Low-voltage and underground cables – Features & applications
Low-voltage cables are widely used for power transmission in Vietnam. Let’s explore the details of this cable type in the article below!
1. Understanding low-voltage cables
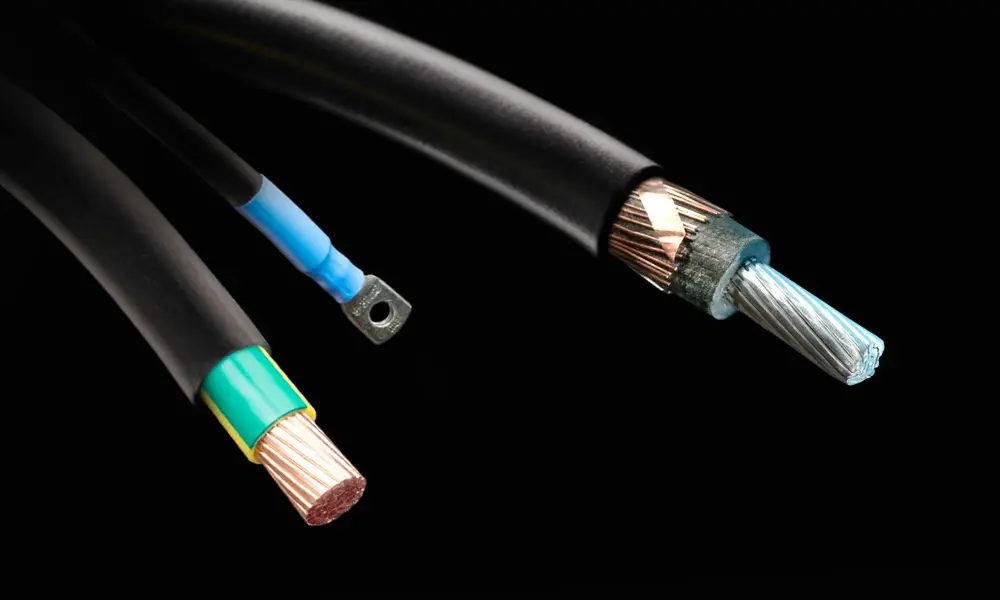

1.1 What are low-voltage cables
Low-voltage cables are a type of electrical cable specifically designed to transmit low-voltage power, typically below 1000V. It is commonly used in residential electrical systems, local area networks (LAN), data transmission, and telecommunications systems.
Low-voltage cables are usually installed using a structured cabling system, which optimizes construction, maintenance, and management of wiring networks. Proper installation is essential to avoid signal interference, data loss, or electrical hazards.
As a critical component in connectivity, communication, and device control, low-voltage cables are foundational in smart home systems, office buildings, automated factories, and various industrial applications.

1.2 Structure of low-voltage cables
The typical structure of low-voltage cables includes the following components: conductor, insulation layer, filler, armor, shielding layer, and outer sheath.
- Conductor: Usually made of copper or aluminum. Copper-conductor cables offer high conductivity, suitable for high-performance and high-reliability applications. Aluminum cores are lighter but typically larger, making them ideal for applications such as wind power.
- Insulation: Usually made of PVC or XLPE material.
- Filler: Typically plastic, used to fill gaps between conductor cores, maintaining the cable’s shape and enhancing mechanical strength.
- Outer sheath: Generally made of PVC.
Some low-voltage cables are equipped with an armor layer, which protects the cable from mechanical impacts such as compression, tension, or vibration in harsh industrial environments. Armor is typically made of aluminum or galvanized steel.

