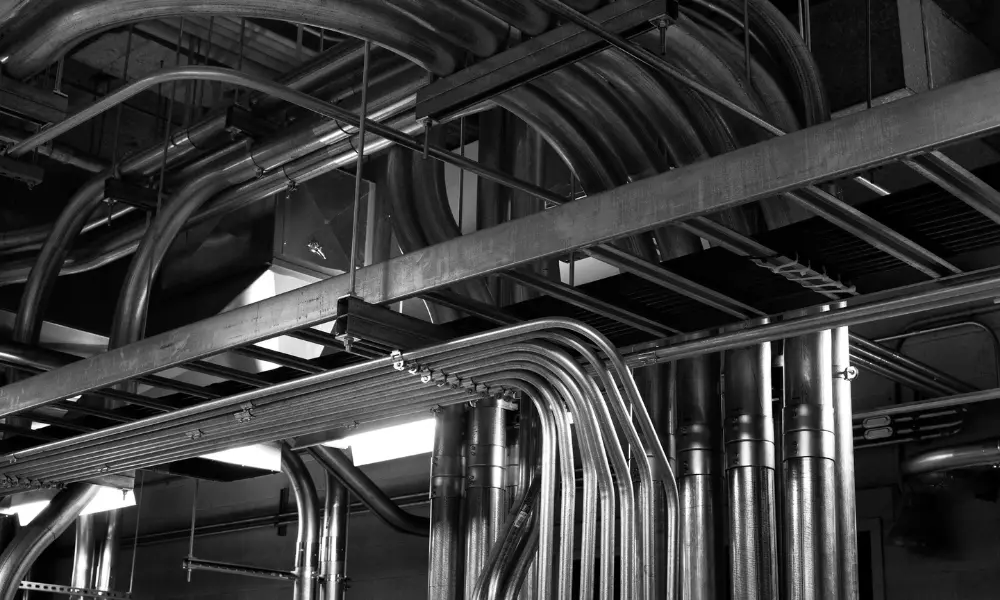

Electrical conduit helps keep wiring tidy
Electrical conduits are used for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Compliance with technical standards: Electrical conduits are often mandatory under regulations such as the U.S. National Electrical Code (NEC) or requirements set by local authorities. In Vietnam, the applicable standard is TCVN 7417-25:2015, which is fully equivalent to IEC 61386-25:2011.
- Protection of electrical wires and cables: These accessories help protect wires and cables from various hazards such as fire, moisture, mechanical impact, chemicals, as well as risks from rodents and insects. Although electrical cables already have their own insulation, conduit systems provide a significantly higher level of protection.
- Meeting design and installation requirements: By acting as an additional protective layer, cable conduits expand installation possibilities. For example, high-strength conduits allow cables to be installed in exposed locations where using standalone wires or cables would not be safe.
- Reduction of EMI: Conduit systems, especially metal conduits can help reduce EMI, improving the performance and stability of electrical wiring and cable systems.
- Improved organization and ease of installation: In complex electrical systems with multiple cables, conduits help keep wiring neat, organized, and easier to manage. The smooth interior surface of conduits allows cables to be pulled and repositioned easily, simplifying installation as well as future maintenance or replacement.
For many electrical systems, cable conduit provides a comprehensive protection solution while offering a high degree of flexibility in both design and installation.
3. Applications of electrical conduit
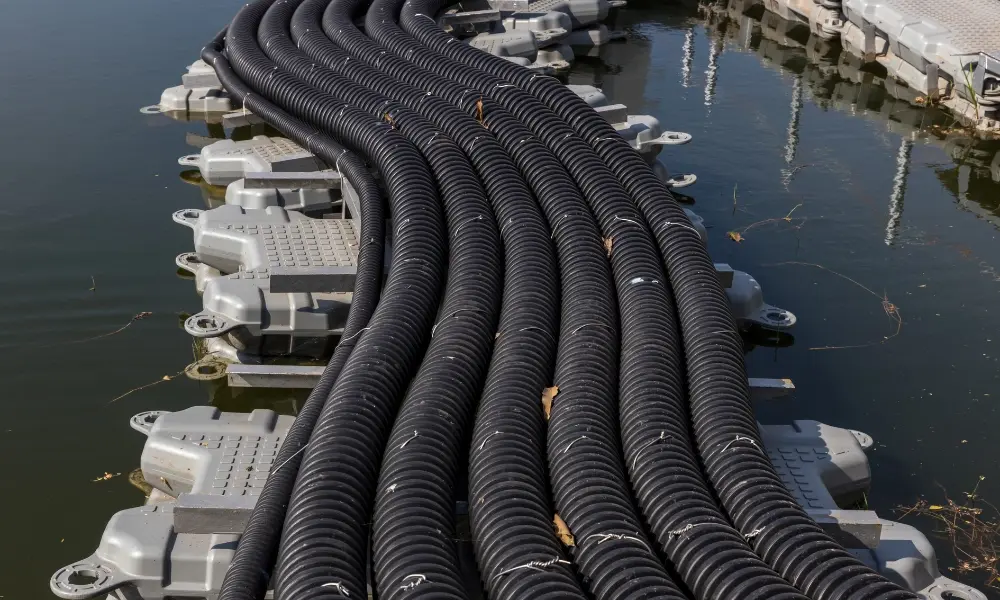

Applications of conduits in floating PV systems
In practice, corrugated electrical conduit systems are widely installed in residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. They help ensure compliance with safety regulations, reduce fire risks, and extend the service life of electrical systems.