1.3 Applications of low-voltage cables
Low-voltage power cables are essential solutions for modern power distribution systems. Due to their stable conductivity and ease of installation, they are widely used in both residential and industrial sectors.
- In residential electrical systems, low-voltage cables are used to transmit electricity from substations to end-use areas such as homes, office buildings, shopping centers, hotels, service facilities, hospitals, and schools.
- In industrial applications, low-voltage power cables play a crucial role in supplying power to machines and motors, running production lines, and connecting automated and control systems.
Thanks to their flexibility and durability, low-voltage cables are considered an optimal solution for systems requiring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
1.4 Types of low-voltage cables
Low-voltage cables can be classified according to various criteria such as voltage rating, conductor material, sheath material, and application.
| Classification criteria | Cable type | Features |
| Voltage | 300/500V – 450/750V | For low-power applications like lighting, home appliances, and wall sockets. |
| 0.6/1kV | Used in industrial and construction projects requiring stable power for high-load and continuous operation systems. | |
| Conductor | Copper | High conductivity, excellent transmission efficiency. |
| Aluminum | Lower conductivity than copper but more cost-effective. | |
| Applications | Power cables | Distributes power in buildings and infrastructure projects. |
| Control cables | Transmits control signals in automation systems. | |
| Instrumentation cables | For accurate signal transmission in monitoring and measurement systems. | |
| Data cables | For networking and data transmission between devices. | |
| Cable structure | CV cables | Copper conductor, PVC insulation |
| CVV cables | Copper conductor, PVC insulation, PVC outer sheath | |
| CXV cables | Copper conductor, XLPE insulation, PVC outer sheath | |
| NYY cables | Copper conductor, PVC insulation, PVC outer sheath 0.6/1kV | |
| NYM cables | Copper conductor, PVC insulation, PVC outer sheath, 300/500V |
2. Understanding underground low-voltage cables
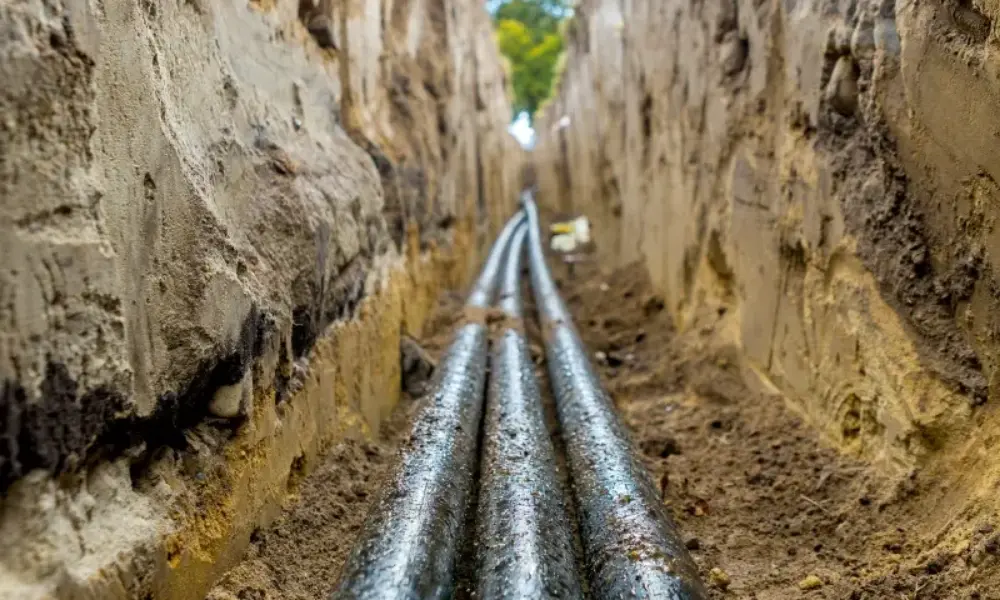