- Commercial buildings (offices, shopping malls, hospitals): Conduits protect complex electrical networks used for lighting, equipment, and security systems. Their use ensures operational safety, compliance with building codes, and easier maintenance - especially in high-reliability environments such as hospitals.
- Industrial automation and manufacturing: In factories and production lines, heavy-duty and chemical-resistant conduits are used to protect wiring for machinery, industrial robots, and control panels. This solution minimizes vibration and mechanical impact, reduces electrical failures, and enhances equipment durability.
- Infrastructure and construction: Projects such as airports, metro systems, and water treatment plants rely on conduits for underground power and control signal wiring, protecting them from environmental impacts while meeting strict safety standards.
- Residential buildings and smart homes: In housing projects, electrical conduits support concealed wall installations and allow easy upgrades for smart home systems, IoT devices, lighting, and security cameras - offering long-term flexibility and safety.
- Renewable energy applications: In solar and wind power systems, conduits protect outdoor cables, improving durability and ensuring stable, reliable operation over time.
4. Flexible conduits vs rigid conduits

Flexible cable conduit
Electrical conduits are available in a wide range of types, designed to meet different installation conditions and application requirements. The market offers various sizes and materials, generally classified into two main categories: flexible conduit and rigid conduit.
4.1 Characteristics of flexible cable conduit
Flexible conduit is designed with high bendability, making it ideal for confined spaces or installations subject to vibration or movement during operation. This type of conduit is commonly used in environments with machinery, industrial robots, or systems that experience motion while operating.
Because it does not require specialized tools for bending or shaping, flexible conduit simplifies installation and significantly reduces labor time and costs.
Today, flexible conduits are available in several versions, including metallic flexible conduit and non-metallic flexible conduit. Plastic (non-metallic) conduits offer advantages such as lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and easy cutting. They are particularly effective in high-humidity or chemically aggressive environments where metal materials are more prone to degradation.

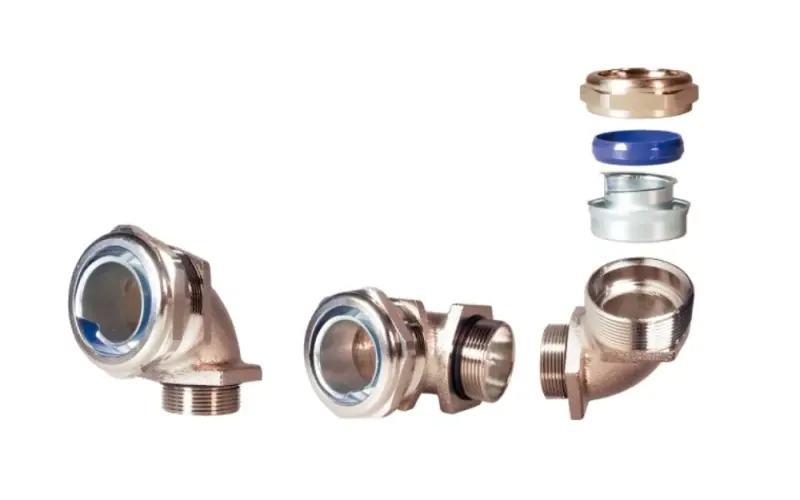
LT elbow 45° brass nickel-plated conduit gland
4.2 Characteristics of rigid cable conduit
Rigid conduit is manufactured from high-strength materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, or aluminum. This type of conduit provides superior mechanical protection, making it suitable for systems that require long-term stability and robustness.
As rigid conduit is not easily bent, it is typically installed in straight runs, with directional changes made using elbows or specialized bending tools.
Rigid conduit is widely used in industrial plants, commercial buildings, and outdoor installations. According to technical standards and electrical codes, it is often mandatory in locations where electrical wiring must be protected from impact, mechanical stress, or harsh environmental conditions. In certain applications, rigid metal conduit can also serve as a grounding conductor, further enhancing overall electrical system safety.
5. Common types of cable conduits
Based on the two main categories: rigid conduit and flexible conduit, electrical conduit systems are further subdivided into several specific types, as outlined below:
5.1 Plastic (non-metal) conduits
Plastic conduit is manufactured from flexible plastic materials, most commonly PVC, and features a ribbed, thin-walled structure. It offers high flexibility and can be bent manually without the need for specialized tools. Compared with metal conduit, PVC conduit is more cost-effective while still providing adequate protection for electrical wires and cables against mechanical abrasion. Certain types are also rated for direct burial underground applications.
Plastic conduit is also available in rigid versions. The key difference is that rigid plastic conduit has thicker walls, resulting in reduced flexibility and greater resistance to bending.
Plastic conduit and its fittings are well suited for indoor installations, including residential and commercial buildings. They can also be used outdoors; however, installation in areas exposed to high temperatures or direct sunlight should be avoided, as prolonged exposure to heat and UV radiation may reduce the durability and service life of PVC materials.
| Heavy-duty stress application | Color | Material | Temperature | Part number |
| HELUcond PA6-S | Black, grey | PA6 | -40°C to +120°C | 920154 |
| HELUcond CO-PP | Black | PP | -40°C to +135°C | 97496 |
| JUMBO PA6 | Black, grey | PA6 | -40°C to +140°C | 90408 |
| JUMBO PA12 | Black, grey | PA12 | -40°C to +120°C | 920378 |
| PVC-IB | Black | PVC | -20°C to +85°C | 91310 |
| PVC-IC | Black, grey, white, yellow, red, orange, purple, brown, green yellow... | PVC | -20°C to +105°C | 92280 |
| Anaconda Sealtite® CNP | Orange | PVC | -20°C to +60°C | 91259 |
| Medium stress application | Color | Material | Temperature | Part number |
| HELUcond PP | Black | PP | -40°C to +130°C | 920170 |
| HELUcond PE | Black, grey | PE | -40°C to +70°C | 91621 |
| Highly flexible platic conduit | Color | Material | Temperature | Part number |
| PT-S | Grey | PVC | -25°C to +90°C | 91219 |
| S-PU | Blue | PUR | -40°C to +100°C | 90464 |
| Airflex-K | Grey | PVC | -25°C to +70°C | 11024498 |
5.2 Galvanized rigid metal conduits
Galvanized rigid conduit is a thick-walled steel conduit with exceptional strength and load-bearing capacity. It is manufactured using a hot-dip galvanization process to provide effective protection against corrosion.
While this type of conduit offers superior mechanical protection for electrical wires and cables, it also comes at a higher cost. In addition, its heavy weight can make installation more challenging. When changes in direction are required, electricians must use threaded fittings along with specialized bending tools.
Applications: Galvanized rigid conduit is widely used in industrial environments and high-risk locations, where corrosion may occur or where an especially high level of mechanical protection is required.
| Color | Material | Temperature | Part number | |
| Anaconda Sealtite® EF | Black, grey | Galvanized steel | -25°C to +70°C | 91229 |
| Anaconda Sealtite® HTDL | Black | Galvanized steel | -45°C to +105°C | 98149 |
| Anaconda Sealtite® HCX | Black | Galvanized steel | -60°C to +150°C | 94735 |
| Anaconda Sealtite® HC | Black | Galvanized steel | -45°C to +105°C | 91238 |
| Anaconda Sealtite® HFX | Black | Galvanized steel | -55°C to +105°C | 94994 |
5.3 Intermediate metal conduits
Intermediate metal conduit has a thinner wall compared to galvanized rigid conduit, making it easier to install and more cost-effective, while still providing a high level of protection for electrical wires and cables.
Applications: This type of conduit is well-suited for commercial and residential projects, especially for installations along walls and ceilings and in areas where there is a risk of corrosion.