2.1 What are underground low-voltage cables?
Underground low-voltage cables, or buried low-voltage cables, are electrical cables installed below ground. These cables play an essential role in modern electrical systems, providing safe and efficient power transmission over long distances.
Compared to overhead lines that are vulnerable to weather conditions, underground cables are protected by the earth, resulting in more stable and reliable power systems with fewer faults.
2.2 Characteristics of underground low-voltage cables
An underground cable typically consists of one or more conductor cores, insulated and encased in a protective sheath to resist external factors. It must meet the following criteria:
- Conductors must be tinned copper or high-conductivity aluminum.
- The cross-sectional area must be large enough to handle the current without overheating and keep voltage drop within acceptable limits.
- The insulation must be thick enough to ensure safety and reliability at the designed voltage.
- A suitable mechanical protection layer must be included to withstand installation and operational impacts.
- Cable materials must offer long-term chemical and physical stability, resisting degradation over time.
2.3 Applications of underground low-voltage cables
Underground low-voltage cables are suitable for a wide range of applications, from small residential projects to large-scale industrial systems:
- Underground power distribution: Used for supplying electricity to street lighting, park lighting, and residential areas with enhanced safety, efficiency, and aesthetics.
- Telecommunications and data networks: Many low-voltage cables are designed for signal transmission, ideal for telecom, internet, and fiber optic networks in both urban and rural settings.
- Security systems: Commonly used for outdoor CCTV systems, access control systems, and other security infrastructure requiring stable and safe operation.
2.4 Installation methods for underground low-voltage cables
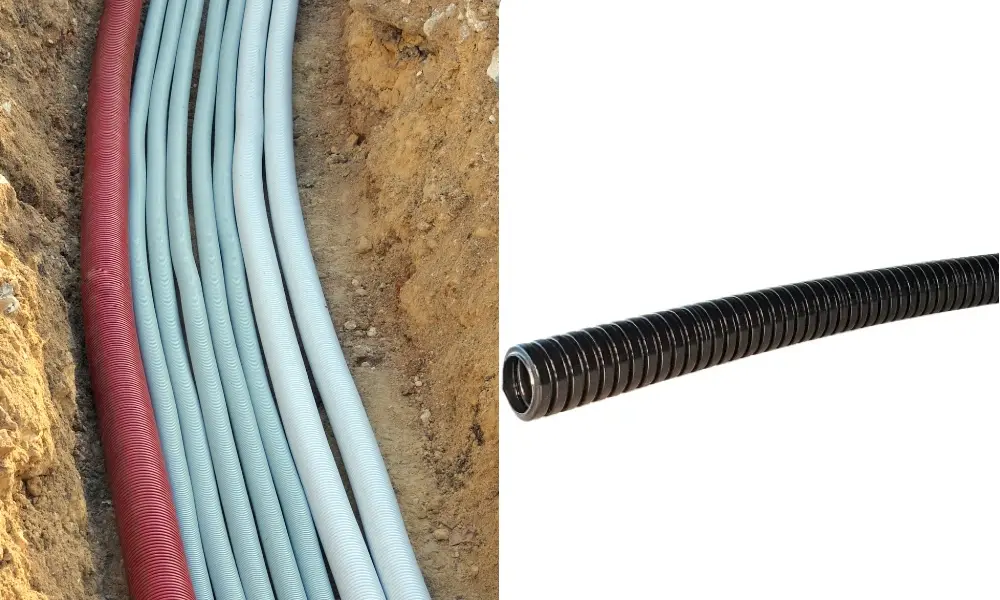

Common installation methods include:
* Direct burial
- Description: Cables are buried directly in the ground without protective conduits.
- Advantages: Quick installation, low cost.
- Disadvantages: Vulnerable to moisture and mechanical impact if soil is unstable.
- Application: Areas with low mechanical impact and soft soil.
* Ducts and conduits
- Description: Cable is inserted into HDPE, PVC, or metal conduits before burial.
- Advantages: Protects against water, insects, chemicals, and mechanical impact. Facilitates cable replacement or upgrades without excavation.
- Application: Urban areas, industrial zones with high infrastructure density.
* Cable trenches
- Description: Specialized trenches lined with sand, concrete, or warning markers for added protection.
- Advantages: Maximum safety in high-risk or high-traffic areas.
- Application: Medium- and high-voltage systems, critical infrastructure zones.
3. HELUKABEL’s portfolio for low-voltage cables
HELUKABEL offers a wide range of low-voltage cable solutions tailored for residential, industrial, commercial, energy, and automation applications. All products comply with European standards, ensuring safety, transmission efficiency, and long service life.
3.1 Underground and distribution cables

| Cables | Features | Part no. |
| NYY-J/NYY-O | Suitable for outdoor, underground, and low-risk mechanical damage areas | 32001 |
| NAYY-J/NAYY-O | 32301 | |
| N2XH | Halogen-free, no toxic/corrosive gases when burned. Flame-retardant. Low smoke emission for increased visibility and safety in fires. | 53100 |
| NYCWY | Corrugated concentric copper core allows multiple joints without cutting the conductor, improving system reliability. | 32260 |
| N2XCH-J/ N2XCH-O | Enhanced fire performance, ideal for substations and safety-critical areas. | 53200 |
| (N)A2XH-J/ (N)A2XH-O | 50073 |
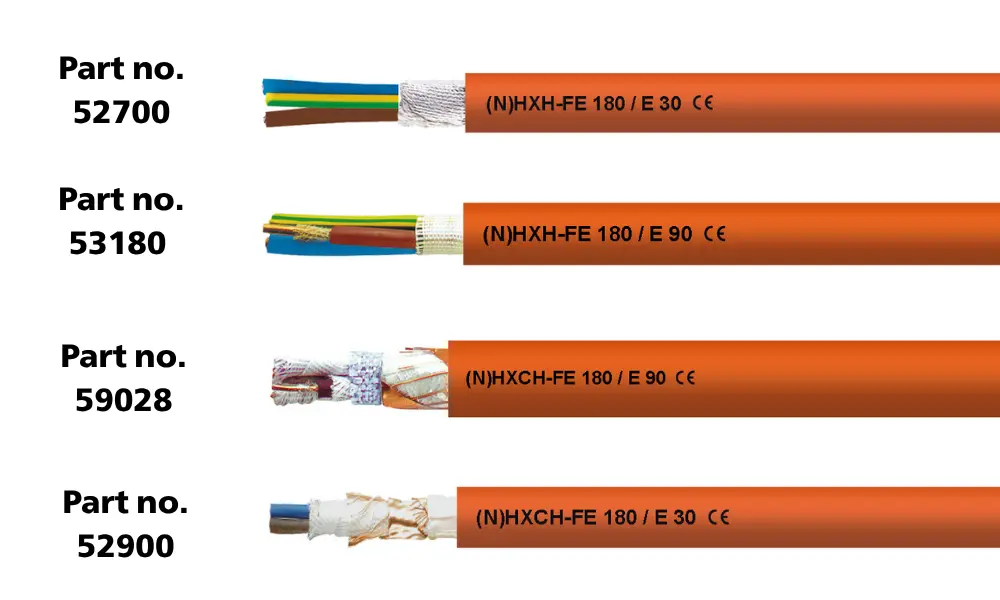
3.2 Security cables
HELUKABEL product range includes:
- (N)HXH-FE 180/E 30 (52700)
- (N)HXH-FE 180/E 90 (53180)
- (N)HXCH-FE 180/E 90 (59028)
- (N)HXCH-FE 180/E 30 (52900)