5.4 Flexible metal conduits
Flexible metal conduit is a type of electrical conduit accessory designed to be highly flexible, allowing installers to bend and adjust it easily during installation. It is constructed from interlocked metal strips in a spiral configuration, providing good mechanical protection and making it particularly effective in tight or confined spaces where the conduit must bend to fit the installation layout.
Applications: Ideal for wiring in restricted spaces, concealed areas, or near machinery, where cables would otherwise be exposed without conduit protection.
5.5 Liquid-tight flexible metal conduit
Liquid-tight flexible metal conduit has a structure similar to standard flexible metal conduit but features an additional outer plastic jacket that provides complete water resistance. This type of conduit is commonly used for outdoor electrical wiring, such as connections to air-conditioning units (AC) and other outdoor-installed equipment.
| Color | Material | IP rating | Temperature | Part number | |
| SPR-AS | Blue | Galvanized steel | 40 | -50°C to +250°C | 97023 |
| SPR-PVC-AS | Black, grey | Galvanized steel | 68 | -25°C to +90°C | 97032 |
| SPR-EDU-AS | Galvanized steel | 40 | -50°C to +250°C | 97584 | |
| SWS-UI | Stainless steel | 40 | -100°C to +600°C | 905804 | |
| SWM-M | Galvanized steel | 40 | -50°C to +250°C | 97014 | |
| SPR-PU-AS | Blue | Galvanized steel | 68 | -50°C to +100°C | 97793 |
5.6 Fiber optic conduits
Fiber optic conduit is designed to enclose and protect the fiber optic cables inside. This type of conduit enhances the level of protection for critical network transmission systems, especially in harsh environments, including underground installations where cables are exposed to corrosive soil, temperature fluctuations, and the risk of accidental damage from excavation work.
Fiber optic conduit is typically manufactured from steel or other high-strength metal materials, and some designs are further reinforced with an additional PVC layer or fiberglass braiding to improve mechanical protection.
Anaconda Sealtite® NMFG-Clean PVC conduit is suitable for use in the F&B industry
5.7 Cable conduits for F&B industry
The F&B industry is subject to strict sanitation and hygiene requirements to prevent contamination during production. If not properly designed and maintained, electrical conduits and their associated fittings can become breeding grounds for bacteria and contaminants, which may reach the processing line or compromise the sterile manufacturing environment.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issues guidelines and requires third-party testing to help manufacturing facilities mitigate contamination risks. As a result, electrical conduits used in food-processing plants must be made from sanitary, easy-to-clean materials and, in certain areas, be safe for indirect food contact. These standards are defined and enforced by organizations such as the NEC (National Electrical Code), OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), UL, and ECOLAB.
HELUKABEL's Anaconda Sealtite® NMFG-Clean PVC flexible conduit is particularly suitable for the F&B, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, chemical, and other industries. Key features of this product include:
- IP67-rated protection against water and dust
- Made from special PVC material compliant with FDA CFR 21 and NSF 51 standards
- Resistant to chemical cleaning and disinfecting agents
- Inhibits the growth of harmful microorganisms
5.8 Conduit for PV systems
Electrical conduits for PV systems provide robust protection for wiring in solar power installations that are required to operate outdoors over long service lifetimes.
- UV resistance and high heat resistance: Specifically engineered to withstand high levels of UV radiation and temperature fluctuations, which are typical conditions in outdoor solar energy systems.
- High durability for outdoor applications: Designed to accommodate thermal expansion caused by prolonged sun exposure, PV conduit ensures long-term protection for solar power components, especially DC and AC cables .
| Color | Material | Temperature | Part number | |
| HELUcond CO-PA | Black | PA6 | -40°C to +120°C | 90061 |
| HELUcond PP | Black | PP | -40°C to +130°C | 920170 |
| HELUcond PA6-L | Grey, black | PA6 | -40°C to +120°C | 99610 |
| HELUcond W-CO-PA-12-MOD-BS-V2 | Black | PA12, MOD BS V2 | -50°C to +110°C | 11020606 |
5.9 Conduit fitting accessories
If you still have questions, don't hesitate to contact HELUKABEL Vietnam's team of engineers for detailed answers.
Contact Information HELUKABEL Vietnam
| HELUKABEL Vietnam 905 Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam | Phone:
+84 28 77755578 Email: info@helukabel.com.vn | Connect with us on |
| Order through our online channels Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder | ||





