3.3 Fire alarm cables
HELUKABEL product range includes:
- JE-H(St)H Bd FE 180/E30-E90 (34081)
- J-H(St)H Bd Fire Alarm Cable (34116)
- JE-H(St)H Bd Fire Alarm Cable FE 180/E90 (34091)
- JE-H(St)H Bd Fire Alarm Cable FE 180/E30 (34157)
These cables feature static screens, effectively blocking electromagnetic interference. They are ideal for permanent installation in critical fire-safety areas to protect people and assets during a fire - commonly used in industrial zones, manufacturing facilities, and public buildings.
3.4 Aluminum cables for wind energy
In addition to copper cables, HELUKABEL also provides low-voltage aluminum-core cables for wind energy applications: HELUWIND® WK POWERLINE ALU 0,6/1 kV (707062), HELUWIND® WK POWERLINE ALU ROBUST 0,6/1 kV (707097).
4. FAQs about low-voltage cables
4.1 Difference between low, medium, and high voltage cables
These cables are categorized by voltage levels:
- Low-voltage: below 1kV
- Medium voltage: 1kV – 35kV
- High voltage: above 35kV
Low-voltage cables have thinner insulation and smaller conductor sizes, typically used for short-distance power distribution. Medium and high voltage cables are designed for large-scale, long-distance power transmission.
4.2 How to choose the right low-voltage cables?
When selecting a low-voltage cable, consider:
- System voltage: The rated voltage of the cable must meet or exceed the operating voltage to avoid overloading or fire hazards.
- Installation environment: Choose insulation and sheath materials that resist water, corrosion, or harsh weather.
- Load and current capacity: Select the appropriate conductor cross-section based on whether the load is stable or fluctuating.
- Installation method and cable length: For direct burial, overhead, cable tray, or conduit installation, choose proper conductor materials (copper/aluminum) and cable structure (single-core/multi-core). For long routes, account for joint numbers and connection types to maintain system reliability.
4.3 How to install low-voltage cables for maximum safety and performance?
Key principles include:
- Compliance with technical standards
- Use of proper cable trays or conduits
- Avoid bending beyond the minimum radius
- Proper grounding/earthing
- Secure, safe terminations
- Protection from mechanical, thermal, and moisture damage
- Consideration for future maintenance or upgrades
Correct installation ensures long-term system reliability and safety.
4.4 What to consider when using cables outdoors or in harsh environments?
Outdoor or extreme condition cables should have:
- UV-resistant sheath for sunlight protection
- Water- and moisture-resistance
- Resistance to chemicals, oils, and industrial environments
- Mechanical armor for core protection
- Suitable temperature range (e.g., -40°C to +90°C)
- Low smoke, halogen-free materials for enclosed spaces
If you still have any concerns or questions, don't hesitate to reach out to HELUKABEL Vietnam's engineering team promptly for detailed assistance.
HELUKABEL® Vietnam
| Address | 905, Nguyen Kiem Street, Hanh Thong Ward, Ho Chi Minh City 700000, Vietnam |
| info@helukabel.com.vn | |
| Hotline | +84 28 77755578 |
| Website | www.helukabel.com.vn |
| Discover our products and place orders | Tiki | Shopee | Lazada | Product finder |
| Follow us on | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram | Youtube | Zalo | WhatsApp | Tiktok | Spotify |